chapter 1 晶體的形成
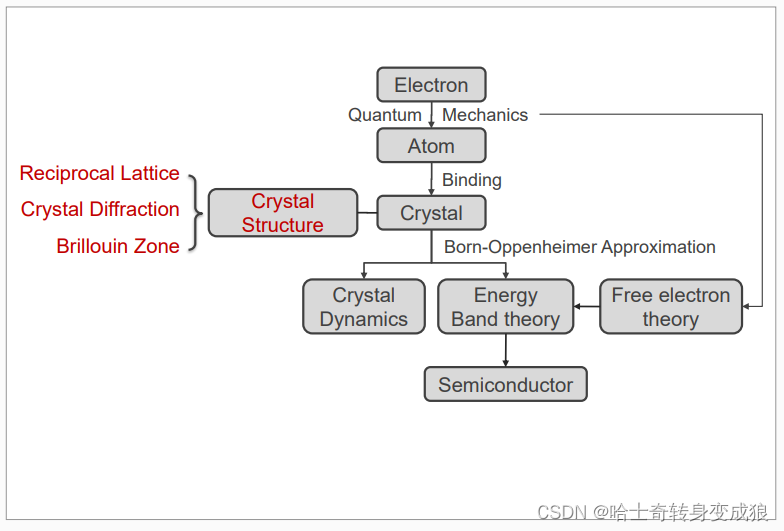
1.1 Quantum Mechanics and atomic structure
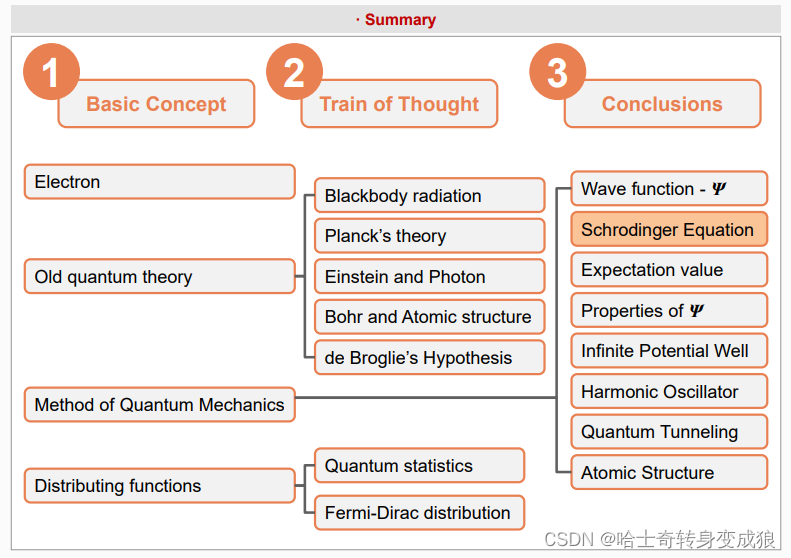
1.1.1 Old Quantum Theory
problems of planetary model:
- atom would be unstable
- radiate EM wave of continuous frequency
to solve the prablom of planetary model:
- Bohr: Quantum atomic structure
- Planck: Quantum
Old Quantum Theory: Planck, Einstein, Bohr, de Broglie
- Planck’s theory: Each atomic oscillator can have only discrete values of energy. E = n h ν , n = 0 , 1 , 2 , … E=nh \nu, n=0, 1, 2, \dots E=nhν,n=0,1,2,…
- Einstein: photon, E = h ν = ? ω E=h\nu=\hbar \omega E=hν=?ω, p = E c n = h ν c n = h λ n = ? k p= \frac{E}{c}n=\frac{h\nu}{c}n=\frac{h}{\lambda}n=\hbar k p=cE?n=chν?n=λh?n=?k
- Bohr: H atom model
- de Broglie: Matter wave, E = h ν = ? ω E=h\nu=\hbar \omega E=hν=?ω, E k = 1 2 m ν 2 = p 2 2 m = ( ? k ) 2 2 m E_k=\frac{1}{2}m\nu^2=\frac{p^2}{2m}=\frac{(\hbar k)^2}{2m} Ek?=21?mν2=2mp2?=2m(?k)2?
from de Broglie’s Hypothesis, the motion of a particle is governed by the wave propagation properties of matter wave, which means wave function.
1.1.2 Method of Quantum Mechanics
In method of Quantum Mechanics, we should get the Schrodinger Equation and solve it, then find the wave function ψ \psi ψ.
Schrodinger Equation (very important):
i ? ? Ψ ? t = ? ? 2 2 m ? 2 Ψ + U Ψ i\hbar \frac{\partial \Psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2 \Psi+U\Psi i??t?Ψ?=?2m?2??2Ψ+UΨ
a. Schrodinger Equation of free particle
KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \pPsi at position 24: …\frac{\partial \?p?P?s?i?}{\partial t}= …
wave function of free particle: ψ ( r ? , t ) = A e ? i ? ( E t ? p ? r ) \psi (\vec r, t)=A e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar} (Et-p \cdot r)} ψ(r,t)=Ae??i?(Et?p?r)
E ? i ? ? ? t E \longrightarrow i \hbar \frac{\partial}{\partial t} E?i??t??
p ? ? i ? ? \mathbf{p} \longrightarrow - i\hbar \nabla p??i??
