3、基礎類型
3.1、簡單變量
變量的命名
carDrip和cardRip
或boat_sport和boats_port
此外,還有有前綴的命名,使用前綴表示數據類型。常見的前綴有:str(表示字符串)、n(表示整數值)、b(表示布爾值)、p(表示指針)、c(表示單個字符)和m(表示一個類成員值)
nMyWeight
整型長度
C++提供了一種靈活的標準,它確保了最小長度
- short至少16位
- int至少與short一樣長
- long至少32位,且至少與int一樣長
- longlong至少64位,且至少與long一樣長
#include <iostream>
#include <climits> //包含整數的限制信息int main() {using namespace std;short n_short = SHRT_MAX;int n_int = INT_MAX;long n_long = LONG_MAX;long long n_llong = LLONG_MAX;//sizeof operator yields size of type or of variablecout << "short is " << sizeof n_short << " bytes." << endl;cout << "int is " << sizeof(int) << " bytes." << endl;cout << "long is " << sizeof n_long << " bytes." << endl;cout << "long long is " << sizeof n_llong << " bytes." << endl << endl;cout << "Maxinum values:" << endl;cout << "short: " << n_short << endl;cout << "int: " << n_int << endl;cout << "long: " << n_long << endl;cout << "long long: " << n_llong << endl << endl;cout << "Minnum int value=" << INT_MIN << endl;cout << "Bits per byte =" << CHAR_BIT << endl; //字節的位數return 0;
}
/*
short:2
int:4
long:4
long:8
*/
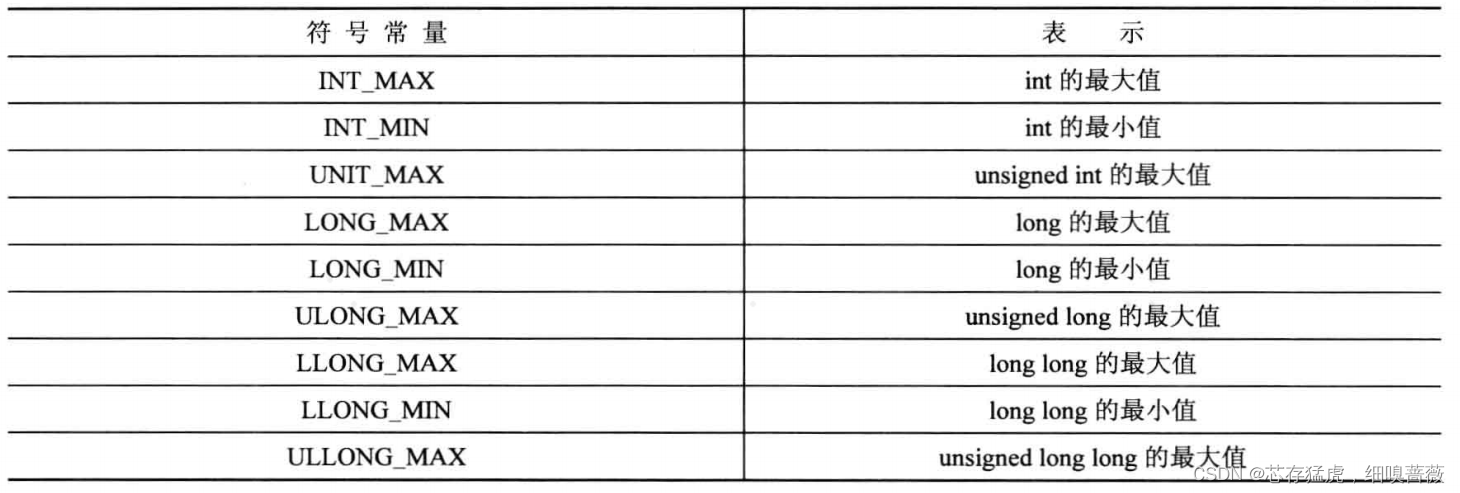
對于整數類型的限制,使用頭文件climits(在老式中為limits.h)。即最大值、最小值等常量
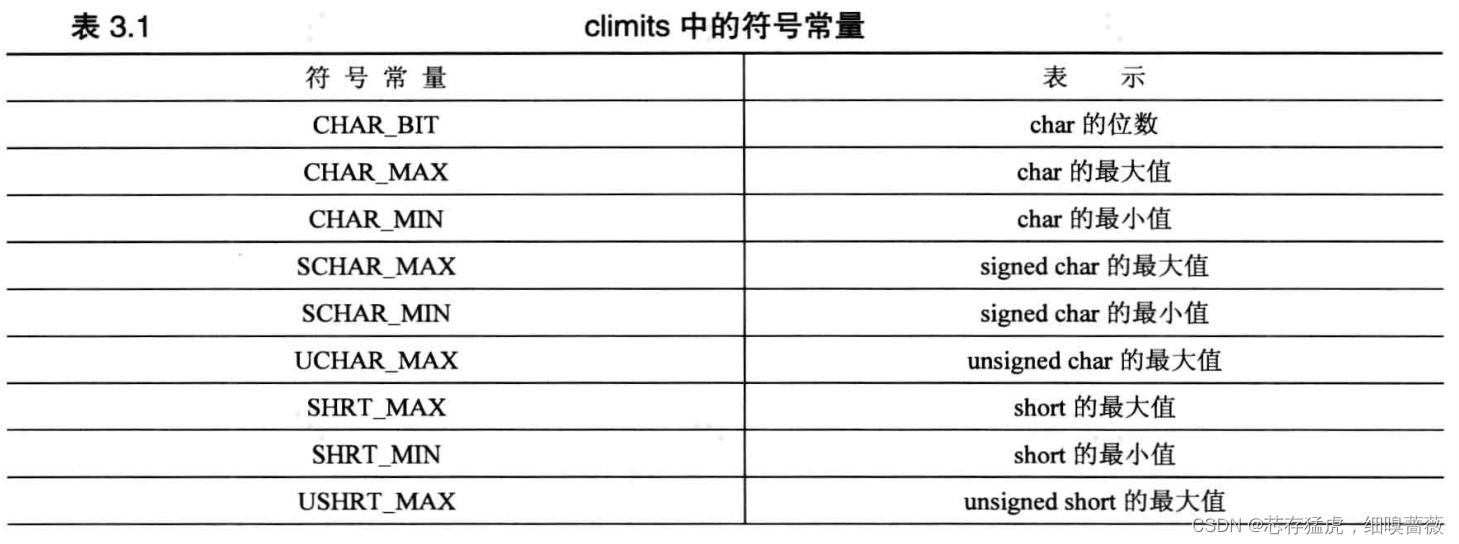
對于int、long、long long
初始化
int owls=100; //傳統C語言初始化,
int wrens(432); //可供選擇的C++初始化
在C++98和C++11中,可以使用大括號對單值進行初始化
在C++98中,將大括號用于單值變量的情形還不多,但是對于C++11標準就多很多了。采用這種方式時,可以使用=,也可以不用
int emus{7};
int rheas={12};其次,大括號內可以不包括任何東西。在這種情況下,變量將被初始化為0.
int rocs ={};
int phy{};
無符號類型
short的表示范圍是-32768到+32768
unsigned short 表示的符號是0-65535
// exceed.cpp -- exceeding some integer limits
#include <iostream>
#define ZERO 0 // makes ZERO symbol for 0 value
#include <climits> // defines INT_MAX as largest int valueint main() {using namespace std;short sam = SHRT_MAX; // initialize a variable to max valueunsigned short sue = sam;// okay if variable sam already definedcout << "Sam has " << sam << " dollars and Sue has " << sue;cout << " dollars deposited." << endl<< "Add $1 to each account." << endl << "Now ";sam = sam + 1; //32767+1,溢出,-32768sue = sue + 1;cout << "Sam has " << sam << " dollars and Sue has " << sue;cout << " dollars deposited.