https://openreview.net/forum?id=B1ElR4cgg
模型結構和明天要發BiGAN模型一模一樣,但是兩篇論文的作者都是獨立完成自己的內容的。而且從寫作的風格來看emmm完全不一樣
ALI跟BiGAN的設計一模一樣,但是就是沒有加Latent regressor。雖然在ALI中也簡要地談到了這個Latent regressor。
并且根據ALI中的模型(G, E,D的架構)更容易實現,條理更加清晰,模型的結構設計實現也很容易。
ALI和BiGAN的對比
整體的設計上一模一樣,這是共同點。并且兩者都是獨立設計的。
ALI雖然提到Latent regressor但是,并沒有使用。(只是說可以用來作為一個正則化,提高精度的額外的方法);BiGAN則放了較大的筆墨在這個regressor上。
ALI結構更加清晰,并且各個模塊的訓練對應的損失也較大的很清晰;BiGAN雖然有在語言上大致描述為什么,但是描述的不夠直觀清晰,而且GAN訓練本來就存在大量的坑,稍微'合理'修改某個小細節,就會導致訓練不出結果。
ALI對于E的解釋上做得比較好(E可以理解為另外的一種G),這樣看來都是來fool D的所以也是一種對抗,較為直觀。并且ALI的數學分析部分和GAN承接的更加好,寫得更加清晰。
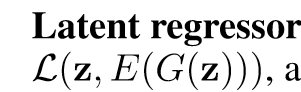
計算方式,使用L2范數。
兩者雖然都談到了Latent regressor,但是ALI更側重筆墨于模型的結構的設計(但是畫圖不行)。BiGAN雖然更側重于Latent?regressor,但是結構畫圖相當不錯。可以說是非常喜劇了。
給個對比:
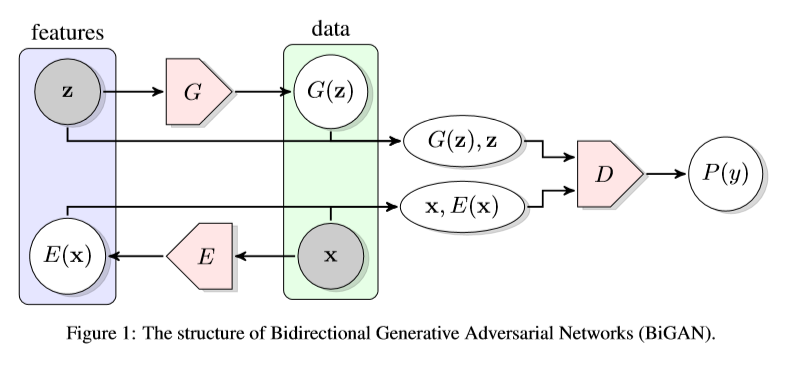
兩個結構說的是一回事,當時看到真的笑死。
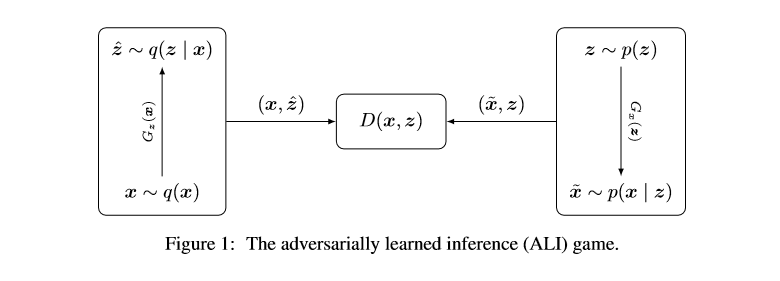
雖然談到了latent regressor,但是算法中并沒有交代使用。
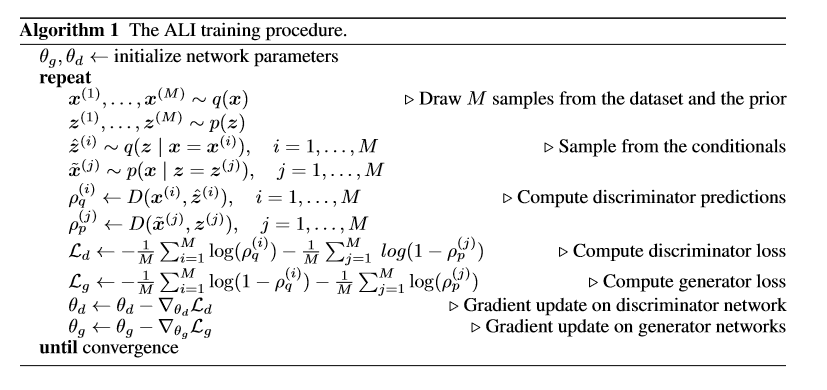
BiGAN雖然交代了使用,但是BiGAN沒有給損失的具體寫法,對于E的訓練要自己設計。
可能是兩者都或多或少有點問題,所以17年的ICLR就把兩篇都錄用了。
(或少:應該是ALI,或多多半是BiGAN)
后來就常用 ALI/BiGAN來表示這個模型。
恰飯
實驗
實驗相比于BiGAN沒有使用latent regressor,但是效果居然也還行。
按照論文實驗操作一樣,第一行是G(E(x)),第二行是x。
x來源是真實數據。通過E學習到x的隱式特征z,輸入給G,讓G生成。




main.py
import osimport torchfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoaderimport torch.nn as nnfrom model import Generator, Discriminator, Encoderimport torchvisionimport itertoolsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport torchvision.utils as vutilsimport numpy as npif __name__ == '__main__': LR = 0.0002 EPOCH = 100 # 50 BATCH_SIZE = 100 N_IDEAS = 128 lam = 1 DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False TRAINED = False mnist_root = '../Conditional-GAN/mnist/' if not (os.path.exists(mnist_root)) or not os.listdir(mnist_root): # not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root=mnist_root, train=True, # this is training data transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to # torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0] download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, ) train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) torch.cuda.empty_cache() if TRAINED: G = torch.load('G.pkl').cuda() D = torch.load('D.pkl').cuda() E = torch.load('E.pkl').cuda() else: G = Generator(N_IDEAS).cuda() D = Discriminator().cuda() E = Encoder(input_size=1, out_size=N_IDEAS).cuda() optimizerG_E = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(G.parameters(), E.parameters()), lr=LR) optimizerD = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=LR) l_c = nn.MSELoss() for epoch in range(EPOCH): tmpD, tmpG_E, tmpE = 0, 0, 0 for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # x x = x.cuda() z = torch.randn((x.shape[0], N_IDEAS, 1, 1)).cuda() # z, G, D G_z = G(z) D_G_z = torch.mean(D(G_z, z)) # fake # x, E, D E_x = E(x) D_E_x = torch.mean(D(x, E_x)) # real