一:背景
我們知道 C++ 是手工管理內存的分配和釋放,對應的操作符就是 new/delete 和 new[] / delete[], ?這給了程序員極大的自由度也給了我們極高的門檻,弄不好就得內存泄露,比如下面的代碼:
void?test()?{int*?i?=?new?int(10);*i?=?10;
}int?main()?{test();
}這段代碼因為用了 new 而忘了 delete,導致在 nt heap 上分配的 i 隨著棧地址的回收而成了一塊孤懸海外的內存占用,所以修正后的代碼如下:
void?test()?{int*?i?=?new?int(10);*i?=?10;delete?i;
}int?main()?{test();
}但這種寫法比較麻煩,智者千慮必有一失,總會有忘記加 delete 的時候,那怎么辦呢?大家應該知道內存自動管理有兩種手段。
引用計數
代表作有 Python,PHP,還有 windows 的句柄管理。
引用跟蹤
代表作有 C#,JAVA 等一眾工程化語言。
因為 引用計數 實現比較簡單,主要就是記錄下對象的引用次數,次數為 0 則釋放,所以可完全借助 類的構造函數析構函數 和 棧的自動回收特性 弄一個簡單的 引用計數 ,對應著如下四個關鍵詞。
auto_ptr
shared_ptr
unique_ptr
weak_ptr
接下來我們逐個聊一聊。
二:關鍵詞解析
1. auto_ptr
這是 C++ 最早出現一個的 簡單引用計數法,參考代碼如下:
void?test()?{auto_ptr<int>?ptr?=?auto_ptr<int>(new?int(10));
}int?main()?{test();
}接下來看下匯編代碼:
auto_ptr<int>?ptr?=?auto_ptr<int>(new?int(10));
...
00771D26??call????????std::auto_ptr<int>::auto_ptr<int>?(07710FAh)??
00771D2B??lea?????????ecx,[ebp-0D8h]??
00771D31??call????????std::auto_ptr<int>::~auto_ptr<int>?(0771159h)可以看到,它分別調用了 構造函數 和 析構函數,接下來找下 auto_ptr 這兩個函數的源碼。
class?auto_ptr?{private:_Ty*?_Myptr;?//?the?wrapped?object?pointerpublic:auto_ptr(auto_ptr_ref<_Ty>?_Right)?noexcept?{_Ty*?_Ptr?=?_Right._Ref;_Right._Ref?=?nullptr;?//?release?old_Myptr?=?_Ptr;?//?reset?this}~auto_ptr()?noexcept?{delete?_Myptr;}