\nPoor Sam!" << endl;sam = ZERO;sue = ZERO; //0-1,溢出,65536cout << "Sam has " << sam << " dollars and Sue has " << sue;cout << " dollars deposited." << endl;cout << "Take $1 from each account." << endl << "Now ";sam = sam - 1;sue = sue - 1;cout << "Sam has " << sam << " dollars and Sue has " << sue;cout << " dollars deposited." << endl << "Lucky Sue!" << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}如果超越了限制,其值將為范圍另一端的取值。C++確保了無符號類型類型的這種行為;但C++并不保證有符號整形超越限制(上溢出和下溢出)時不出錯。

如果知道變量表示的數值可能大于16位整數的最大值,則使用long。【因為在移植到別的操作系統中,int可能由32位變成16位】。
如果short比int小,則使用short可以節省內存。如果節省內存很重要,則應使用short而不是int,計時它們的長度是一樣的。例如,假設要將程序從int是16位的系統移植到int是32位的系統,則用于存儲int的數組的內存量將加倍,但是short的數組是不受影響的。
如果只需要一個字節,可使用char。
進制
有8進制、10進制、16進制,默認的是10進制
// hexoct1.cpp -- shows hex and octal literals
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int chest = 42; // decimal integer literalint waist = 0x42; // hexadecimal integer literalint inseam = 042; // octal integer literalcout << "Monsieur cuts a striking figure!\n";cout << "chest = " << chest << " (42 in decimal)\n";cout << "waist = " << waist << " (0x42 in hex)\n";cout << "inseam = " << inseam << " (042 in octal)\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
對于C++,如果要以16進制或8進制方式顯示值,則可以使用cout的一些特殊性。cout<<hex、cout<<oct
int main() {using namespace std;int chest = 42;int waist = 42;int inseam = 42;cout << "Monsieur cuts a striking figure!" << endl;cout << "chest = " << chest << " (decimal for 42)" << endl;cout << hex; // manipulator for changing number basecout << "waist = " << waist << " (hexadecimal for 42)" << endl;cout << oct; // manipulator for changing number basecout << "inseam = " << inseam << " (octal for 42)" << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
標識符hex位于名稱空間std中,而程序使用了該名稱空間。
如果省略編譯指令using,而使用std::cout、std::endl、std::hex、std::oct。
字符類型