D_loss = -torch.mean(torch.log(D_E_x) + torch.log(1 - D_G_z)) Latent_regress = l_c(z, E(G_z)) G_E_loss = -torch.mean(torch.log(1 - D_E_x) + torch.log(D_G_z)) # + lam * Latent_regress optimizerD.zero_grad() D_loss.backward(retain_graph=True) optimizerD.step() optimizerG_E.zero_grad() G_E_loss.backward(retain_graph=True) optimizerG_E.step() tmpD_ = D_loss.cpu().detach().data tmpG_E_ = G_E_loss.cpu().detach().data tmpE_ = Latent_regress.cpu().detach().data tmpD += tmpD_ tmpG_E += tmpG_E_ tmpE += tmpE_ tmpD /= (step + 1) tmpG_E /= (step + 1) tmpE /= (step + 1) print( 'epoch %d avg of loss: D: %.6f, G_E: %.6f, latent: %.6f' % (epoch, tmpD, tmpG_E, tmpE) ) if epoch % 2 == 0: # x = x.cuda() G_imgs = G(E(x)).cpu().detach() fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) plt.axis("off") plt.imshow( np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(torch.cat([G_imgs, x.cpu().detach()]), nrow=10, padding=0, normalize=True, scale_each=True), (1, 2, 0))) plt.savefig('E_%d_.png' % step) plt.show() torch.save(G, 'G.pkl') torch.save(D, 'D.pkl') torch.save(E, 'E.pkl')model.py
import osimport torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.utils.data as Dataimport torchvisionfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoaderclass Generator(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size): super(Generator, self).__init__() strides = [1, 2, 2, 2] padding = [0, 1, 1, 1] channels = [input_size, 256, 128, 64, 32] # 1表示一維 kernels = [4, 3, 4, 4] model = [] for i, stride in enumerate(strides): model.append( nn.ConvTranspose2d( in_channels=channels[i], out_channels=channels[i + 1], stride=stride, kernel_size=kernels[i], padding=padding[i] ) ) model.append( nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[i + 1]) ) model.append( nn.LeakyReLU(.1) ) self.Conv_T = nn.Sequential(*model) self.Conv = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(kernel_size=1, stride=1, in_channels=channels[-1], out_channels=channels[-1]), nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[-1]), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(kernel_size=1, stride=1, in_channels=channels[-1], out_channels=1), nn.Sigmoid() ) def forward(self, x): x = self.Conv_T(x) x = self.Conv(x) return xclass Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size=1, out_size=128): super(Encoder, self).__init__() strides = [2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1] padding = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0] channels = [input_size, 32, 64, 128, 256, out_size, out_size] # 1表示一維 kernels = [4, 4, 4, 3, 1, 1] model = [] for i, stride in enumerate(strides): model.append( nn.Conv2d( in_channels=channels[i], out_channels=channels[i + 1], stride=stride, kernel_size=kernels[i], padding=padding[i] ) ) if i != len(strides) - 1: model.append( nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[i + 1]) ) model.append( nn.ReLU() ) self.main = nn.Sequential(*model) def forward(self, x): x = self.main(x) return xclass Discriminator(nn.Module): def __init__(self, x_in=1, z_in=128): super(Discriminator, self).