在正式介紹順序表之前,我們有必要先了解一個名詞:線性表。
線性表:
線性表是,具有n個相同特性的數據元素的有限序列。常見的線性表:順序表、鏈表、棧、隊列、數組、字符串...
線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,但在物理結構上并不一定是連續的。

1. 順序表概念
順序表是用一段物理地址連續的儲存單元、依次存儲數據元素的線性結構,一般情況下采用數組存儲。

?
2. 順序表定義
typedef int SLDataType;// 順序表數據類型typedef struct SeqList
{SLDataType* arr; // 指向動態開辟的數組int size; // 有效數據個數int capacity; // 容量
}SL;3. 順序表的初始化
順序表的初始化,是使用 動態內存管理 開辟空間構造一個空的順序表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>#define DefaultCapacity 4 // 默認初始化空間大小void SLInit(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * DefaultCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = DefaultCapacity;ps->size = 0;
}4. 在pos位置插入元素
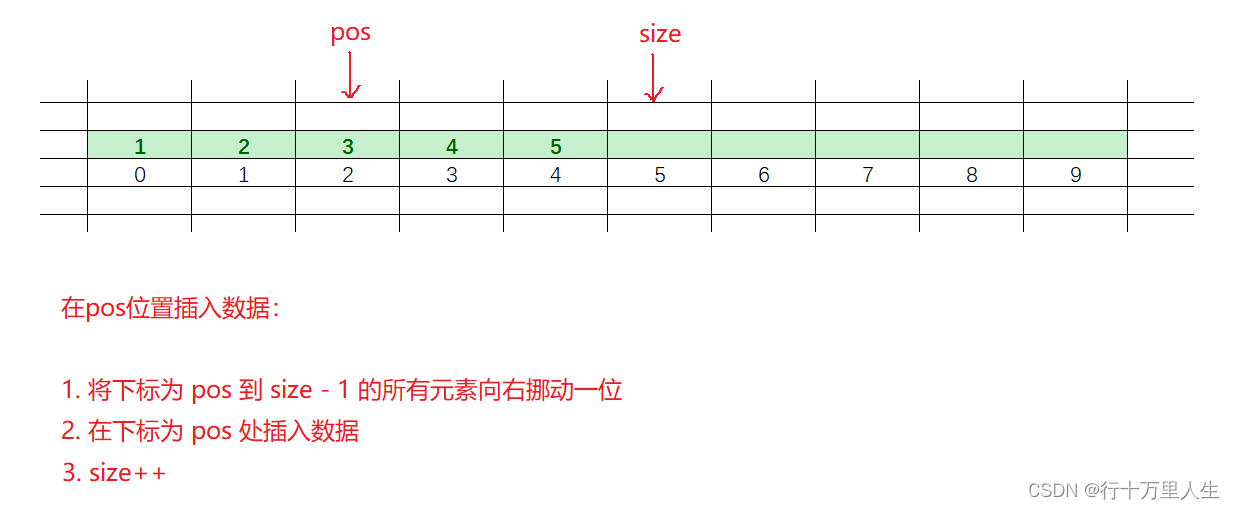
在pos位置插入數據之前,要檢查動態順序表的容量是否足夠 ,
不夠則利用 realloc函數 開辟一塊更大的空間給順序表。
檢查容量/擴容:
void SLCapacityCheck(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(SLDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc");exit(-1);}ps->capacity *= 2;ps->arr = tmp;}
}
插入:
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);SLCapacityCheck(ps);for (int i = ps->size - 1; i >= pos; i--){ps->arr[i + 1] = ps->arr[i];}ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}5. 刪除pos位置元素
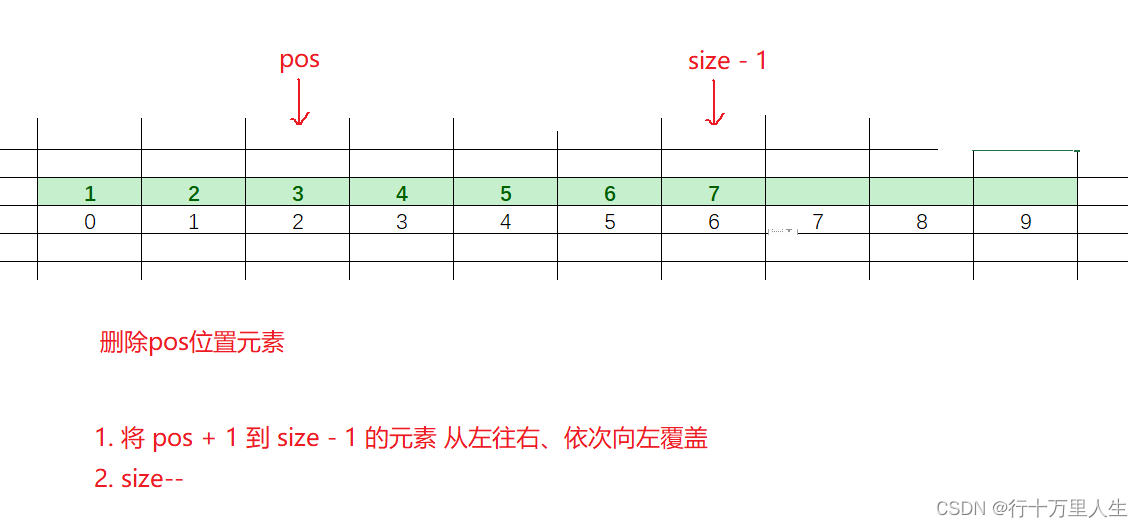
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);for (int i = pos + 1; i < ps->size; i++){ps->arr[i - 1] = ps->arr[i];}ps->size--;
}6. 順序表查找(按值查找)
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){if (ps->arr[i] == x)return i;}// 找不到所查找的元素return -1;
}在主函數中使用 SLFind函數 時,應檢驗 “返回值” 是否為非 -1,再使用
7. 順序表的打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}8. 順序表銷毀
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->arr);ps->capacity = 0;ps->size = 0;
}銷毀 arr 所指向的空間,將空間還給操作系統。









-->軟件定義架構(SDF with GraphEngine))


LangChain中的重連(retry)機制)

)
多國語言系統開發、國際化、中英文語言切換!)



)