傳統布局
傳統布局即是早期在平板電腦、智能手機等移動設備并不流行的時候使用的布局方式。
一、表格布局
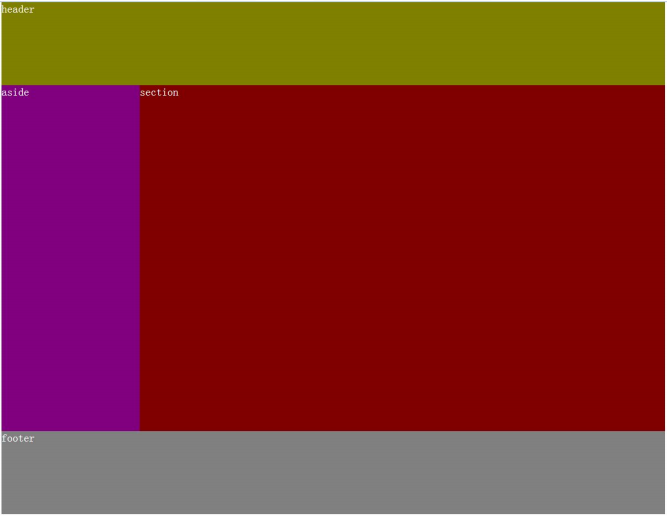
例如:采用表格方式實現如下簡單模型的布局
(1)固定布局
即用具體的像素值來確定模型的寬和高等值。
HTML代碼如下所示
<table border="0"><tr><td colspan="2" class="header">header</td></tr><tr><td class="aside">aside</td><td class="section">section</td></tr><tr><td colspan="2" class="footer">footer</td></tr>
</table>css代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {margin: 0;
}table {margin: 0 auto;width: 960px;border-spacing: 0;
}.header {height: 120px;background-color: olive;
}.aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;
}.section {width: 760px;height: 500px;background-color: maroon;
}.footer {height: 120px;background-color: gray;
}(2)流體布局
即采用百分比設置寬度等值,表格的固定布局采用流體布局的方式比較簡單,只需要將table的width值設置為100%.
流體布局css代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {margin: 0;
}table {margin: 0 auto;width: 960px;border-spacing: 0;
}.header {height: 120px;background-color: olive;
}.aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;
}.section {width: 760px;height: 500px;background-color: maroon;
}.footer {height: 120px;background-color: gray;
}二、浮動布局
浮動布局主要采用float和clear方式兩個屬性來構建
(1)固定布局
HTML代碼片段
<body><header>header</header><aside>aside</aside><section>section</section><footer>footer</footer>
</body>CSS代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {width: 960px;margin: 0 auto;
}header {height: 120px;background-color: olive;
}aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;float: left; //左浮動
}section {width: 760px;height: 500px;background-color: maroon;float: right; //右浮動
}footer {height: 120px;background-color: gray;clear: both;
}注意:aside和section這兩部分必須要添加浮動并且兩者總長度不能超過body的總長度,否則無法將兩者并排顯示