b. Schrodinger Equation of particle in a force field
i ? ? Ψ ? t = ? ? 2 2 m ? 2 Ψ + U Ψ i \hbar \frac{\partial \Psi}{\partial t}= - \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2\Psi + U \Psi i??t?Ψ?=?2m?2??2Ψ+UΨ
We consider time-independent Schrodinger Equation:
U ( r , t ) ? U ( r ) U(\mathbf{r},t) \longrightarrow U(\mathbf{r}) U(r,t)?U(r)
then separation of variables: KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \math at position 28: …f{r} ,t)= \psi(\?m?a?t?h?{r})f(t)
Halmiton operator: H ^ = ? ? 2 2 m ? 2 + U \hat H = -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \nabla^2+U H^=?2m?2??2+U
so the Schrodinger Equ becomes a new style:
H ^ ψ = E ψ \hat H \psi = E \psi H^ψ=Eψ
H ^ Ψ = i ? ? ? t Ψ \hat H \Psi = i\hbar \frac{\partial }{\partial t} \Psi H^Ψ=i??t??Ψ
c. Infinite Potential Well
? ( ? 2 2 m d 2 d x 2 + U ( x ) ) ψ ( x ) = E ψ ( x ) -(\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+U(x))\psi (x) = E \psi(x) ?(2m?2?dx2d2?+U(x))ψ(x)=Eψ(x)
ψ ( x ) = 2 a s i n n π a x \psi (x) = \sqrt{\frac{2}{a}}sin{\frac{n \pi}{a}x} ψ(x)=a2??sinanπ?x
E = E n = π 2 ? 2 2 m a 2 n 2 , n = 1 , 2 , 3 , … E=E_n = \frac{\pi^2 \hbar^2}{2ma^2}n^2, n = 1, 2, 3, \dots E=En?=2ma2π2?2?n2,n=1,2,3,…
d. Harmonic Oscillator 1D
? ( ? 2 2 m d 2 d x 2 + 1 2 m ω 2 x 2 ) ψ ( x ) = E ψ ( x ) -(\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2 x^2)\psi (x) = E \psi(x) ?(2m?2?dx2d2?+21?mω2x2)ψ(x)=Eψ(x)
E n = ( n + 1 2 ) ? ω = ( n + 1 2 ) h ν , n = 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , … E_n = (n + \frac{1}{2})\hbar \omega = (n+\frac{1}{2})h \nu, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, \dots En?=(n+21?)?ω=(n+21?)hν,n=0,1,2,3,…
- E m i n = 1 2 h ν ( ≠ 0 ) E_{min}= \frac{1}{2}h\nu(\neq 0) Emin?=21?hν(=0), which is different from Planck’s blackbody theory ( E = n h ν , E m i n = 0 E=nh\nu, E_{min}=0 E=nhν,Emin?=0)
- In classical mechanics, the particle can bot exceed x(max), but in quantum mechanics, the particle may exceed x(max) (qith low probabilities)
e. Finite Potential Well
( ? ? 2 2 m d 2 d x 2 + U ( x ) ) ψ ( x ) = E ψ ( x ) (-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+U(x))\psi(x) = E\psi(x) (?2m?2?dx2d2?+U(x))ψ(x)=Eψ(x)
Quantum Tunneling
f. Atomic Structure, Schrodinger Equ. for H Atom
( ? ? 2 2 m ? 2 + U ) ψ = E ψ , ? 2 = ? 2 ? x 2 + ? 2 ? y 2 + ? 2 ? z 2 (-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2 + U)\psi = E\psi, \nabla^2 = \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2}+\frac{\partial^2}{\partial z^2} (?2m?2??2+U)ψ=Eψ,?2=?x2?2?+?y2?2?+?z2?2?
Schrodinger equ. becomes:
1 r 2 ? ? r ( r 2 ? ψ ? r ) + 1 r 2 sin ? θ ? ? θ ( sin ? θ ? ψ ? θ ) + 1 r 2 sin ? 2 θ ? 2 θ ? ? 2 + 2 m ? ( E ? U ) ψ = 0 \frac{1}{r^2} \frac{\partial}{\partial r}(r^2 \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial r}) +\frac{1}{r^2 \sin{\theta}} \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta}(\sin{\theta} \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial \theta}) + \frac{1}{r^2\sin^2{\theta}}\frac{\partial^2\theta}{\partial \phi^2} +\frac{2m}{\hbar}(E-U)\psi = 0 r21??r??(r2?r?ψ?)+r2sinθ1??θ??(sinθ?θ?ψ?)+r2sin2θ1???2?2θ?+?2m?(E?U)ψ=0
use seperation of variables: ψ ( r , θ , ? ) = R ( r ) Θ ( θ ) Φ ( ? ) \psi(r, \theta, \phi) = R(r) \Theta(\theta) \Phi(\phi) ψ(r,θ,?)=R(r)Θ(θ)Φ(?)
Schrodinger equ. becomes:
? sin ? 2 θ R d d r ( r 2 d R d r ) ? 2 m ? 2 r 2 sin ? 2 θ ( E ? U ) ? sin ? θ Θ = 0 \frac{-\sin^2{\theta}}{R} \frac{d}{dr}(r^2\frac{dR}{dr}) -\frac{2m}{\hbar^2} r^2 \sin^2{\theta} (E-U) -\frac{\sin{\theta}}{\Theta} = 0 R?sin2θ?drd?(r2drdR?)??22m?r2sin2θ(E?U)?Θsinθ?=0
Both Equal to a constant
{ 1 Φ d 2 Φ d ? 2 = ? m l 2 m l 2 sin ? 2 θ ? 1 Θ 1 sin ? θ d d θ ( sin ? θ d Θ d t h e t a ) = l ( l + 1 ) 1 R d d r ( r 2 d R d r ) + 2 m ? 2 r 2 ( E ? U ) = l ( l + 1 ) \begin{cases} \frac{1}{\Phi} \frac{d^2\Phi}{d\phi^2} = -m_l^2 \\ \frac{m_l^2}{\sin^2{\theta}} -\frac{1}{\Theta} \frac{1}{\sin{\theta}} \frac{d}{d\theta} (\sin{\theta} \frac{d\Theta}{dtheta}) =l(l+1) \\ \frac{1}{R} \frac{d}{dr}(r^2 \frac{dR}{dr})+\frac{2m}{\hbar^2} r^2(E-U) = l(l+1) \end{cases} ? ? ??Φ1?d?2d2Φ?=?ml2?sin2θml2???Θ1?sinθ1?dθd?(sinθdthetadΘ?)=l(l+1)R1?drd?(r2drdR?)+?22m?r2(E?U)=l(l+1)?
(1) ? \phi ? must be single-valued: m l = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , … m_l = 0, \pm 1, \pm2, \dots ml?=0,±1,±2,…
(2) Θ \Theta Θ must be finite: l = 0 , 1 , 2 , … a n d l ≥ ∣ m l ∣ l = 0, 1, 2, \dots and \ \ l \ge |m_l| l=0,1,2,…and??l≥∣ml?∣
(3) R must be finite: E = E n = ? Z 2 e 4 m 8 ? 0 2 h 2 1 n 2 , n = 1 , 2 , 3 , … a n d l < n E=E_n = -\frac{Z^2e^4 m}{8 \epsilon_0^2 h^2}\frac{1}{n^2}, \ n= 1, 2, 3, \dots \ \ and \ \ l<n E=En?=?8?02?h2Z2e4m?n21?,?n=1,2,3,…??and??l<n
{ 主量子數?? n : p r i n c i p l e q u a n t u m n u m b e r ? d e c i d e E n 角量子數?? l : o r b i t a l q u a n t u m n u m b e r ? 0 , 1 , 2 , … , n ? 1 磁量子數?? m l : m a g n e t i c q u a n t u m n u m b e r ? 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3 , … , ± l \begin{cases} 主量子數 \ \ n:\ principle\ quantum\ number\ \longrightarrow\ decide\ E_n\\ 角量子數 \ \ l:\ orbital\ quantum\ number\ \longrightarrow\ 0, 1, 2, \dots , n-1 \\ 磁量子數 \ \ m_l: \ magnetic\ quantum\ number\ \longrightarrow\ 0, \pm 1, \pm2, \pm 3, \dots, \pm l \end{cases} ? ? ??主量子數??n:?principle?quantum?number???decide?En?角量子數??l:?orbital?quantum?number???0,1,2,…,n?1磁量子數??ml?:?magnetic?quantum?number???0,±1,±2,±3,…,±l?
