14 - matlab m_map地學繪圖工具基礎函數 - 一些數據轉換函數(一)
- 0. 引言
- 1. 關于m_ll2xy和m_xy2ll
- 2. 關于m_lldist
- 3. 關于m_xydist
- 4 關于m_fdist
- 5 關于m_idist
- 6. 總結
0. 引言
?? 通過前面篇節已經將m_map繪圖工具中大多繪圖有關的函數進行過介紹,已經能夠滿足基本的繪圖需求,下面幾節介紹下m_map中關于數據類型轉換的一些函數,在特定應用場景下也是極為重要的。首先介紹下面幾種數據轉換函數:。
1. 關于m_ll2xy和m_xy2ll
?? m_ll2xy函數用于將經緯度坐標轉換為地圖投影坐標,m_xy2ll函數為m_ll2xy函數的逆過程,用于將投影坐標轉換為經緯度坐標。需要在地圖上標記點或繪制特定區域時這兩個命令就極為重要了。
??m_ll2xy函數的一般形式為:
[X,Y,I]=m_ll2xy(lon,lat,varargin)
[long,lat]=m_xy2ll(X,Y)
??其中:
lon和lat為經緯度坐標向量;x和y為平面投影坐標,向量長度和lon和lat向量的長度一致;varargin為可選參數,以輸入’clip’, ( ‘on’ | ‘off’ | ‘patch’ | ‘point’ )等一些屬性值,用于對超出研究范圍的區域的Nan值進行處理;
??m_ll2xy函數 和 m_xy2ll函數函數使用示例,經過m_ll2xy、m_xy2ll的互轉之后,lon和lon2數值一致,表明在坐標轉換上二者功能可逆,經過m_ll2xy函數轉換后的坐標具備平面坐標特征;
m_proj('miller', 'lon', [-180 180], 'lat', [-90 90]); %lon = linspace(-180, 180, 10);
lat = linspace(-90, 90, 10);[x,y] = m_ll2xy(lon, lat);
[lon2,lat2] = m_xy2ll(x,y);
m_grid
scatter(lon2,lat2)

2. 關于m_lldist
??m_lldist函數用于計算兩個地球表面上的點之間的球面距離。這個函數可以計算兩點之間的大圓距離(最短距離)或測地線距離(大圓弧長度)。
??m_lldist函數的一般形式為:
[dist,lons,lats] = m_lldist(long,lat,N)
??其中:
long,lat球面上兩點A、B的經緯度坐標;N是用于近似大圓弧的點的數量;dist為A、B兩點間的大圓弧距離;[lons lats]A-B路徑中的坐標點;
??m_lldist函數使用示例:
m_proj('miller','lat',[-77 77]);
m_coast('patch',[.7 1 .7],'edgecolor','none');
m_grid('box','fancy','linestyle','-','gridcolor','w','backcolor',[.2 .65 1]);cities={'Cairo','Washington','Buenos Aires'};
lons=[ 30+2/60 -77-2/60 -58-22/60];
lats=[ 31+21/60 38+53/60 -34-45/60];
for k=1:3[range,ln,lt]=m_lldist([-123-6/60 lons(k)],[49+13/60 lats(k)],40); m_line(ln,lt,'color','r','linewi',2); m_text(ln(end),lt(end),sprintf('%s - %d km',cities{k},round(range)));
end
title('Great Circle Routes','fontsize',14,'fontweight','bold');set(gcf,'color','w'); % Need to do this otherwise 'print' turns the lakes black

3. 關于m_xydist
??m_xydist 函數用于計算地圖投影坐標系下兩點之間的直線距離。
??m_xydist 函數的一般形式:
dist = m_xydist(x,y)
??其中,x、y為坐標向量,表示投影坐標上的兩點;dist 為兩點之間的直線距離:
??m_xydist函數適用示例:
lon1 = -73.98;
lat1 = 40.78;
lon2 = -122.40;
lat2 = 37.77;
distance = m_xydist([lon1 lon2], [lat1, lat2]);
fprintf('直線距離為 %f 單位\n', distance);
輸出結果為>> 直線距離為 3954.971314 單位
4 關于m_fdist
??m_fdist函數用于計算橢球上給定點在某方位/距離上的位置。
??m_fdist函數的一般形式為:
[lon2,lat2,a21] = m_fdist(lon1,lat1,a12,s,spheroid)
其中:
lon1,lat1球面上的1點坐標;a12,s第2個點的方位角a12和距第一個點的距離s;spheroid坐標系,默認為WGS84坐標系統;-
lon2,lat2,a21返回第二個點的坐標和相對于第一個點的方位角;
??m_fdist函數使用示例:
clf;
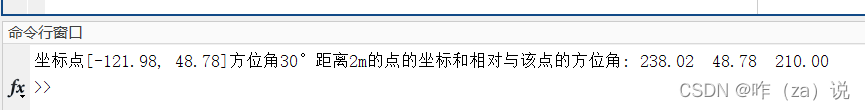
m_proj('lambert','long',[-130 -121.5],'lat',[47 51.5],'rectbox','on');[lon2 lat2 a21] = m_fdist(-121.98, 48.78,30,2);
fprintf('坐標點[-121.98, 48.78]方位角30°距離2m的點的坐標和相對與該點的方位角: %.2f %.2f %.2f \n', lon2,lat2,a21);
5 關于m_idist
??m_idist函數用于計算地圖上兩點之間的距離或方位。具體來說,m_idist 用于在地圖投影上計算兩個點之間的直線距離、大圓距離或方位角。
??m_idist函數的一般形式為:
[s,a12,a21] = m_idist(lon1,lat1,lon2,lat2,spheroid)
% lon1,lat1,lon2,lat2 兩點坐標
% spheroid 默認WGs84坐標系
??m_idist函數使用示例:
m_proj('mercator', 'lon', [69.5 105.5], 'lat', [24.5 40.5]);% 計算兩點之間的距離和方位角
[dist, az] = m_idist(70, 80,27,28);% 顯示結果
fprintf('Distance between New York and Los Angeles: %.2f km\n', dist);
fprintf('Azimuth from New York to Los Angeles: %.2f degrees\n', az);
??打印結果
>> Distance between New York and Los Angeles: 6114934.62 km
>> Azimuth from New York to Los Angeles: 227.39 degrees
6. 總結
?? 本篇介紹了m_map中數據轉換的有關函數,對各函數的功能及使用方法進行描述。希望對繪圖的你有所幫助
😜
😜😜
😜😜😜😜

主屏副屏配置)

函數深度解析與高效應用)

跳轉到指定路徑時會無限循環)

![從零開始[進階版]深入學習圖像分類:使用Python和TensorFlow](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/從零開始[進階版]深入學習圖像分類:使用Python和TensorFlow)






)