__init__() self.D_x = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels=x_in, out_channels=32, kernel_size=4, stride=2), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=4, stride=2), nn.BatchNorm2d(64), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=4, stride=2), nn.BatchNorm2d(128), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), ) self.D_z = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels=z_in, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), ) self.D_x_z = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256 + 128, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.LeakyReLU(.1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1), nn.Dropout2d(.2), nn.Sigmoid(), ) def forward(self, x, z): x = self.D_x(x) z = self.D_z(z) cat_x_z = torch.cat([x, z], dim=1) return self.D_x_z(cat_x_z)if __name__ == '__main__': N_IDEAS = 128 G = Generator(N_IDEAS, ) rand_noise = torch.randn((10, N_IDEAS, 1, 1)) print(G(rand_noise).shape) E = Encoder(input_size=1, out_size=N_IDEAS) print(E(G(rand_noise)).shape) D = Discriminator() print(D(G(rand_noise), rand_noise).shape)judge.py
import numpy as npimport torchimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom model import Generator, Discriminatorimport torchvision.utils as vutilsimport osimport torchvisionfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoaderif __name__ == '__main__': BATCH_SIZE = 100 N_IDEAS = 12 TIME = 10????G?=?torch.load("G.pkl").cuda() mnist_root = '../Conditional-GAN/mnist/' DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False if not (os.path.exists(mnist_root)) or not os.listdir(mnist_root): # not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root=mnist_root, train=True, # this is training data transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to # torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0] download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, ) train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=10, shuffle=True) E = torch.load('E.pkl') for t in range(TIME): tmp = [] for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # x x = x.cuda() G_imgs = G(E(x)).cpu().detach() tmp.append(torch.cat([G_imgs, x.cpu().detach()])) if step == 5: break fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) plt.axis("off") plt.imshow( np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(torch.cat(tmp), nrow=10, padding=0, normalize=True, scale_each=True), (1, 2, 0))) plt.savefig('E_%d.png' % t) plt.show()







...)











