apt:
@Retention后面的值,設置的為CLASS,說明就是編譯時動態處理的。一般這類注解會在編譯的時候,根據注解標識,動態生成一些類或者生成一些xml都可以,在運行時期,這類注解是沒有的~~會依靠動態生成的類做一些操作,因為沒有反射,效率和直接調用方法沒什么區別~~~
RUNTIME, 說明就是運行時動態處理,這個大家見得應該最多,在運行時拿到類的Class對象,然后遍歷其方法、變量,判斷有無注解聲明,然后做一些事情。
SOURCE,標記一些信息,這么說可能太抽象,那么我說,你見過@Override、@SuppressWarnings等,這類注解就是用于標識,可以用作一些檢驗?
?
@Target表示該注解可以用于什么地方,可能的類型TYPE(類),FIELD(成員變量)
1 public enum ElementType { 2 /** 3 * Class, interface or enum declaration. 4 */ 5 TYPE, 6 /** 7 * Field declaration. 8 */ 9 FIELD, 10 /** 11 * Method declaration. 12 */ 13 METHOD, 14 /** 15 * Parameter declaration. 16 */ 17 PARAMETER, 18 /** 19 * Constructor declaration. 20 */ 21 CONSTRUCTOR, 22 /** 23 * Local variable declaration. 24 */ 25 LOCAL_VARIABLE, 26 /** 27 * Annotation type declaration. 28 */ 29 ANNOTATION_TYPE, 30 /** 31 * Package declaration. 32 */ 33 PACKAGE 34 }
TypeElement ?:類
JavaPoet源碼初探
TypeSpec是類型元素的抽象,通過Kind枚舉定義class、interface、enum、annotation四種類型。
MethodSpec代表方法的抽象。
1 // 元素操作的輔助類 2 Elements elementUtils; 3 //文件相關的輔助類 4 private Filer mFiler; 5 //日志相關的輔助類 6 private Messager mMessager;
1、先添加兩個java library,一個annotation,一個compiler:
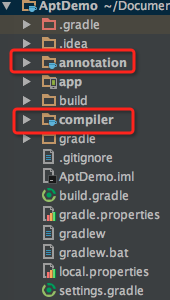
annotation library:用于放置注解。
build.gradle文件:注意屬于java library,不使用android library。
1 apply plugin: 'java' 2 3 sourceCompatibility = 1.7 4 targetCompatibility = 1.7 5 dependencies { 6 compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar']) 7 }
compile library:用于放置根據注解生成代碼類。
build.gradle文件:注意屬于java library,不使用android library。
1 apply plugin: 'java' 2 3 sourceCompatibility = 1.7 4 targetCompatibility = 1.7 5 dependencies { 6 compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar']) 7 8 compile 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc2' 9 compile 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.7.0' 10 <!-- 引用annotation library --> 11 compile project(':annotation') 12 }
app module:android app
build.gradle文件:
1 apply plugin: 'com.android.application' 2 apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt' 3 4 android { 5 compileSdkVersion 23 6 buildToolsVersion "23.0.2" 7 8 defaultConfig { 9 applicationId "com.example.aptdemo" 10 minSdkVersion 15 11 targetSdkVersion 23 12 versionCode 1 13 versionName "1.0" 14 } 15 buildTypes { 16 release { 17 minifyEnabled false 18 proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro' 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 23 dependencies { 24 compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar']) 25 testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12' 26 compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:24.0.0' 27 28 compile project(':annotation') 29 apt project(':compiler') 30 }
官方有一個列子的:生成一個java類,然后java 類里面有個main函數:
// 注解類 (目錄:annotation library)
package com.example;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) public @interface Test { }
// apt生成類 (目錄:compiler library)