char類型是專為存儲字符(如數字和字母)而設計的。此外,char也可以看作是 比short更小的整形
輸入時,cin將鍵盤輸入的M轉換為77;輸出時,cout將值77轉換為所顯示的字符M。
// chartype.cpp -- the char type
#include <iostream>
int main( )
{using namespace std;char ch; // declare a char variablecout << "Enter a character: " << endl;cin >> ch;cout << "Hola! ";cout << "Thank you for the " << ch << " character." << endl;// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}下面程序說明了這一單。cin和cout的行為都是由變量類型引導的。如果將77存儲在int變量中,則cout將把它顯示為77。字符使用單引號’M’,對于字符串使用雙引號。
最后,引入cout的一項特性——cout.put()函數
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;char ch = 'M'; // assign ASCII code for M to chint i = ch; // store same code in an intcout << "The ASCII code for " << ch << " is " << i << endl;cout << "Add one to the character code:" << endl;ch = ch + 1; // change character code in chi = ch; // save new character code in icout << "The ASCII code for " << ch << " is " << i << endl;// using the cout.put() member function to display a charcout << "Displaying char ch using cout.put(ch): ";cout.put(ch);// using cout.put() to display a char constantcout.put('!');cout << endl << "Done" << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
The ASCII code for M is 77
Add one to the character code:
The ASCII code for N is 78
Displaying char ch using cout.put(ch): N!
Done
*/
在Release2.0之后,C++將字符常量存儲為char類型,而不是int類型。這意味著cout現在可以正確處理字符常量了。
在C++中,有一些轉義字符,如下圖所示。
[外鏈圖片轉存失敗,源站可能有防盜鏈機制,建議將圖片保存下來直接上傳(img-bsfcFQ4A-1691999308835)(.\pics\8-9-7.png)]
// bondini.cpp -- using escape sequences
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;cout << "\aOperation \"HyperHype\" is now activated!\n";cout << "Enter your agent code:________\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b";long code;cin >> code;cout << "\aYou entered " << code << "...\n";cout << "\aCode verified! Proceed with Plan Z3!\n";// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Operation "HyperHype" is now activated!
Enter your agent code:23456___
You entered 23456...
Code verified! Proceed with Plan Z3!
