JMS是Java Message Service的縮寫,它提供了一種以松散耦合,靈活的方式集成應用程序的機制。 JMS以存儲和轉發的方式跨應用程序異步傳遞數據。 應用程序通過充當中介的MOM(面向消息的中間件)進行通信,而無需直接通信。
JMS體系結構
JMS的主要組件是:
- JMS Provider:一種消息傳遞系統,它實現JMS接口并提供管理和控制功能
- 客戶端:發送或接收JMS消息的Java應用程序。 消息發送者稱為生產者,而接收者稱為消費者
- 消息:在JMS客戶端之間傳遞信息的對象
- 受管對象:管理員為使用客戶端而創建的預配置JMS對象。
有幾種JMS提供程序可用,例如Apache ActiveMQ和OpenMQ。 在這里,我使用了Apache ActiveMQ。
在Windows上安裝和啟動Apache ActiveMQ
- 下載ActiveMQ Windows二進制分發版
- 將其提取到所需位置
- 使用命令提示符將目錄更改為ActiveMQ安裝文件夾中的bin文件夾,然后運行以下命令以啟動ActiveMQ
activemq
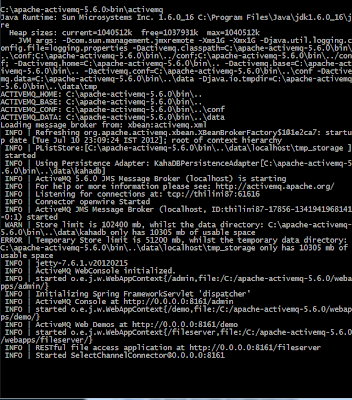
啟動ActiveMQ之后,您可以使用http:// localhost:8161 / admin /訪問管理控制臺并執行管理任務
JMS消息傳遞模型
JMS具有兩種消息傳遞模型,即點對點消息傳遞模型和發布者訂戶消息傳遞模型。
點對點消息傳遞模型
生產者將消息發送到JMS提供程序中的指定隊列,并且只有一個監聽該隊列的使用者才能接收該消息。
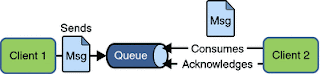
示例1和示例2幾乎相似,唯一的區別是示例1在程序內創建隊列,示例2使用jndi.properties文件命名查找和創建隊列。
例子1
package com.eviac.blog.jms;import javax.jms.*;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;public class Producer {public Producer() throws JMSException, NamingException {// Obtain a JNDI connectionInitialContext jndi = new InitialContext();// Look up a JMS connection factoryConnectionFactory conFactory = (ConnectionFactory) jndi.lookup('connectionFactory');Connection connection;// Getting JMS connection from the server and starting itconnection = conFactory.createConnection();try {connection.start();// JMS messages are sent and received using a Session. We will// create here a non-transactional session object. If you want// to use transactions you should set the first parameter to 'true'Session session = connection.createSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);Destination destination = (Destination) jndi.lookup('MyQueue');// MessageProducer is used for sending messages (as opposed// to MessageConsumer which is used for receiving them)MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(destination);// We will send a small text message saying 'Hello World!'TextMessage message = session.createTextMessage('Hello World!');// Here we are sending the message!producer.send(message);System.out.println('Sent message '' + message.getText() + ''');} finally {connection.close();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException {try {BasicConfigurator.configure();new Producer();} catch (NamingException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}package com.eviac.blog.jms;import javax.jms.*;import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnection;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;public class Consumer {// URL of the JMS serverprivate static String url = ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_BROKER_URL;// Name of the queue we will receive messages fromprivate static String subject = 'MYQUEUE';public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException {BasicConfigurator.configure();// Getting JMS connection from the serverConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url);Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();connection.start();// Creating session for seding messagesSession session = connection.createSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);// Getting the queueDestination destination = session.createQueue(subject);// MessageConsumer is used for receiving (consuming) messagesMessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);// Here we receive the message.// By default this call is blocking, which means it will wait// for a message to arrive on the queue.Message message = consumer.receive();// There are many types of Message and TextMessage// is just one of them. Producer sent us a TextMessage// so we must cast to it to get access to its .getText()// method.if (message instanceof TextMessage) {TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;System.out.println('Received message '' + textMessage.getText()+ ''');}connection.close();}
}
jndi.properties
# START SNIPPET: jndijava.naming.factory.initial = org.apache.activemq.jndi.ActiveMQInitialContextFactory# use the following property to configure the default connector
java.naming.provider.url = vm://localhost# use the following property to specify the JNDI name the connection factory
# should appear as.
#connectionFactoryNames = connectionFactory, queueConnectionFactory, topicConnectionFactry# register some queues in JNDI using the form
# queue.[jndiName] = [physicalName]
queue.MyQueue = example.MyQueue# register some topics in JNDI using the form
# topic.[jndiName] = [physicalName]
topic.MyTopic = example.MyTopic# END SNIPPET: jndipackage com.eviac.blog.jms;import javax.jms.*;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;public class Producer {public Producer() throws JMSException, NamingException {// Obtain a JNDI connectionInitialContext jndi = new InitialContext();// Look up a JMS connection factoryConnectionFactory conFactory = (ConnectionFactory) jndi.lookup('connectionFactory');Connection connection;// Getting JMS connection from the server and starting itconnection = conFactory.createConnection();try {connection.start();// JMS messages are sent and received using a Session. We will// create here a non-transactional session object. If you want// to use transactions you should set the first parameter to 'true'Session session = connection.createSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);Destination destination = (Destination) jndi.lookup('MyQueue');// MessageProducer is used for sending messages (as opposed// to MessageConsumer which is used for receiving them)MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(destination);// We will send a small text message saying 'Hello World!'TextMessage message = session.createTextMessage('Hello World!');// Here we are sending the message!producer.send(message);System.out.println('Sent message '' + message.getText() + ''');} finally {connection.close();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException {try {BasicConfigurator.configure();new Producer();} catch (NamingException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}package com.eviac.blog.jms;import javax.jms.