在操作系統中,線程可以劃分優先級,優先級較高的線程得到CPU資源較多,也就是CPU優先執行優先級較高的線程對象中的任務(其實并不是這樣)。
在java中,線程的優先級用setPriority()方法就行,線程的優先級分為1-10這10個等級,如果小于1或大于10,則拋出異常throw new IllegalArgumentException(),默認是5。
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
new Random().nextInt();
addResult+=i;
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread1 use time--->"+(endTime-startTime));
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
new Random().nextInt();
addResult+=i;
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread2 use time--->"+(endTime-startTime));
}
}
public class MyThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThread1 t1=new MyThread1();
t1.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
}
}
}
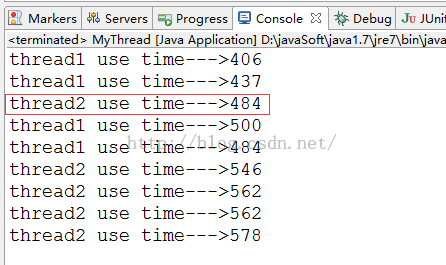
從結果中可以發現,也有thread2比thread1先執行完,也就驗證了線程的優先級于代碼執行順序無關。
public class MyThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThread1 t1=new MyThread1();
t1.setPriority(6);
t1.start();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
t2.setPriority(5);
t2.start();
}
}
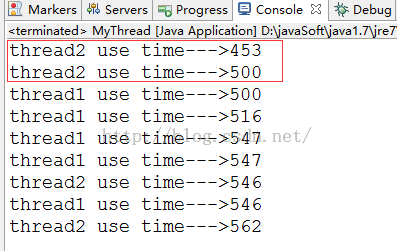
如果我們把優先級設置近點的話,發現優先級較高的線程不一定沒一次都執行完,線程的優先級與打印的順序無關,不要將這兩點的關系相關聯,他們的關系是不確定性和隨機性。
線程的優先級仍然無法保障線程的執行次序。只不過,優先級高的線程獲取CPU資源的概率較大,優先級低的并非沒機會執行。
版權聲明:本文為博主原創文章,未經博主允許不得轉載。


 -- MIME郵件的組織結構)
















暗模式)