不考慮自旋,量子數=波函數個數=量子態數=軌道數
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle: not 2 electrons in a system ( an atom or a solid ) can be in the same quantum state ( have the same n, l, m l m_l ml?, m s m_s ms?)
1.1.3 Distributing functions of micro-particles
A system with N identical micro-particles, without either generation of new particles or vanishing of existed particles, without energy exchange—an isolated system
energy level: E 1 , E 2 , E 3 , … , E l , … E_1, E_2, E_3, \dots,E_l, \dots E1?,E2?,E3?,…,El?,…
degeneracy: ω 1 , ω 2 , ω 3 , … . ω l , … \omega_1, \omega_2,\omega_3,\dots.\omega_l,\dots ω1?,ω2?,ω3?,….ωl?,…
particle number: a 1 , a 2 , a 3 , … , a l , … a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots,a_l,\dots a1?,a2?,a3?,…,al?,…
全同性原理給量子統計和經典統計帶來重要差別;
泡利不相容原理又給費米子和玻色子的統計帶來重要差別。
自旋為 ± 1 2 \pm\frac{1}{2} ±21?的粒子服從泡利不相容原理。
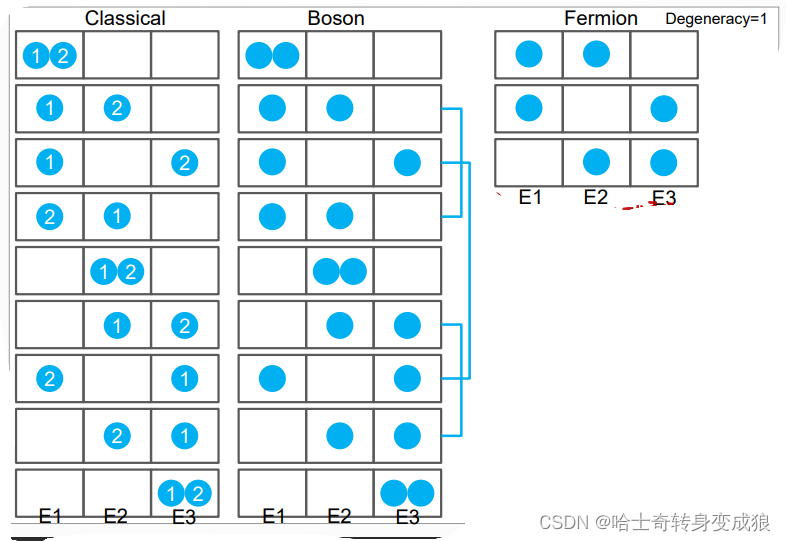
a. Boltzmann system
Every particle is identified, the number of particles in an quantum state is unlimited.
標號可分辨,能級上粒子數無限制
a l = ω l e α + β E l a_l = \frac{\omega_l}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l}} al?=eα+βEl?ωl??
Boltzmann statistics: f l = a l ω l = 1 e α + β E l = 1 e E l ? μ k B T f_l = \frac{a_l}{\omega_l} = \frac{1}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l}} = \frac{1}{e^{ \frac{E_l-\mu}{k_B T} }} fl?=ωl?al??=eα+βEl?1?=ekB?TEl??μ?1?
b. Bose system
Every particle is unidentified, the number of particles in an quantum state is unlimited.
(photon,phonon…) - Boson
玻色子:聲子、光子
不可分辨,能級上粒子無限
a l = ω l e α + β E l ? 1 a_l = \frac{\omega_l}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l} -1} al?=eα+βEl??1ωl??
Bose-Einstein statistics: f l = a l ω l = 1 e α + β E l ? 1 = 1 e E l ? μ k B T ? 1 f_l = \frac{a_l}{\omega_l} = \frac{1}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l}-1} = \frac{1}{e^{ \frac{E_l-\mu}{k_B T} } -1} fl?=ωl?al??=eα+βEl??11?=ekB?TEl??μ??11?
c.Femi system
Every particle is unidentified, the number of particles in an quantum state is limited by Pauli repulsive principle.
(electron, proton…) - Fermion
費米子:電子、質子
不可分辨,能級上粒子個數有限
a l = ω l e α + β E l + 1 a_l = \frac{\omega_l}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l} +1} al?=eα+βEl?+1ωl??
Fermi-Dirac statistics: f l = a l ω l = 1 e α + β E l + 1 = 1 e E l ? μ k B T + 1 f_l = \frac{a_l}{\omega_l} = \frac{1}{e^{\alpha+\beta E_l}+1} = \frac{1}{e^{ \frac{E_l-\mu}{k_B T} } +1} fl?=ωl?al??=eα+βEl?+11?=ekB?TEl??μ?+11?
α = ? μ k B T , β = 1 k B t \alpha = - \frac{\mu}{k_B T},\ \ \ \beta = \frac{1}{k_B t} α=?kB?Tμ?,???β=kB?t1?
1.2 binding
1.2.1 interatomic bonding
potential between two atoms: U ( R ) = ? a R m + b R n U(R)=\frac{-a}{R^m}+\frac{b}{R^n} U(R)=Rm?a?+Rnb?
 A higher binding energy means a higher melting point!
A higher binding energy means a higher melting point!
1.2.2 ionic bond
Ionic bond is formed between atoms with large differences in electronegativity. (電負性相差較大)
binding energy: 150~370 kcal/mol
Cohesive Energy in Ionic Crystal
U ( r ) = ? N a q 2 4 π ? 0 2 r + N B ′ r n U(r) = - \frac{Naq^2}{4\pi \epsilon_0^2 r} +\frac{NB'}{r^n} U(r)=?4π?02?rNaq2?+rnNB′?
Madelung constant: B ′ = ∑ j = 1 2 N ? 1 b l j n , α = ∑ j = 1 2 N ? 1 δ j l j B' = \sum_{j=1}^{2N-1} \frac{b}{l_j^n}, \ \ \ \ \alpha = \sum_{j=1}^{2N-1} \frac{\delta_j}{l_j} B′=j=1∑2N?1?ljn?b?,????α=j=1∑2N?1?lj?δj??
