在上一篇迪瑞克斯拉算法中將功能實現了出來,完成了圖集中從源點出發獲取所有可達的點的最短距離的收集。
但在代碼中getMinDistanceAndUnSelectNode()方法的實現并不簡潔,每次獲取minNode時,都需要遍歷整個Map,時間復雜度太高。這篇文章主要是針對上一篇文章代碼的一個優化。
其優化的過程中主要是用到了加強堆的數據結構,如果不了解的強烈建議先看加強堆的具體實現。
回顧:
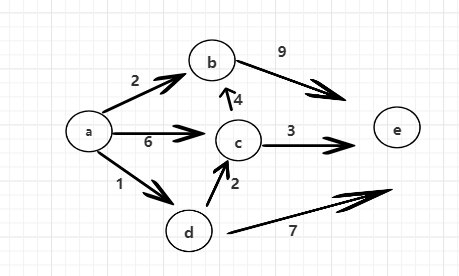
上一篇中,將確定不變的點放入Set中, 每個點之間的距離關系放入Map中,每次遍歷Map獲取最小minNode,并根據該點找到所有的邊,算出最小距離后,放入set中,最終確定最小距離表。
優化
利用加強堆,來維護點和距離的關系,并利用小根堆的優勢,讓最小的點總是在最上面,需要注意的是,以往的的加強堆中,如果移除了這個元素會直接remove,但是在這里不能remove,因為要記錄這個點是否在堆上,是否加入過堆,所以對于確定了的元素,value要改成 -1,用來標記當前元素已經確定,不用再動。
加強堆代碼
NodeHeap中的distanceMap用來表示點和距離的關系,根據value的大小動態變化堆頂元素。
主方法是addOrUpdateOrIgnore()。
如果當前元素在堆中并且value != 1(inHeap),說明元素還沒有確定,則判斷進來的node和value是否大于當前堆中的node對應的value,取小的更新,如果更新,還需要改變元素在堆中位置,因為只可能越更新越小。所以要調用insertHeapify方法去改變堆結構。
如果元素還未加入過堆(!isEntered),則掛在堆尾,并insertHeapify檢查是否上移。
pop方法中,如果彈出堆,正常要刪除,但是不能刪除,除了和最后一個元素交換,下移外,將distanceMap中對應的值改為 -1。否則無法判斷該元素是否已經加入過堆,是否已經確定。
public static class NodeHeap {//Node類型的堆private Node[] nodes;//key對應的Node在堆中的位置是valueprivate HashMap<Node, Integer> heapIndexMap;//key對應的Node當前距離源點最近距離private HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap;//堆大小private int size;public NodeHeap(int size) {nodes = new Node[size];heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();distanceMap = new HashMap<>();this.size = 0;}public boolean isEmpty() {return this.size == 0;}public boolean isEntered(Node head) {return heapIndexMap.containsKey(head);}public boolean inHeap(Node head) {return isEntered(head) && heapIndexMap.get(head) != -1;}public void swap(int index1, int index2) {heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1], index2);heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2], index1);Node tmp = nodes[index1];nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];nodes[index2] = tmp;}public void heapify(int index, int size) {int left = (index * 2) - 1;while (left < size) {int smallest = left + 1 < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left + 1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[left]) ? left + 1 : left;smallest = distanceMap.get(nodes[smallest]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) ? smallest : index;if (smallest == index) {break;}swap(smallest, index);index = smallest;left = (index * 2) - 1;}}public void insertHeapify(Node node, int index) {while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get((index - 1) / 2)) {swap(distanceMap.get(nodes[index]), distanceMap.get((index - 1) / 2));index = (index - 1) / 2;}}public NodeRecord pop() {NodeRecord nodeRecord = new NodeRecord(nodes[0], distanceMap.get(0));swap(0, size - 1);heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1);distanceMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]);heapify(0, --size);return nodeRecord;}public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node, int distance) {if (inHeap(node)) {distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distanceMap.get(node), distance));insertHeapify(node, distanceMap.get(node));}if (!isEntered(node)) {nodes[size] = node;heapIndexMap.put(node, size);distanceMap.put(node, distance);insertHeapify(node, size++);}}}
主方法邏輯
上來將給定的點添加到堆中,并且彈出,遍歷所有的邊放到加強堆中去搞。
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra2(Node head, int size) {NodeHeap nh = new NodeHeap(size);nh.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(head, 0);HashMap<Node, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();while (!nh.isEmpty()) {NodeRecord record = nh.pop();Node cur = record.node;int distance = record.distance;for (Edge edge : cur.edges) {nh.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to, distance + edge.weight);}result.put(cur, distance);}return result;}

)

-CAM自定義銑加工的出口環境)

)









![[4G/5G/6G專題基礎-161]:常見的濾波技術](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[4G/5G/6G專題基礎-161]:常見的濾波技術)



)