*;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;public class Consumer {public Consumer() throws NamingException, JMSException {Connection connection;// Obtain a JNDI connectionInitialContext jndi = new InitialContext();// Look up a JMS connection factoryConnectionFactory conFactory = (ConnectionFactory) jndi.lookup('connectionFactory');// Getting JMS connection from the server and starting it// ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new// ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url);connection = conFactory.createConnection();// // Getting JMS connection from the server// ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new// ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url);// Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();try {connection.start();// Creating session for seding messagesSession session = connection.createSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);// Getting the queueDestination destination = (Destination) jndi.lookup('MyQueue');// MessageConsumer is used for receiving (consuming) messagesMessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);// Here we receive the message.// By default this call is blocking, which means it will wait// for a message to arrive on the queue.Message message = consumer.receive();// There are many types of Message and TextMessage// is just one of them. Producer sent us a TextMessage// so we must cast to it to get access to its .getText()// method.if (message instanceof TextMessage) {TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;System.out.println('Received message '' + textMessage.getText()+ ''');}} finally {connection.close();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException {BasicConfigurator.configure();try {new Consumer();} catch (NamingException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}
}
發布者訂閱者模型
發布者將消息發布到JMS提供程序中的指定主題,并且訂閱該主題的所有訂閱者都將收到該消息。 請注意,只有活動的訂戶才能收到該消息。
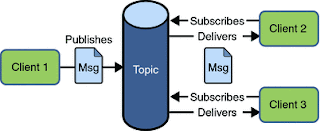
點對點模型示例
package com.eviac.blog.jms;import javax.jms.*;
import javax.naming.*;import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;public class DemoPublisherSubscriberModel implements javax.jms.MessageListener {private TopicSession pubSession;private TopicPublisher publisher;private TopicConnection connection;/* Establish JMS publisher and subscriber */public DemoPublisherSubscriberModel(String topicName, String username,String password) throws Exception {// Obtain a JNDI connectionInitialContext jndi = new InitialContext();// Look up a JMS connection factoryTopicConnectionFactory conFactory = (TopicConnectionFactory) jndi.lookup('topicConnectionFactry');// Create a JMS connectionconnection = conFactory.createTopicConnection(username, password);// Create JMS session objects for publisher and subscriberpubSession = connection.createTopicSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);TopicSession subSession = connection.createTopicSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);// Look up a JMS topicTopic chatTopic = (Topic) jndi.lookup(topicName);// Create a JMS publisher and subscriberpublisher = pubSession.createPublisher(chatTopic);TopicSubscriber subscriber = subSession.createSubscriber(chatTopic);// Set a JMS message listenersubscriber.setMessageListener(this);// Start the JMS connection; allows messages to be deliveredconnection.start();// Create and send message using topic publisherTextMessage message = pubSession.createTextMessage();message.setText(username + ': Howdy Friends!');publisher.publish(message);}/** A client can register a message listener with a consumer. A message* listener is similar to an event listener. Whenever a message arrives at* the destination, the JMS provider delivers the message by calling the* listener's onMessage method, which acts on the contents of the message.*/public void onMessage(Message message) {try {TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;String text = textMessage.getText();System.out.println(text);} catch (JMSException jmse) {jmse.printStackTrace();}}public static void main(String[] args) {BasicConfigurator.configure();try {if (args.length != 3)System.out.println('Please Provide the topic name,username,password!');DemoPublisherSubscriberModel demo = new DemoPublisherSubscriberModel(args[0], args[1], args[2]);BufferedReader commandLine = new java.io.BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));// closes the connection and exit the system when 'exit' enters in// the command linewhile (true) {String s = commandLine.readLine();if (s.equalsIgnoreCase('exit')) {demo.connection.close();System.exit(0);}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
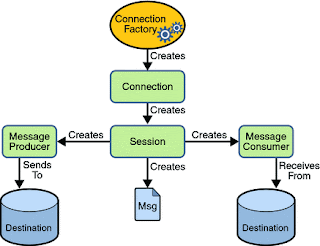
}
參考: 和ActiveMQ JMS從我們JCG伙伴 Pavithra Siriwardena在EVIAC博客。
翻譯自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2012/07/jms-with-activemq.html


)








 - 下載 - 搜珍網...)





)