(2)流體布局
流體布局只要更改 body 元素的限定長度為 auto 或 100%。然后左右兩列分別設置 20% 和 80%即可。
流體布局css代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {width: auto; //此處改為auto或者100%margin: 0 auto;
}header {height: 120px;background-color: olive;
}aside {width: 20%; //此處改為百分比height: 500px;background-color: purple;float: left;
}section {width: 80%; //此處改為百分比height: 500px;background-color: maroon;float: right;
}footer {height: 120px;background-color: gray;clear: both;
}三、定位布局
在使用布局前先了解一下css2關于position屬性的用法。
屬性 說明 static 默認值,沒有定位 absolute 絕對定位,使用top,right,bottom,left來進行位移 relative 相對定位,使用top,right,bottom,left來進行位移 fixed 以窗口參考定位,使用top,right,bottom,left來進行位移
//absolute 絕對定位:,脫離文檔流,以窗口文檔左上角 0,0 為起點
CSS代碼
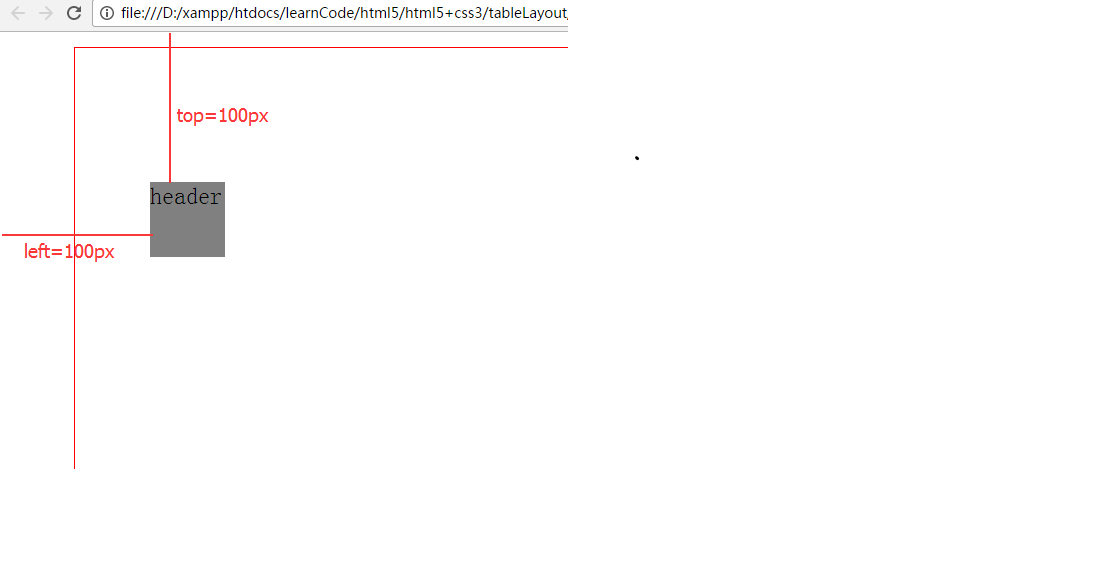
@charset "utf-8";body {margin: 10px auto;width: 800px;height: 500px;border: 1px solid red;
}header {position: absolute;top: 100px;left: 100px;width: 50px;height: 50px;background-color: grey;
}效果圖如圖所示
所謂脫離文檔流的意思,就是本身這個元素在文檔流是占位的。如果脫離了,就不占有文檔的位置,好像浮在了空中一般,有了層次感。
由于絕對定位脫離了文檔流,出現層次概念。那么每個元素到底在那一層,會不會沖突覆蓋。這時通過 z-index 屬性來判定它們的層次關系。
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| auto | 默認層次 |
| 數字 | 設置層次,數字越大,層次越高 |
示例如下:
html代碼
<body>
body
<header><div class="div1">div1</div><div class="div2">div2</div><div class="div3">div3</div>
</header>
</body>css代碼
header {position: relative;
}div {width: 150px;height: 150px;position: absolute;
}.div1 {background-color: olive;left: 0px;z-index: -1; //設置在-1層。
}.div2 {background-color: purple;top: 100px;left: 100px;z-index: 10; //設置在第10層
}.div3 {background-color: gray;top: 200px;left: 0;z-index: 100; //設置在100層
}//relative 相對定位,不脫離文檔流,占位偏移
CSS代碼
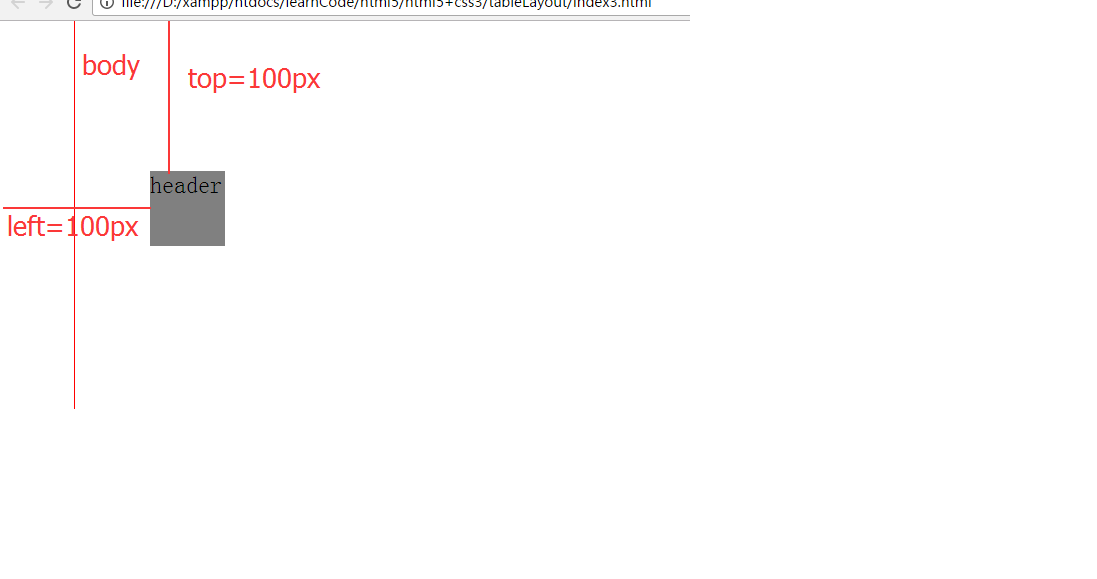