The bigger the cell, the more exactness the Madelung constant is.

1.2.3Van der Waals bond
1.2.4 Hydrogen bond
1.2.5 Covalent bond
1.2.6 Metallic bond
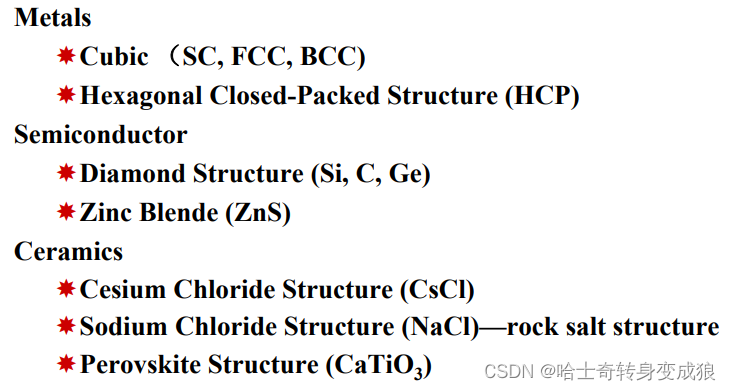
1.3 crystal structure and typical crystals
1.3.1 crystal structure
basic concept:
- 無定形晶體 Amorphous (Non-crystalline) Solid: All atoms have order only within a few atomic or molecular dimensions. — random arrangement in a bigger size
- 長程有序 Crystal: All atoms or molecules in the solid have a regular geometric arrangement or periodicity. — highly ordered
- 平移對稱性 Periodicity: The quality of recurring at regular intervals.
- 基元 Basis: Repeatable structure units.
- 格點 Latice site: The dot representing a basis.
- 晶格 Lattice (Crystal lattice): Geometric pattern of crystal structure
Crystal Structure = Lattice + Basis
primitive vectors 基矢
position vectors 格矢
primitive unit cell 原胞
conventional unit cell 晶胞
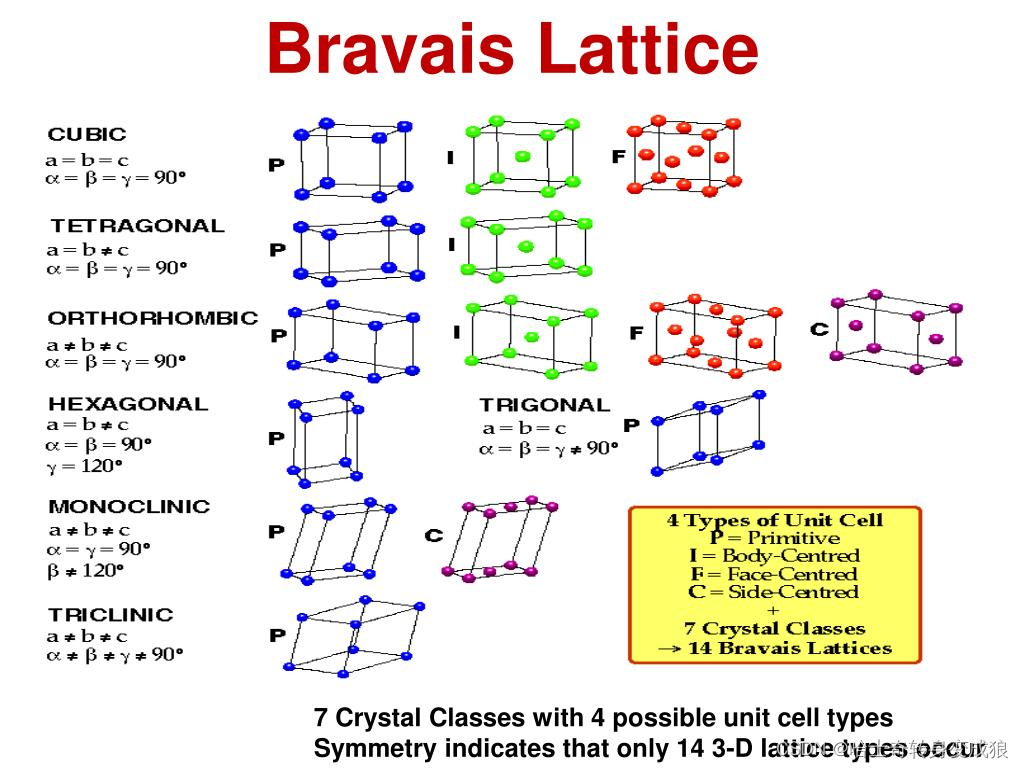
Bravais Lattice 布拉伐點陣:The geometric pattern of basis’ arrangement; all points of the lattice is identical.
Bravais lattice only summarizes the geometry of crystals, regardless of what the actual units may be.
The basis consists of the atoms, their spaces and bond angles.
Bravais lattice:
- Cubic 立方
- Hexahonal 六方
- Tetragonal 四方
- Trigonal 三方
- Monoclinic 單斜
- Orthorhomic 正交
- Triclinic 三斜
7種bravais晶系,14種bravais點陣,32點群
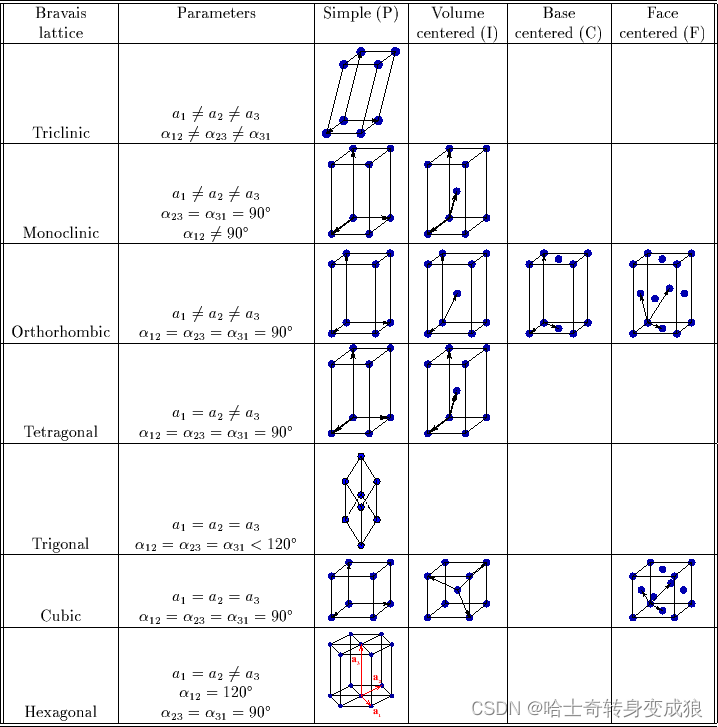
1.3.2 typical crystal structure
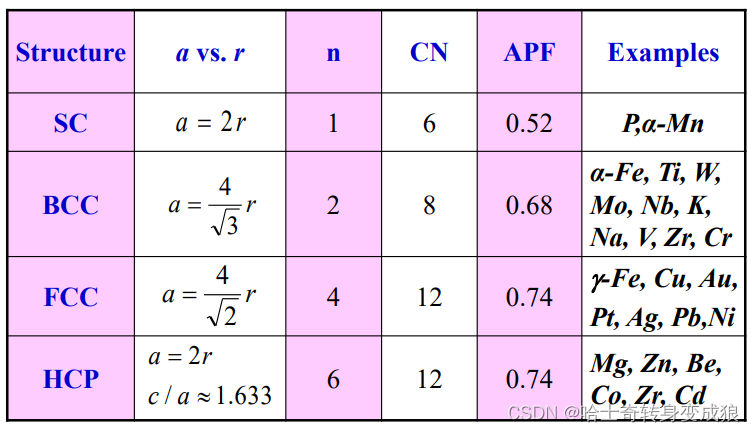
a. important parameters in crystal structure
number of atoms per unit cell: n
the number of nearest neighbors, or Coordination Number: CN 配位數
Atomic Packing Factor: APF 原子堆積因數
A P F = v o l u m e o f a t o m s i n u n i t c e l l v o l u m e o f u n i t c e l l APF = \frac{volume\ \ of \ \ atoms \ \ in \ \ unit \ \ cell}{volume \ \ of \ \ unit\ \ cell} APF=volume??of??unit??cellvolume??of??atoms??in??unit??cell?