1 package com.example; 2 3 import com.google.auto.service.AutoService; 4 import com.squareup.javapoet.JavaFile; 5 import com.squareup.javapoet.MethodSpec; 6 import com.squareup.javapoet.TypeSpec; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.util.Collections; 9 import java.util.Set; 10 import javax.annotation.processing.AbstractProcessor; 11 import javax.annotation.processing.Processor; 12 import javax.annotation.processing.RoundEnvironment; 13 import javax.lang.model.SourceVersion; 14 import javax.lang.model.element.Modifier; 15 import javax.lang.model.element.TypeElement; 16 17 @AutoService(Processor.class) 18 public class TestProcessor extends AbstractProcessor { 19 20 /*** 21 package com.example.helloworld; 22 23 public final class HelloWorld { 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 System.out.println("Hello, JavaPoet!"); 26 } 27 } 28 */ 29 30 @Override 31 public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() { 32 return Collections.singleton(Test.class.getCanonicalName()); 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) { 37 38 MethodSpec main = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("main") 39 .addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.STATIC) 40 .returns(void.class) 41 .addParameter(String[].class, "args") 42 .addStatement("$T.out.println($S)", System.class, "Hello, JavaPoet!") 43 .build(); 44 45 TypeSpec helloWorld = TypeSpec.classBuilder("HelloWorld") 46 .addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.FINAL) 47 .addMethod(main) 48 .build(); 49 50 JavaFile javaFile = JavaFile.builder("com.example.helloworld", helloWorld) 51 .build(); 52 53 try { 54 javaFile.writeTo(processingEnv.getFiler()); 55 } catch (IOException e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 59 return false; 60 } 61 62 @Override 63 public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() { 64 return SourceVersion.RELEASE_7; 65 } 66 }
// 使用:
在隨意一個類上面加上@Test,編譯時,代碼就會生成。
下面就是簡單的view注解生成代碼:
// 注解類 (目錄:annotation library)
1、activity 注解 :作用于類,所以目標類型是類。
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) 3 public @interface DIActivity { 4 }
2、view 注解:作用于字段,所以目標類型是字段。
1 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 public @interface DIView { 4 5 int value() default 0; 6 }
3、onClick 注解:作用于方法,所以目標類型是方法。
1 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 public @interface DIOnClick { 4 5 int[] value() default 0; 6 }
// 使用工具類:
ViewInject:用于統一activity 使用方法,注入。
1 public class ViewInject { 2 3 public final static void bind(Activity activity){ 4 5 String className = activity.getClass().getName(); 6 try { 7 Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className + "$ViewInject"); 8 Inject inject = (Inject) aClass.newInstance(); 9 inject.bindView(activity); 10 } catch (Exception e){ 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 }
Inject:用于apt生成類繼承,統一父類。
1 public interface Inject<T> { 2 3 void bindView(T host); 4 }
// apt生成類 (目錄:compiler library)
DIProcessor:


1 @AutoService(Processor.class) 2 public class DIProcessor extends AbstractProcessor { 3 4 // 元素操作的輔助類 5 Elements elementUtils; 6 //文件相關的輔助類 7 private Filer mFiler; 8 //日志相關的輔助類 9 private Messager mMessager; 10 11 @Override 12 public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv) { 13 super.init(processingEnv); 14 // 元素操作的輔助類 15 elementUtils = processingEnv.getElementUtils(); 16 mFiler = processingEnv.getFiler(); 17 mMessager = processingEnv.getMessager(); 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * 指定哪些注解應該被注解處理器注冊 22 * @return 23 */ 24 @Override 25 public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() { 26 /** 27 * Set<String> types = new LinkedHashSet<>(); 28 types.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName()); 29 types.add(OnClick.class.getCanonicalName()); 30 return types; 31 * */ 32 // 規定需要處理的注解 33 return Collections.singleton(DIActivity.class.getCanonicalName()); 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) { 38 39 Set<? extends Element> elements = roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(DIActivity.class); 40 41 for(Element element : elements){ 42 43 // 判斷是否Class 44 TypeElement typeElement = (TypeElement) element; 45 46 List<? extends Element> members = elementUtils.getAllMembers(typeElement); 47 48 MethodSpec.Builder bindViewMethod = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("bindView") 49 .addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC) 50 .returns(TypeName.VOID) 51 .addParameter(ClassName.get(typeElement.asType()), "activity", Modifier.FINAL); 52 53 bindViewMethod.addStatement("mContext = activity"); 54 55 MethodSpec.Builder onClickMethod = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("onClick") 56 .addAnnotation(Override.class) 57 .addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC) 58 .returns(TypeName.VOID) 59 .addParameter(ClassName.get("android.view", "View"), "view"); 60 61 // TypeSpec.Builder listener = TypeSpec.anonymousClassBuilder("") 62 // .addSuperinterface(ClassName.get("android.view", "View", "OnClickListener")); 63 64 mMessager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, "非常厲害"); 65 66 // bindViewMethod.addStatement("View.OnClickListener listener = null"); 67 onClickMethod.addCode("switch(view.getId()) {"); 68 69 for (Element item : members) { 70 // handler the findViewById 71 DIView diView = item.getAnnotation(DIView.class); 72 if (diView != null){ 73 74 bindViewMethod.addStatement(String.format("activity.%s = (%s) activity.findViewById(%s)" 75 ,item.getSimpleName(), ClassName.get(item.asType()).toString(), diView.value())); 76 continue; 77 } 78 79 // handler the setOnViewClick 80 DIOnClick diOnClick = item.getAnnotation(DIOnClick.class); 81 if(diOnClick != null) { 82 83 if(diOnClick.value().length > 1) { 84 for (int index = 0; index < diOnClick.value().length; index++) { 85 onClickMethod.addCode("case $L: ", diOnClick.value()[index]); 86 87 bindViewMethod.addStatement("activity.findViewById($L).setOnClickListener(this)", diOnClick.value()[index]); 88 } 89 90 onClickMethod.addStatement("mContext.$N()", item.getSimpleName()); 91 92 onClickMethod.addStatement("break"); 93 } 94 95 if(diOnClick.value().length == 1) { 96 onClickMethod.addCode("case $L: ", diOnClick.value()[0]); 97 onClickMethod.addStatement("mContext.$N()", item.getSimpleName()); 98 onClickMethod.addStatement("break"); 99 100 bindViewMethod.addStatement("activity.findViewById($L).setOnClickListener(this)", diOnClick.value()[0]); 101 } 102 continue; 103 } 104 } 105 106 onClickMethod.addStatement("}"); 107 108 // TypeSpec onClickListener = listener.addMethod(onClickMethod.build()).build(); 109 // bindViewMethod.addStatement("listener = $L ", onClickListener); 110 111 List<MethodSpec> methodSpecs = new ArrayList<>(); 112 methodSpecs.add(bindViewMethod.build()); 113 methodSpecs.add(onClickMethod.build()); 114 115 List<TypeName> typeNames = new ArrayList<>(); 116 typeNames.add(ClassName.get("android.view", "View", "OnClickListener")); 117 typeNames.add(ParameterizedTypeName.get(ClassName.get("com.example.charles.aptdemo.inject", "Inject"), TypeName.get(typeElement.asType()))); 118 119 FieldSpec fieldSpec = FieldSpec.builder(TypeName.get(typeElement.asType()), "mContext").build(); 120 121 TypeSpec typeSpec = TypeSpec.classBuilder(element.getSimpleName() + "$ViewInject") 122 // .superclass(TypeName.get(typeElement.asType())) 123 .addSuperinterfaces(typeNames) 124 .addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.FINAL) 125 .addMethods(methodSpecs) 126 .addField(fieldSpec) 127 .build(); 128 129 JavaFile javaFile = JavaFile.builder(getPackageName(typeElement), typeSpec).build(); 130 131 try { 132 javaFile.writeTo(processingEnv.getFiler()); 133 } catch (IOException e) { 134 e.printStackTrace(); 135 } 136 137 mMessager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, "完成"); 138 } 139 140 return true; 141 } 142 143 private String getPackageName(TypeElement type) { 144 return elementUtils.getPackageOf(type).getQualifiedName().toString(); 145 } 146 147 /** 148 * 指定使用的 Java 版本。通常返回SourceVersion.latestSupported()。 149 * @return 150 */ 151 @Override 152 public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() { 153 return SourceVersion.RELEASE_7; 154 } 155 }
// 使用方式:
1 @DIActivity 2 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 3 4 @DIView(R.id.text) 5 public TextView textView; 6 7 @Override 8 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 9 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 10 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 11 12 ViewInject.bind(this); 13 14 textView.setText("我不是這樣子的"); 15 } 16 17 @DIOnClick({R.id.btn_change_text, R.id.btn_change}) 18 public void changeTextView(){ 19 textView.setText("我被點擊了"); 20 } 21 22 @DIOnClick(R.id.btn_change_new) 23 public void changeNew(){ 24 textView.setText("new"); 25 } 26 }
關于javapoet:
JavaPoet?是一個用來生成 .java源文件的Java API。
下列文章為apt
Android注解-編譯時生成代碼 (APT)
下列文章為反射:
?Android 打造編譯時注解解析框架 這只是一個開始
Android 進階 教你打造 Android 中的 IOC 框架 【ViewInject】 (上)
Android 進階 教你打造 Android 中的 IOC 框架 【ViewInject】 (下)
)
與元素交互)


》)


![C語言試題四十七之程序定義了N×M的二維數組,并在主函數中自動賦值。請編寫函數function(int a[N][M], int m),該函數的功能是:將數組右上半三角元素中的值乘以m。](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/C語言試題四十七之程序定義了N×M的二維數組,并在主函數中自動賦值。請編寫函數function(int a[N][M], int m),該函數的功能是:將數組右上半三角元素中的值乘以m。)





比較大的數據庫為多個bak文件)

)