*/
新增的類型
char16_t和char32_t。底層時一種內置的整形
char16_t ch1=u'q';
char32_t ch2=U'\U0000222B';
bool類型
C++標準中添加了bool的新類型。
在計算中,布爾變量的值可以是true或false。C++將非零解釋為true,將零解釋為false。
bool is_ready = true;
//字面值true和false都可以通過提升轉換為int類型,true被轉換位1,而false被轉換為0
int ans=true;
int promise=false;
//任何數字值或指針值都可以被隱式轉換(即不用顯式強制轉換)為bool值。任何非零值都被轉換位true,而零被轉換為false
bool start =-100;
bool stop = 0;3.2、const
創建常量的通用格式如下:
const type name =value;const int val=10;
相較于#define語句,const有以下的好處
- 它能夠明確指定類型
- 可以使用C++的作用域規則將定義限制在特定的函數或文件中
- 可以將const用于更復雜的類型中,如數組和結構
3.3、浮點數
C++有兩種浮點數的表示方法
3.3.1、表示方法
1、標準小數點表示法
12.34
0.000023
8.0
45678.2345678
2、E表示法
2.52e+8
8.33e-4
7E5
3.3.2、浮點類型
float至少32位;double至少48位,且不少于float;long double不少于double
通常,float為32位;double為64為;long double為80、96或128位
對于不同類型的浮點數,小數點后的精確度不同
// floatnum.cpp -- floating-point types
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); // fixed-pointfloat tub = 10.0 / 3.0; // good to about 6 placesdouble mint = 10.0 / 3.0; // good to about 15 placesconst float million = 1.0e6;cout << "tub = " << tub;cout << ", a million tubs = " << million *tub;cout << ",\nand ten million tubs = ";cout << 10 * million *tub << endl;cout << "mint = " << mint << " and a million mints = ";cout << million *mint << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
3.3.3、浮點常量
如果希望常量為float類型,使用f或F后綴。如果時long double類型,可以使用l或L的后綴
1.234f
2.45E20F
2.456345E28 //double
2.2L //long double
3.3.4、浮點數優缺點
兩大優點
- 它們可以表示整數之間的值
- 由于有縮放因子,它們表示的范圍大很多
另一方面,浮點運算的速度通常比整數運算慢,且精度將降低。
// fltadd.cpp -- precision problems with float
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;float a = 2.34E+22f;float b = a + 1.0f;cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b - a = " << b - a << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
float僅能表示數字的前6位或前7位。
類型的分類
類型signed char、short、int和long統稱為符號整型;它們的無符號版本統稱為無符號整型。
C++11新增了long long、bool、char、wchar_t。
符號整數和無符號整型統稱為整型。C++11新增了char16_t和char32_t。
float、double和long double統稱為浮點型。整數和浮點型統稱算數類型。
3.4、C++算數運算符
// arith.cpp -- some C++ arithmetic
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;float hats, heads;cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); // fixed-pointcout << "Enter a number: ";cin >> hats;cout << "Enter another number: ";cin >> heads;cout << "hats = " << hats << "; heads = " << heads << endl;cout << "hats + heads = " << hats + heads << endl;cout << "hats - heads = " << hats - heads << endl;cout << "hats * heads = " << hats * heads << endl;cout << "hats / heads = " << hats / heads << endl;// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter a number: 50.25
Enter another number: 11.17
hats = 50.250000; heads = 11.170000
hats + heads = 61.419998
hats - heads = 39.080002
hats * heads = 561.292480
hats / heads = 4.498657
*/
在C++中,對于float,僅保證6位或7位有效位
3.4.1、運算符優先級
C++的運算符優先級
![[外鏈圖片轉存失敗,源站可能有防盜鏈機制,建議將圖片保存下來直接上傳(img-u2y9NYPn-1691999308836)(.\pics\8-10-0.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/96aaf4cd711e4559b3926d76476df611.png)
后續
![[外鏈圖片轉存失敗,源站可能有防盜鏈機制,建議將圖片保存下來直接上傳(img-x4wxWQpS-1691999308836)(.\pics\8-10-1.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bf26709e1ab5475496c1ee887ad4ea10.png)
后續
![[外鏈圖片轉存失敗,源站可能有防盜鏈機制,建議將圖片保存下來直接上傳(img-zERjaCJ7-1691999308836)(.\pics\8-10-2.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/515fd8187caf40889be1cda757a442ed.png)
3.4.2、除法分支
// divide.cpp -- integer and floating-point division
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);cout << "Integer division: 9/5 = " << 9 / 5 << endl;cout << "Floating-point division: 9.0/5.0 = ";cout << 9.0 / 5.0 << endl;cout << "Mixed division: 9.0/5 = " << 9.0 / 5 << endl;cout << "double constants: 1e7/9.0 = ";cout << 1.e7 / 9.0 << endl;cout << "float constants: 1e7f/9.0f = ";cout << 1.e7f / 9.0f << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Integer division: 9/5 = 1
Floating-point division: 9.0/5.0 = 1.800000
Mixed division: 9.0/5 = 1.800000
double constants: 1e7/9.0 = 1111111.111111
float constants: 1e7f/9.0f = 1111111.125000
*/
最后兩行的相對精度表明,如果兩個操作數都是double類型,則結果為double類型;如果兩個操作數都是float類型,則結果為float類型。浮點常量在默認的情況下,為double類型。
運算符重載

3.4.3、求模運算符
// modulus.cpp -- uses % operator to convert lbs to stone
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;const int Lbs_per_stn = 14;int lbs;cout << "Enter your weight in pounds: ";cin >> lbs;int stone = lbs / Lbs_per_stn; // whole stoneint pounds = lbs % Lbs_per_stn; // remainder in poundscout << lbs << " pounds are " << stone<< " stone, " << pounds << " pound(s).\n";// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter your weight in pounds: 181
181 pounds are 12 stone, 13 pound(s).