Atomic Radius: 原子半徑
b. typical cubic structure of metal
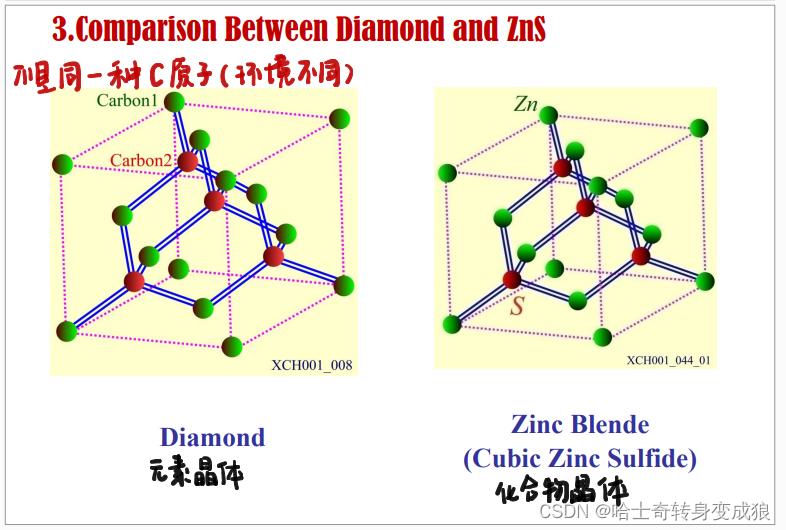
c. typical crystal structure of semiconductor

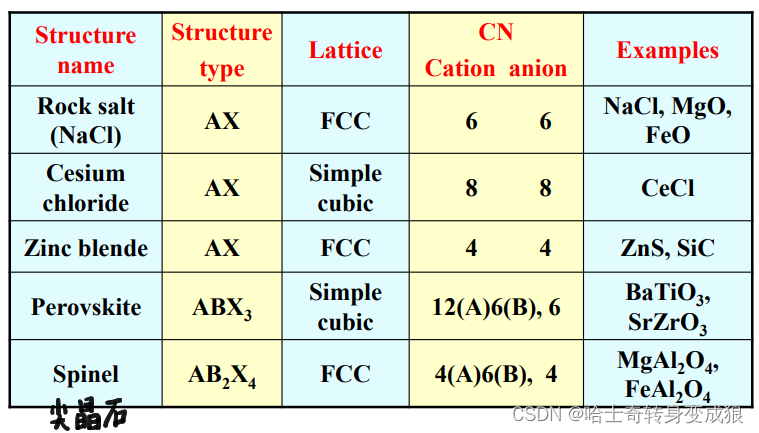
d. typical crystal structure of Ionic Crystal
e. typical crystal structure and the Bravais Lattice
1.4 Reciprocal Lattice and Brillouin Zone
1.4.1 Reciprocal Lattice 倒易點陣
晶體衍射得到的圖象(衍射斑點)是倒易點陣的二維投影空間放大。
Fourier series: 傅里葉級數
f ( x + 2 π ) = f ( x ) f(x+2\pi) = f(x) f(x+2π)=f(x)
f ( x ) = a 0 2 + ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( a n cos ? n x + b n sin ? n x ) f(x) = \frac{a_0}{2}+\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}(a_n \cos {nx} +b_n \sin{nx}) f(x)=2a0??+n=1∑∞?(an?cosnx+bn?sinnx)
f ( x ) = ∑ n c n e i n x , c n = 1 2 π ∫ ? π π f ( x ) e ? i n x d x f(x) =\sum_n c_n e^{inx},\ \ \ c_n = \frac{1}{2\pi} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} f(x)e^{-inx}dx f(x)=n∑?cn?einx,???cn?=2π1?∫?ππ?f(x)e?inxdx
Reciprocal lattice (space): 倒易點陣,晶體空間周期性
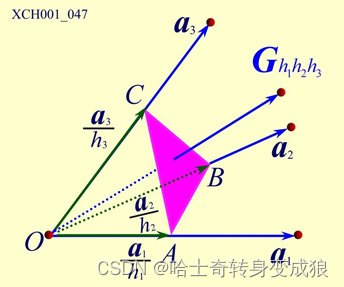
- 如何求倒格矢?
- 點陣和倒易點陣的原胞體積關系?
- 正格矢和倒格矢晶面的關系?
- 互為倒易?