}源碼一看就明白了,在構造函數中,將 new int 的地址塞給了內部的 _Myptr 指針,在析構函數中對 _Myptr 進行 delete ,真好,這樣就不用整天擔心有沒有加 delete 啦。
值得注意的是,現在 C++ 不推薦這個了,而是建議使用新增的:shared_ptr,unique_ptr,weak_ptr, 怎么說呢?auto_ptr 有一個不好處理的問題,就是現實開發中會出現這么個場景,多個 ptr 指向同一個 引用,如下圖:
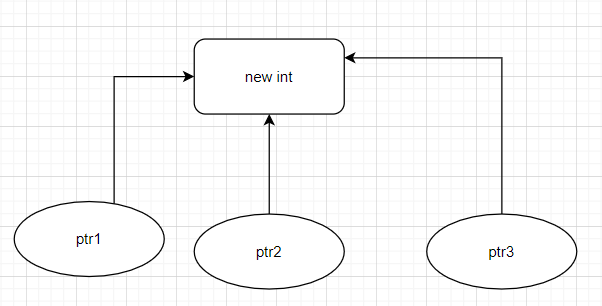
2. auto_ptr 多引用問題
方式1:
定義三個 ptr,然后包裝同一個 new int 地址,參考代碼如下:
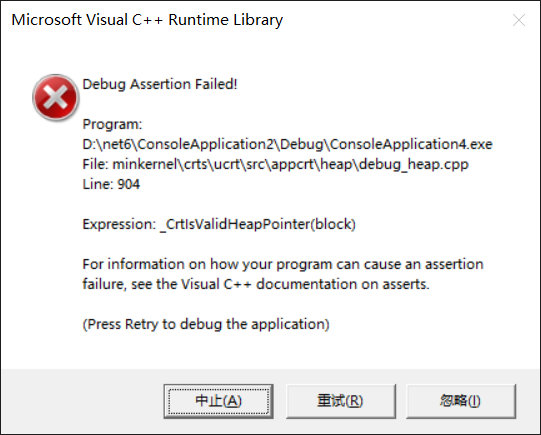
void?test()?{int*?i?=?new?int(10);auto_ptr<int>?ptr1(i);auto_ptr<int>?ptr2(i);auto_ptr<int>?ptr3(i);
}這種寫法有沒有問題呢?肯定有問題啦,還記得 auto_ptr 的析構是 delete 嗎?對同一塊內存多次 delete 會拋異常的,如下圖所示:
方式2:
既然定義三個有問題, 那就用賦值運算符= 讓 ptr1,ptr2,ptr3 指向同一個地址是不是就可以啦?參考代碼如下:
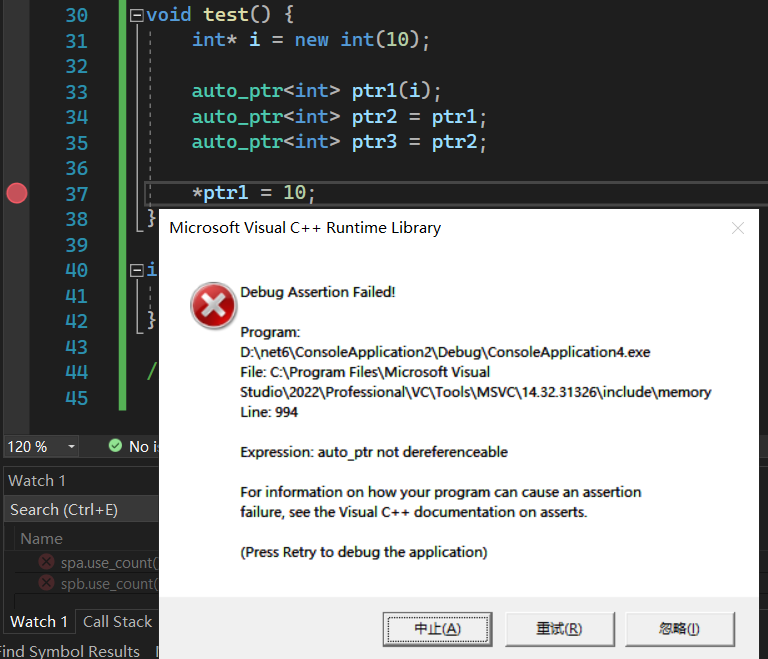
void?test()?{int*?i?=?new?int(10);auto_ptr<int>?ptr1(i);auto_ptr<int>?ptr2?=?ptr1;auto_ptr<int>?ptr3?=?ptr2;
}int?main()?{test();
}那這段代碼有沒有問題呢?有沒有問題得要看 = 運算符是如何重寫的😪,扒一下源碼看看。
template?<class?_Other>
auto_ptr&?operator=(auto_ptr<_Other>&?_Right)?noexcept?{reset(_Right.release());return?*this;
}
_Ty*?release()?noexcept?{_Ty*?_Tmp?=?_Myptr;_Myptr?=?nullptr;return?_Tmp;
}從源碼看有一個很惡心的點,他會將 _Right 下的 _Myptr 設為 nullptr,也就是說此時的 ptr1 報廢了,言外之意就是后續再訪問 ptr1 會拋 訪問違例。
哈哈,C++里面的專業術語叫 控制權轉移。
好了,本篇就說這么多吧,下一篇聊聊新增的這些關鍵詞,看看如何將 auto_ptr 更合理的分權。






第二和參數是字典)




)






)
)