*/
3.4.4、類型轉換
C++中會有多種類型的轉換
- 賦值時,類型不同,會進行轉換
- 表達式中包含不同的類型時,C++將對值進行轉換
- 將參數傳遞給函數時,C++將對值進行轉換
對于類型的轉換,可能會出現一些問題。

// assign.cpp -- type changes on assignment
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);float tree = 3; // int converted to floatint guess = 3.9832; // float converted to intint debt = 7.2E12; // result not defined in C++cout << "tree = " << tree << endl;cout << "guess = " << guess << endl;cout << "debt = " << debt << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
tree = 3.000000
guess = 3
debt = 2147483647
*/
在將整數變量初始化為浮點值時,有時編譯器將會警告。int變量無法存儲7.2E12,這導致C++沒有對結果進行定義的情況發生。
整型級別
有符號整型按級別從高到低依次是:long long、long、int、short和signed char。
無符號整型的排列順序與有符號整型相同。類型char、signed char和unsigned char的級別相同。類型bool的級別最低。wchar_t、char16_t和char32_t的級別與其底層類型相同。
強制類型轉換
static_cast<>可用于將值從一種數值類型轉換為另一種數值類型。
static_cast (value)
// typecast.cpp -- forcing type changes
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int auks, bats, coots;// the following statement adds the values as double,// then converts the result to intauks = 19.99 + 11.99;// these statements add values as intbats = (int) 19.99 + (int) 11.99; // old C syntaxcoots = int (19.99) + int (11.99); // new C++ syntaxcout << "auks = " << auks << ", bats = " << bats;cout << ", coots = " << coots << endl;char ch = 'Z';cout << "The code for " << ch << " is "; // print as charcout << int(ch) << endl; // print as intcout << "Yes, the code is ";cout << static_cast<int>(ch) << endl; // using static_cast// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
auks = 31, bats = 30, coots = 30
The code for Z is 90
Yes, the code is 90
*/
3.4.5、auto聲明
在初始化聲明中,使用關鍵字auto,而不指定變量的類型,編譯器將把變量的類型設置成與初始值相同
auto n=100; //n is int
auto x=1.5; //x is double
auto y=1.3e12L; //y is long double
4、復合類型
4.1、數組
聲明需要以下3點
- 存儲在每個元素中的值的類型
- 數組名
- 數組中的元素數
聲明數組的通用格式如下:
typeName arrayName[arraySize];
float loans[20];
loans的類型不是“數組”,而是“float數組”。這強調了loans數組是使用float類型創建的。為復合類型
// arrayone.cpp -- small arrays of integers
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int yams[3]; // creates array with three elementsyams[0] = 7; // assign value to first elementyams[1] = 8;yams[2] = 6;int yamcosts[3] = {20, 30, 5}; // create, initialize array
// NOTE: If your C++ compiler or translator can't initialize
// this array, use static int yamcosts[3] instead of
// int yamcosts[3]cout << "Total yams = ";cout << yams[0] + yams[1] + yams[2] << endl;cout << "The package with " << yams[1] << " yams costs ";cout << yamcosts[1] << " cents per yam.\n";int total = yams[0] * yamcosts[0] + yams[1] * yamcosts[1];total = total + yams[2] * yamcosts[2];cout << "The total yam expense is " << total << " cents.\n";cout << "\nSize of yams array = " << sizeof yams;cout << " bytes.\n";cout << "Size of one element = " << sizeof yams[0];cout << " bytes.\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Total yams = 21
The package with 8 yams costs 30 cents per yam.
The total yam expense is 410 cents.Size of yams array = 12 bytes.
Size of one element = 4 bytes.