@charset "utf-8";body {margin: 10px auto;width: 800px;height: 500px;border: 1px solid red;
}header {position: relative; //相對定位top: 100px;left: 100px;width: 50px;height: 50px;background-color: grey;
}效果圖如下
//fixed 以窗口參考定位,脫離文檔流,會隨滾動條滾動而滾動
css代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {margin: 10px auto;width: 800px;height: 500px;border: 1px solid red;
}header {position: fixed; // 以窗口參考定位top: 100px;left: 100px;width: 50px;height: 50px;background-color: grey;
}這三種分別都在各自的情況下使用,均比較常用。但還有一種情況,就是:1.既要脫離文檔流(這樣元素之間不會相互沖突);2.以父元素,比如 body 或其他父元素為參考點(這樣可以實現區域性絕對定位);3.還必須是絕對定位。
HTML代碼
<body><header>header</header><aside>aside</aside><section>section</section><footer>footer</footer>
</body>CSS代碼
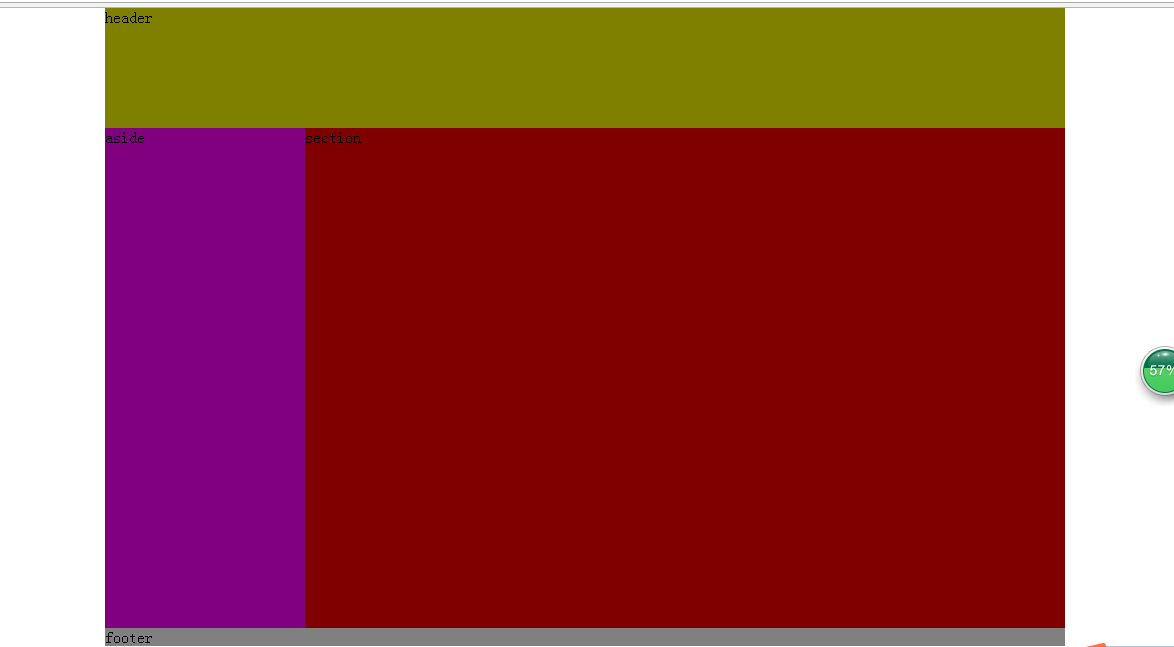
@charset "utf-8";body {width: 960px;margin: 0 auto;//第一步,將需要設置參考點的父元素設置為相對,且不設置坐標position: relative;
}header {width: 960px;height: 120px;background-color: olive;//第二步,如果父元素設置了參考點,子元素的絕對定位將以它為基準 position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;
}aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;position: absolute;top: 120px;left: 0;
}section {width: 760px;height: 500px;background-color: maroon;position: absolute;top: 120px;right: 0;
}footer {width: 960px;height: 120;background-color: gray;position: absolute;top: 620px;left: 0;
}效果圖
四、box-sizing
在盒模型中,元素盒子如果加入了內邊距 padding 和邊框 border 后,它的總長度會增加。那么如果這個元素用于非常精確的布局時,我們就需要進行計算增減。
為了解決這個精確計算的問題,CSS3 提供了一個屬性 box-sizing,這個屬性可以定義元素盒子的解析方式,從而可以選擇避免掉布局元素盒子增加內邊距和邊框的長度增減問題。
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| content-box | 默認值,border 和 padding 設置后用于元素的總長度。 |
| border-box | border 和 padding 設置后不用于元素的總長度。 |
| inherit | 規定應從父元素繼承 box-sizing 屬性的值。 |