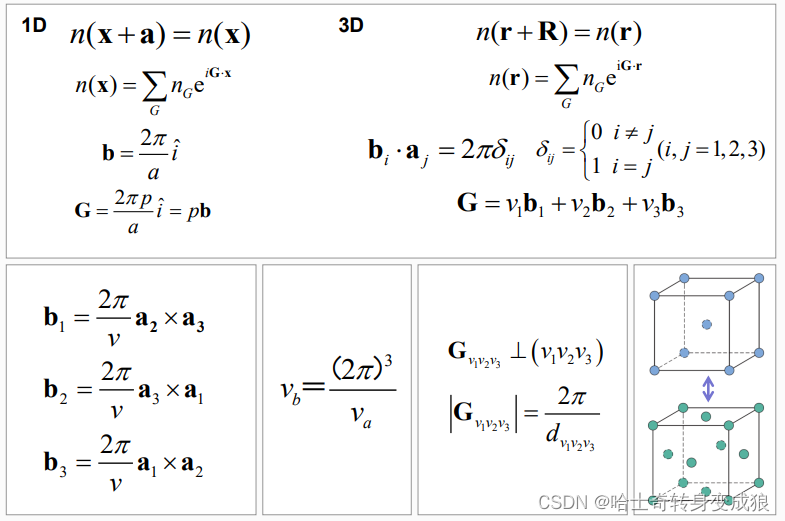
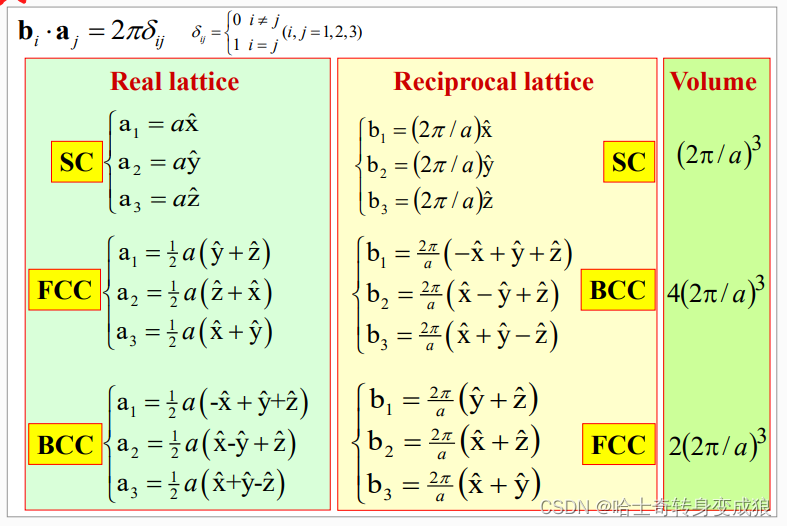
reciprocal space & wave-vector space (k-space): 倒易空間和波矢空間(k空間)
u ( x , t ) = A cos ? ( ω t ? k x + ? 0 ) u(x,t) = A \cos (\omega t - k x +\phi_0) u(x,t)=Acos(ωt?kx+?0?)
u ~ ( x , t ) = A ~ e i ( ω t ? k x ) \widetilde{u}(x,t) =\widetilde{A} e^{i(\omega t - k x)} u (x,t)=A ei(ωt?kx)
k = 2 π λ n ^ , b = 2 π a i ^ , G = 2 π p a i ^ \mathbf{k} = \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda} \hat n ,\ \ \mathbf{b} = \frac{2\pi}{a} \hat i ,\ \ \mathbf{G} = \frac{2\pi p}{a}\hat i k=λ2π?n^,??b=a2π?i^,??G=a2πp?i^