*/
sizeof運算符返回類型或數據對象的長度(單位為字節)。注意,如果將sizeof運算符用于數組名,得到的將是整個數組的字節數。但如果將sizeof用于數組元素,則得到的將是元素的長度(單位為字節)。
初始化的方法
初始化禁止縮窄轉換。
long plifs[]={25,92,3.0}; //not allowed
char slifs[4]{'h','i',12208,'\0'}; //not allowed
char tlifs[4]{'h','i',112,'\0'}; //allowed
第1條語句不能通過編譯,因為將浮點數轉換為整型是縮窄操作,即使浮點數的小數點后面為零。
第2條語句也不能通過編譯,因為12208超出了char變量的取值范圍(這里假設char變量的長度為8位)。
第3條語句可通過編譯,因為雖然112是一個int值,但它在char變量的取值范圍內。
C++標準模板庫(STL)提供了一種數組替代品——模板類vector,而C++11新增了模板類array。
4.2、字符串
可以使用字符數組初始化為字符串,但需要使用大量單引號,且必須加上空字符。可以使用括號括起字符串,這種字符串被稱為字符串常量或字符串字面值。
char bird[11]="Mr. Cheeps";
char fish[]="Bubbles";
**注意:**字符常量(使用單引號)和字符串常量(使用雙引號)不能互換。
char shirt_size ='s'; //this is fine
char shirt_size ="S"; //illegal type mismatch
字符串的拼接
**注意:**拼接時不會在被連接的字符串之間添加空格,第二個字符串的第一個字符將緊跟在第一個字符串的最后一個字符(不考慮\0)后面。第一個字符串中的\0字符將被第二個字符串的第一個字符取代。
// strings.cpp -- storing strings in an array
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // for the strlen() functionint main() {using namespace std;const int Size = 15;char name1[Size]; // empty arraychar name2[Size] = "C++owboy"; // initialized array// NOTE: some implementations may require the static keyword// to initialize the array name2cout << "Howdy! I'm " << name2;cout << "! What's your name?\n";cin >> name1;cout << "Well, " << name1 << ", your name has ";cout << strlen(name1) << " letters and is stored\n";cout << "in an array of " << sizeof(name1) << " bytes.\n";cout << "Your initial is " << name1[0] << ".\n";name2[3] = '\0'; // set to null charactercout << "Here are the first 3 characters of my name: ";cout << name2 << endl;// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Howdy! I'm C++owboy! What's your name?
Basicman
Well, Basicman, your name has 8 letters and is stored
in an array of 15 bytes.
Your initial is B.
Here are the first 3 characters of my name: C++
*/
sizeof運算符指出整個數組的長度:15字節;strlen()函數返回的是存儲在數組中的字符串的長度,而不是數組本身的長度。另外,strlen()只計算可見的字符,而不把空字符計算在內,因此為8。
可以將name2[3]設置為空字符。這使得字符號在第3個字符后即結束,達到截斷字符串的效果。
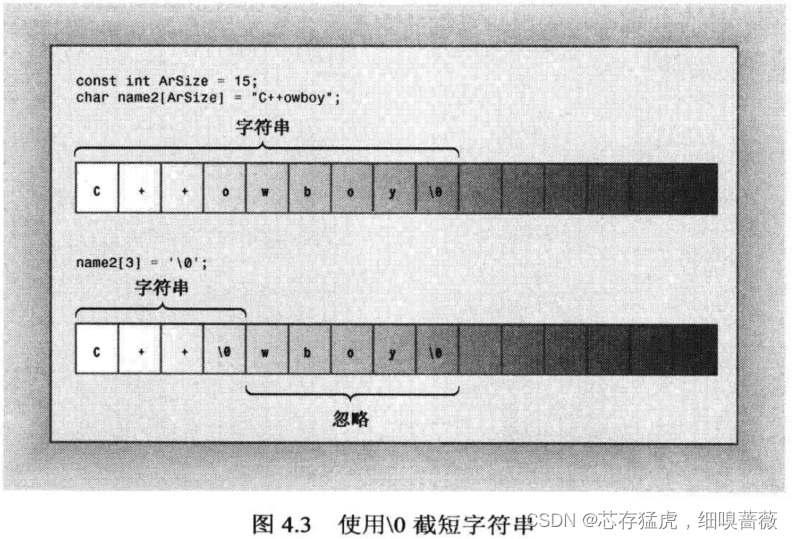
字符串的輸入
// instr1.cpp -- reading more than one string
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;const int ArSize = 20;char name[ArSize];char dessert[ArSize];cout << "Enter your name:\n";cin >> name;cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";cin >> dessert;cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter your name:
Ali dreeb
Enter your favorite dessert:
I have some delicious dreeb for you, Ali.