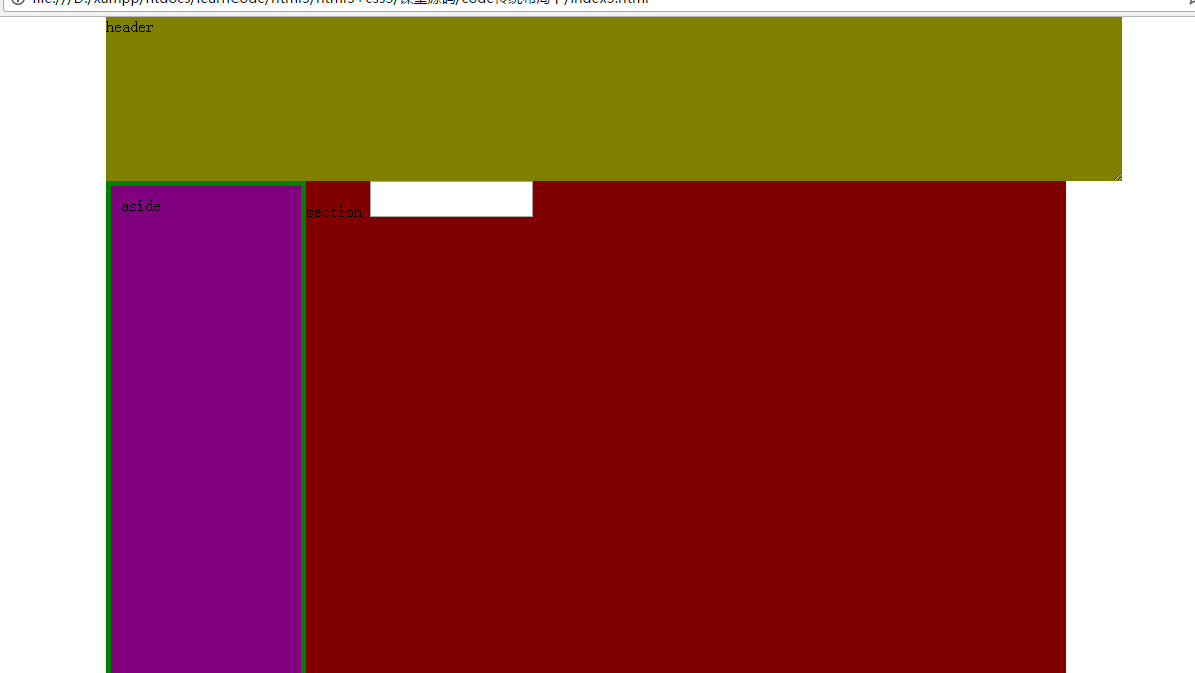
示例:設置 border-box 讓 border 和 padding 不在額外增加元素大小
aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;border: 5px solid green;padding: 10px;box-sizing: border-box;float: left;
}box-sizing 是 CSS3 推出的,各個廠商在實現時設置了私有前綴。
| Opera | Firefox | Chrome | Safari | IE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 支持需帶前綴 | 無 | 2 ~ 28 | 4 ~ 9 | 3.1 ~ 5 |
| 支持不帶前綴 | 10.1+ | 29+ | 10+ | 6+ |
//完整形式
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
-moz-box-sizing: border-box;
-ms-box-sizing: border-box;
box-sizing: border-box;五:resize
CSS3 提供了一個 resize 屬性,來更改元素尺寸大小。
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| none | 默認值,不允許用戶調整元素大小。 |
| both | 用戶可以調節元素的寬度和高度。 |
| horizontal | 用戶可以調節元素的寬度 |
| vertical | 用戶可以調節元素的高度。 |
一般普通元素,默認值是不允許的。但如果是表單類的 textarea 元素,默認是允許的。而普通元素需要設置 overflow:auto,配合 resize 才會出現可拖拽的圖形。
示例如下
HTML代碼
<body><header>header</header><aside>aside</aside><section>section<textarea></textarea></section><footer>footer</footer>
</body>css代碼
@charset "utf-8";body {width: 960px;margin: 0 auto;
}header {height: 120px;background-color: olive;overflow: auto; //必須resize: both; //設置為用戶可以調節元素的寬度和高度。
}aside {width: 200px;height: 500px;background-color: purple;border: 5px solid green;padding: 10px;box-sizing: border-box;float: left;
}section {width: 760px;height: 500px;background-color: maroon;float: right;
}footer {width: 960px;height: 120;background-color: gray;clear: both;
}textarea {resize: none;
}效果圖如下
附 W3School中css3文檔
學習參考資料:李炎恢HTML5第一季視頻教程





![[POI2007]MEG-Megalopolis](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[POI2007]MEG-Megalopolis)

