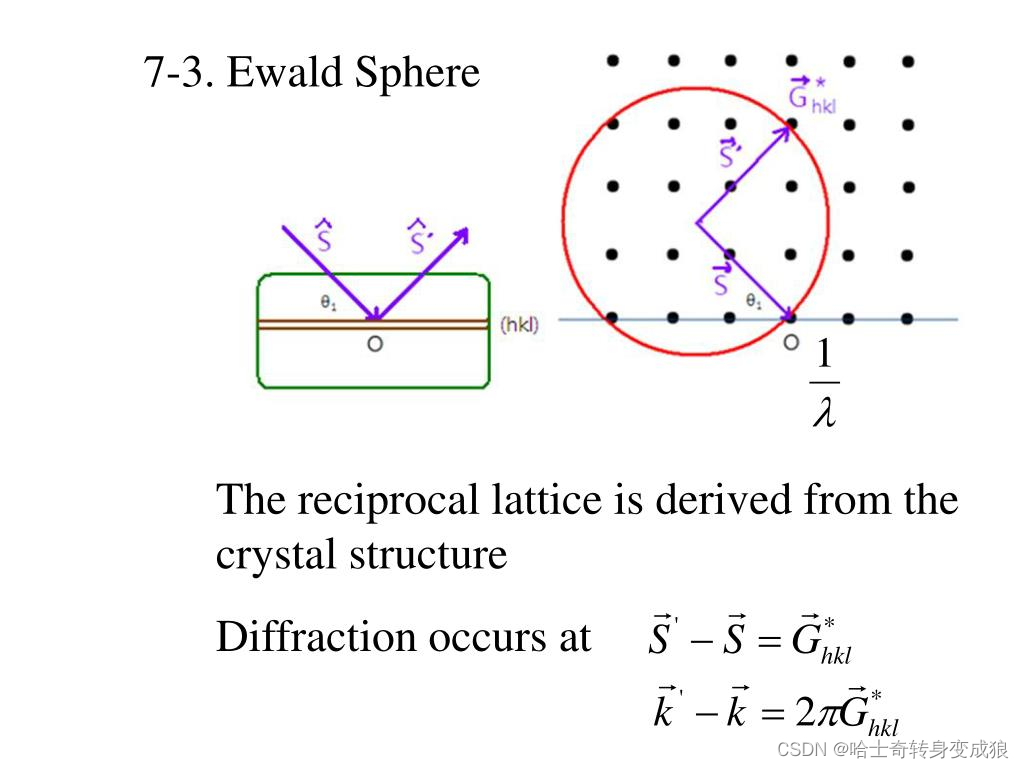
1.4.2 Crystal Diffraction 晶體衍射
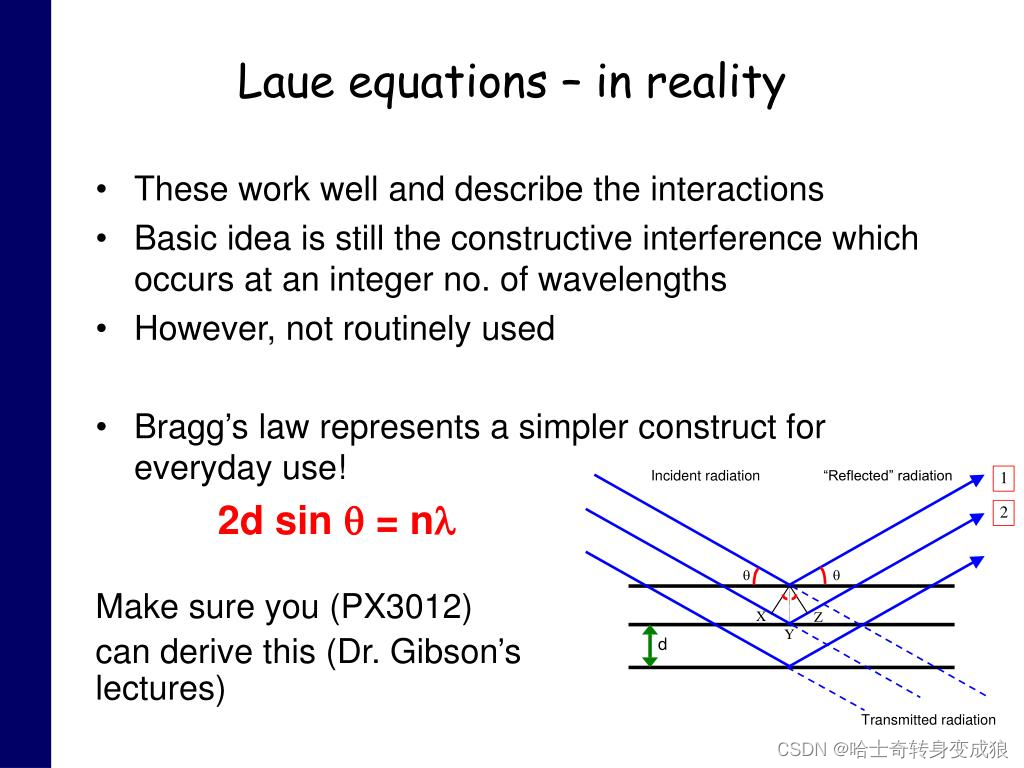
The Bragg Law:將晶體視作平行等距的晶面,將晶體對電磁波的衍射看作一組組晶面對電磁波的反射
2 d sin ? θ = n λ 2d \sin{\theta} = n\lambda 2dsinθ=nλ
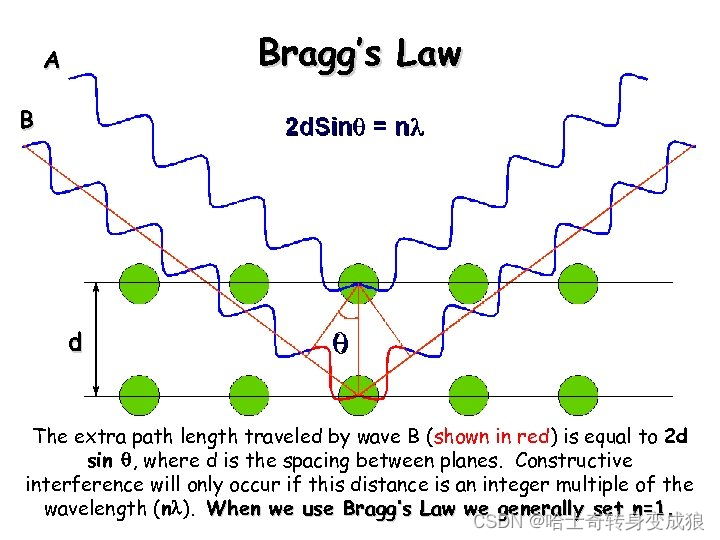

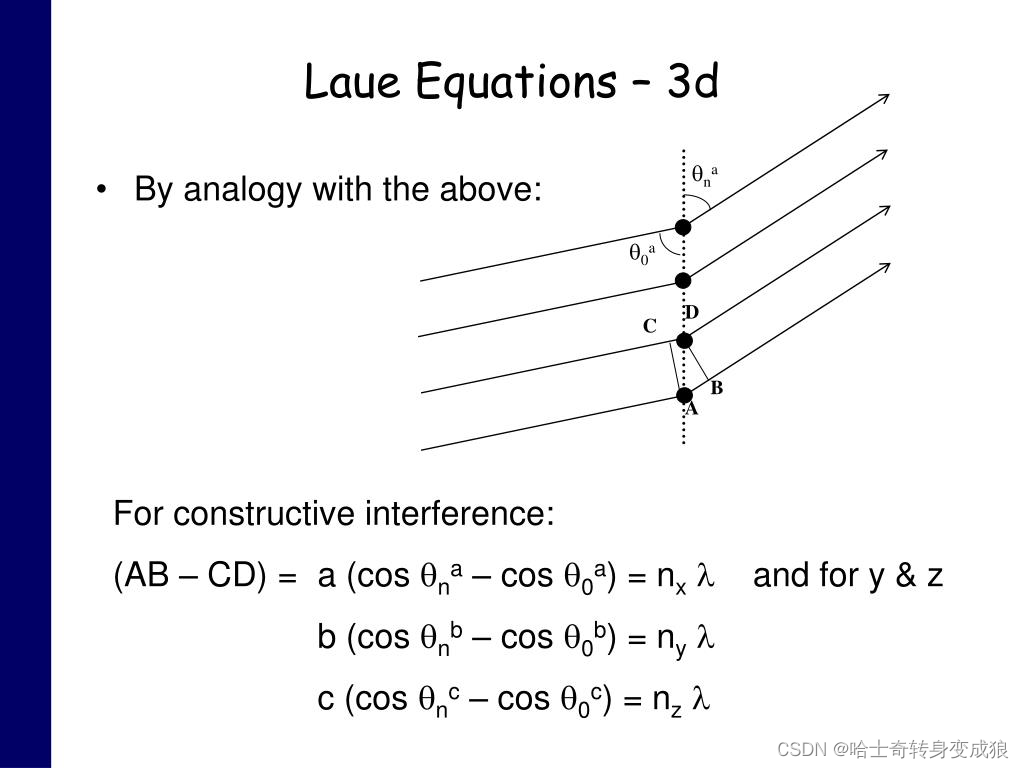
Laue equation
入射和散射的電磁波波程差:
KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \mathcf at position 35: …cos \theta ' = \?m?a?t?h?c?f?{d} \cdot (\mat…$
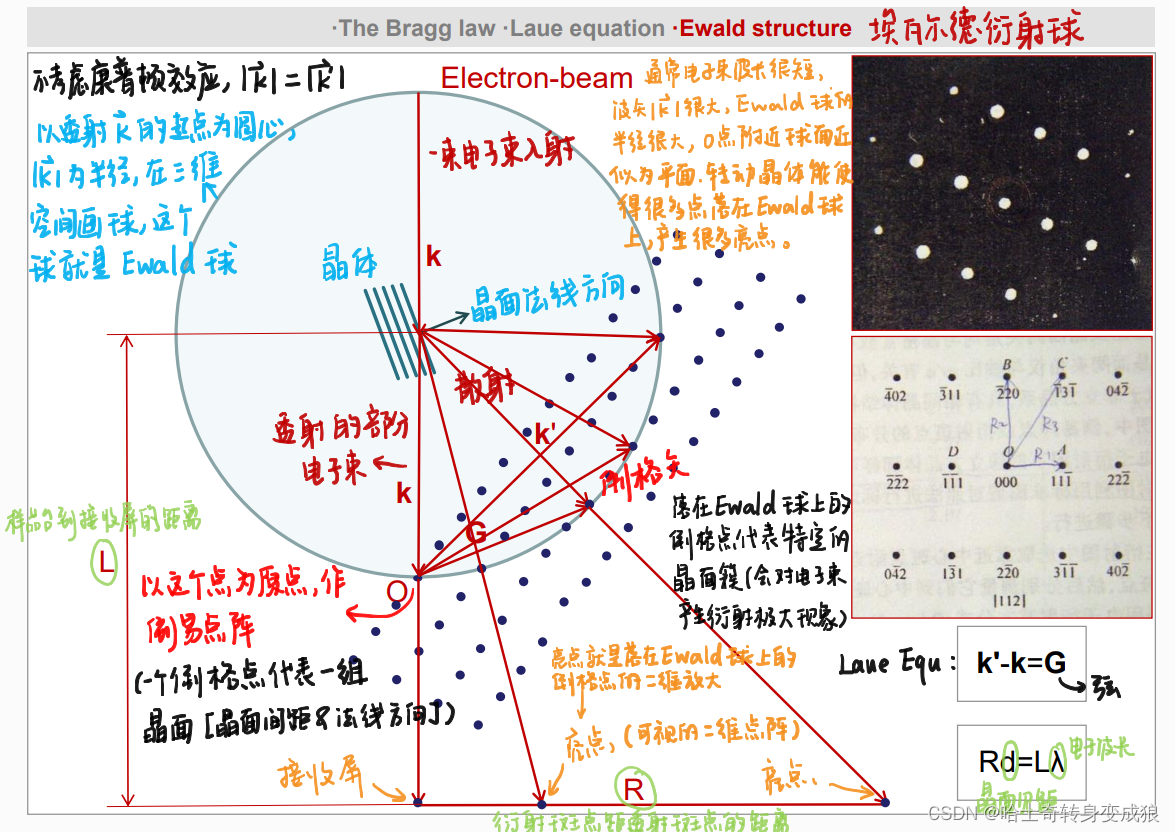
Laue Equ (與布拉格定律等價的晶體衍射關系): k ′ ? k = G , Δ k = G \mathbf{ k' - k = G, \ \ \ \Delta k = G} k′?k=G,???Δk=G
2 k ? G = G 2 2 \mathbf{k} \cdot \mathbf{G} = G^2 2k?G=G2