*/
如下圖所示:

- 面向行的輸入:getline()
cin.getline(name,20)
// instr2.cpp -- reading more than one word with getline
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;const int ArSize = 20;char name[ArSize];char dessert[ArSize];cout << "Enter your name:\n";cin.getline(name, ArSize); // reads through newlinecout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";cin.getline(dessert, ArSize);cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter your name:
Mai Par
Enter your favorite dessert:
Chocolate Mousse
I have some delicious Chocolate Mousse for you, Mai Par.
*/
- 面向行的輸入:get()
cin.get(name,Arsize);
cin.get();
cin.get(dessert,Arsize);//另一種方式
cin.get(name,Arsize).get();
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;const int ArSize = 20;char name[ArSize];char dessert[ArSize];cout << "Enter your name:\n";cin.get(name, ArSize).get(); // read string, newlinecout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";cin.get(dessert, ArSize).get();cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
Enter your name:
Mai Per
Enter your favorite dessert:
Chocolate Mousse
I have some delicious Chocolate Mousse for you, Mai Per.
*/
混合輸入字符串和數字
// numstr.cpp -- following number input with line input
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;cout << "What year was your house built?\n";int year;cin >> year; //可與下面結合(cin>>year).get()或(cin>>year).get(ch)
// cin.get(); 或cin.get(ch)cout << "What is its street address?\n";char address[80];cin.getline(address, 80);cout << "Year built: " << year << endl;cout << "Address: " << address << endl;cout << "Done!\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}4.3、string類
// strtype1.cpp -- using the C++ string class
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class availableint main() {using namespace std;char charr1[20]; // create an empty arraychar charr2[20] = "jaguar"; // create an initialized arraystring str1; // create an empty string objectstring str2 = "panther"; // create an initialized stringcout << "Enter a kind of feline: ";cin >> charr1;cout << "Enter another kind of feline: ";cin >> str1; // use cin for inputcout << "Here are some felines:\n";cout << charr1 << " " << charr2 << " "<< str1 << " " << str2 // use cout for output<< endl;cout << "The third letter in " << charr2 << " is "<< charr2[2] << endl;cout << "The third letter in " << str2 << " is "<< str2[2] << endl; // use array notation// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter a kind of feline: ocelot
Enter another kind of feline: tiger
Here are some felines:
ocelot jaguar tiger panther
The third letter in jaguar is g
The third letter in panther is n
*/
賦值、拼接
使用string類時,某些操作比使用數組時更簡單。例如,不能將一個數組賦給另一個數組,但可以將一個string對象賦給另一個string對象。
string str3;
str3=str1+str2;
str1+=str2;
例子
int main() {using namespace std;string s1 = "penguin";string s2, s3;cout << "You can assign one string object to another: s2 = s1\n";s2 = s1;cout << "s1: " << s1 << ", s2: " << s2 << endl;cout << "You can assign a C-style string to a string object.\n";cout << "s2 = \"buzzard\"\n";s2 = "buzzard";cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;cout << "You can concatenate strings: s3 = s1 + s2\n";s3 = s1 + s2;cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl;cout << "You can append strings.\n";s1 += s2;cout << "s1 += s2 yields s1 = " << s1 << endl;s2 += " for a day";cout << "s2 += \" for a day\" yields s2 = " << s2 << endl;//cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
You can assign one string object to another: s2 = s1
s1: penguin, s2: penguin
You can assign a C-style string to a string object.
s2 = "buzzard"
s2: buzzard
You can concatenate strings: s3 = s1 + s2
s3: penguinbuzzard
You can append strings.
s1 += s2 yields s1 = penguinbuzzard
s2 += " for a day" yields s2 = buzzard for a day
*/
其他操作
strcpy(charr1,charr2); //copy charr2 to charr1
strcat(charr1,charr2); //append contents of charr2 to char1
// strtype3.cpp -- more string class features
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
#include <cstring> // C-style string library
int main()
{using namespace std;char charr1[20]; char charr2[20] = "jaguar"; string str1; string str2 = "panther";// assignment for string objects and character arraysstr1 = str2; // copy str2 to str1strcpy(charr1, charr2); // copy charr2 to charr1// appending for string objects and character arraysstr1 += " paste"; // add paste to end of str1strcat(charr1, " juice"); // add juice to end of charr1// finding the length of a string object and a C-style stringint len1 = str1.size(); // obtain length of str1int len2 = strlen(charr1); // obtain length of charr1cout << "The string " << str1 << " contains "<< len1 << " characters.\n";cout << "The string " << charr1 << " contains "<< len2 << " characters.\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
The string panther paste contains 13 characters.