Ewald structure
晶體衍射的實際過程真實存在的:電子束,樣品臺(晶體),接收屏上的衍射斑點。
其他的(倒易點陣、Laue Equ、Ewald球)都是虛擬的,但是它們可以幫助分析衍射的過程和原理、以及衍射斑點的位置。
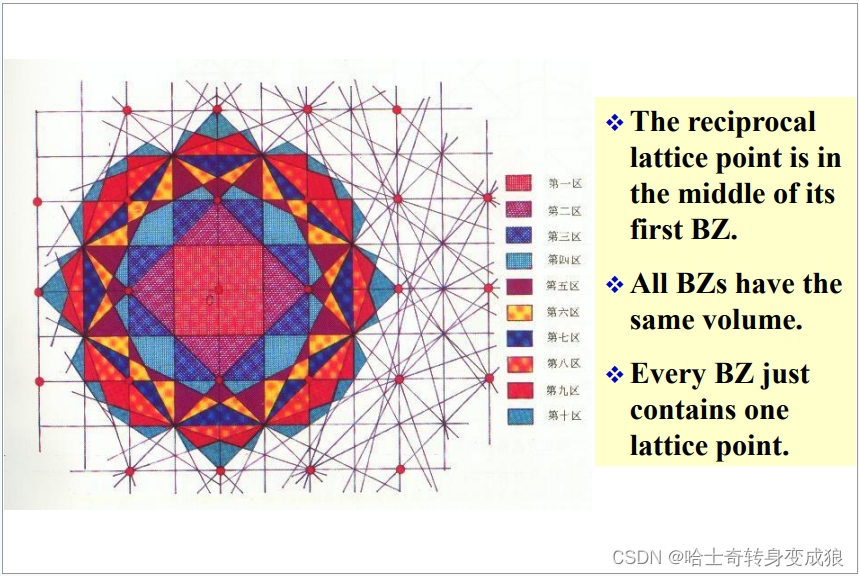
1.4.3 Brillouin Zone 布里淵區
以一個格點為原點O,找到原點O與其他格點的連線的中垂面,這些中垂面形成許多封閉區域,即布里淵區。
包圍原點且最近的叫做第一布里淵區,此后稱為第二、第三,以此類推。
- 倒易點陣的倒格原點在第一布里淵區的中點。
- 所有布里淵區具有相同的體積。
- 每個布里淵區含有且僅有一個格點。
- 一個布里淵區的體積等于一個原胞的體積。
- 布里淵區是晶格振動和能帶理論中的常用概念。電子在跨越倒格矢中垂面(布里淵區界面)時會發生能量不連續變化。

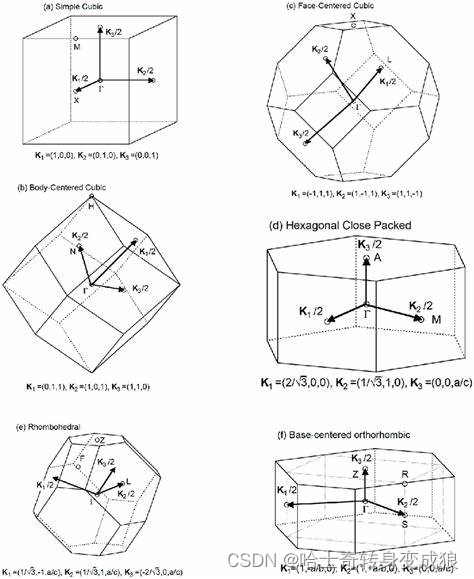
Brillouin Zone Interface & Crystal diffraction
發生晶體衍射的條件:
- 滿足布拉格定律;
- 滿足Laue Equ.;
- 波矢 k ? \vec k k的端點落在布里淵區界面上。





)








之 “ 上傳圖片功能實現”)