The string jaguar juice contains 12 characters.
*/
string類I/O
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
#include <cstring> // C-style string libraryint main() {using namespace std;char charr[20];string str;cout << "Length of string in charr before input: "<< strlen(charr) << endl;cout << "Length of string in str before input: "<< str.size() << endl;cout << "Enter a line of text:\n";cin.getline(charr, 20); // indicate maximum lengthcout << "You entered: " << charr << endl;cout << "Enter another line of text:\n";getline(cin, str); // cin now an argument; no length specifiercout << "You entered: " << str << endl;cout << "Length of string in charr after input: "<< strlen(charr) << endl;cout << "Length of string in str after input: "<< str.size() << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Length of string in charr before input: 1
Length of string in str before input: 0
Enter a line of text:
puagj letter
You entered: puagj letter
Enter another line of text:
fghjdfgh hjd
You entered: fghjdfgh hjd
Length of string in charr after input: 12
Length of string in str after input: 12
*/
其他形式的字符串字面值
除了char類型,C++還有類型wchar_t;而C++11新增了類型char16_t和char32_t。可以分別使用前綴L、u和U表示
wchar_t title[]=L"Chief Ast";
char16_t name[]=u"FFF WANG"
char32_t car[]=U"Humber Super snipe"
Q
01、sizeof()&strlen()
char str[20]="0123456789";
int a=strlen(str); // a=10; >>>> strlen 計算字符串的長度,以結束符 0x00 為字符串結束。
int b=sizeof(str); // 而 b=20; >>>> sizeof 計算的則是分配的數組 str[20] 所占的內存空間的大小,不受里面存儲的內容改變。
對于指針
char* ss = "0123456789";
sizeof(ss) 結果 4 ===》ss 是指向字符串常量的字符指針,sizeof 獲得的是一個指針的之所占的空間,應該是長整型的,所以是 4。
sizeof(*ss) 結果 1 ===》*ss 是第一個字符 其實就是獲得了字符串的第一位 '0' 所占的內存空間,是 char 類型的,占了 1 位
strlen(ss)= 10 ===》 如果要獲得這個字符串的長度,則一定要使用 strlen。strlen 用來求字符串的長度;而 sizeof 是用來求指定變量或者變量類型等所占內存大小。
() << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
/*
Length of string in charr before input: 1
Length of string in str before input: 0
Enter a line of text:
puagj letter
You entered: puagj letter
Enter another line of text:
fghjdfgh hjd
You entered: fghjdfgh hjd
Length of string in charr after input: 12
Length of string in str after input: 12
*/
**其他形式的字符串字面值**除了char類型,C++還有類型wchar_t;而C++11新增了類型char16_t和char32_t。可以分別使用前綴L、u和U表示wchar_t title[]=L"Chief Ast";
char16_t name[]=u"FFF WANG"
char32_t car[]=U"Humber Super snipe"
# Q## 01、sizeof()&strlen()```c++
char str[20]="0123456789";
int a=strlen(str); // a=10; >>>> strlen 計算字符串的長度,以結束符 0x00 為字符串結束。
int b=sizeof(str); // 而 b=20; >>>> sizeof 計算的則是分配的數組 str[20] 所占的內存空間的大小,不受里面存儲的內容改變。
對于指針
char* ss = "0123456789";
sizeof(ss) 結果 4 ===》ss 是指向字符串常量的字符指針,sizeof 獲得的是一個指針的之所占的空間,應該是長整型的,所以是 4。
sizeof(*ss) 結果 1 ===》*ss 是第一個字符 其實就是獲得了字符串的第一位 '0' 所占的內存空間,是 char 類型的,占了 1 位
strlen(ss)= 10 ===》 如果要獲得這個字符串的長度,則一定要使用 strlen。strlen 用來求字符串的長度;而 sizeof 是用來求指定變量或者變量類型等所占內存大小。




)




新增接口頁面布局)






TransactionManager是哪里來的?是什么類型的?)


