1、引入日志
- 在這里我們引入SLF4J的日志門面,使用logback的具體日志實現;
- 引入相關依賴:
<!--日志的依賴--><dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId><version>1.7.30</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId><artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId><version>1.2.3</version></dependency>
- 添加logback的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true"><!--追加器:日志以哪種方式輸出,name:自定義追加器的名稱,class:追加器實現類的全限定名(不同實現類輸出的方式不同,下面是以控制臺方式輸出)--><appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"><encoder><!--設置日志輸出格式--><pattern>%d{YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} ---> %msg%n</pattern><charset>UTF-8</charset></encoder></appender><!--設置全局日志級別--><root level="INFO"><!--設置當前日志級別輸出到哪個追加器上--><appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" /></root><!--設置某個包或者某個類的局部日志級別--><logger name="org.example.mapper" level="debug" /><logger name="org.apache.ibatis.transaction" level="debug" /></configuration>
- 測試結果:

2、全局配置文件
在mybatis的項目中,有一個mybatis-config.xml的配置文件,這個配置文件是mybatis的全局配置文件,用來進行相關的全局配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration><properties resource="db.properties"></properties><settings> </settings><typeAliases> </typeAliases><environments></environments><mappers></mappers>
</configuration>
1、propertis(屬性)
<!--配置外部屬性資源文件,通過 ${} 來進行引用--><properties resource="db.properties"><!--也可以在內部自定義屬性--><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/trs-db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&tinyInt1isBit=false&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&allowMultiQueries=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="rootxq"/></properties>
2、setting(設置)
<settings><!-- 設置默認執行器:SIMPLE(普通執行器)、REUSE(可重復使用執行器,會重用預處理語句)、BATCH(批量執行器,不僅重用預處理語句,而且可以批量更新)--><setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/><!-- 開啟駝峰命名自動映射--><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/><!-- 在懶加載下,哪些方法會觸發立即加載,默認:equals、toString、hashCode--><!--<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value=""/>--><!-- 開啟全局的延遲加載:true 所有的嵌套查詢都是懶加載,false 所有嵌套查詢都會被立即加載--><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><!-- 設置加載的數據是否按需加載--><setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/><!-- 開啟二級緩存--><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
3、typeAliases(類型別名)
<!--設置類的別名,可以降低冗余的全局限定名的書寫--><typeAliases><!--1、可以設置包下所有類的別名:會使用類名作為別名(是忽略大小寫的)--><!--<package name="org.example.pojo"/>--><!--2、可以自定義設置某個類的別名--><typeAlias type="org.example.pojo.Emp" alias="emp"/><typeAlias type="org.example.pojo.Dept" alias="dept"/></typeAliases>
4、environments(環境配置)
<!--配置數據源連接信息--><!--可以配置多個數據源(environment),例如:測試環境、生產環境各配置一個數據源,default:設置默認使用哪個數據源--><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><!--事務管理器:type 設置事務管理類型(1)JDBC:使用JDBC的事務管理方式(2)MANAGED:不運用事務 --><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><!--數據源:type 設置數據源類型(1)UNPOOLED:不使用連接池(2)POOLED:使用Mybatis的連接池--><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${db.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${db.url}"/><property name="username" value="${db.username}"/><property name="password" value="${db.password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments>
5、mappers(映射器)
<!--映射器:有4種配置方式--><mappers><!--1、設置MapperXML的方式,適用于根據statementId進行操作--><mapper resource="mapper/DeptMapper.xml"/><mapper resource="mapper/EmpMapper.xml"/><!--2、設置Mapper接口的方式,適用于接口綁定的方式--><!--<mapper class="org.example.mapper.EmpMapper"/>--><!--<mapper class="org.example.mapper.DeptMapper"/>--><!--3、使用磁盤的絕對路徑(基本不用)--><!--4、根據包路徑設置該包下的所有Mapper接口,適用于接口綁定和注解的方式(應用最多的方式)--><!--<package name="org.example.mapper"/>--></mappers>
3、SQL映射文件
- MyBatis 的真正強大之處在于它的語句映射。由于它的異常強大,映射器的XML 文件就顯得相對簡單。MyBatis 致力于減少使用成本,讓用戶能更專注于 SQL 代碼。
- 映射文件中極其重要的幾大標簽:
select:映射查詢語句insert:映射插入語句update:映射更新語句delete:映射刪除語句sql:定義可重用的sql語句;cache:設置當前命名空間下的緩存配置;cache-ref:引用其他命名空間下的緩存配置;resultMap:描述如何從數據庫的結果集中加載對象;
- 每個頂級元素標簽中可以添加很多個屬性,下面介紹相關屬性的作用
- (1)id:設置當前命名空間中各個映射標簽的唯一標識符(同一個命名空間中的id不允許重復,對應mapper接口中的方法名稱);
- (2)paramType:設置SQL的參數類型(mybatis會根據接口方法的參數自動讀取參數的類型,所以不強制要求設置);
- (3)statementType:設置當前的Statement類型(默認為PREPARED):
- STATEMENT:代表JDBC的Statement,不支持參數預解析;
- PREPARED:代表JDBC的PreparedStatement,支持參數預解析;
- CALLABLE:代表JDBC的CallableStatement,支持存儲過程調用;
- (4)useGeneratedKeys:啟用主鍵生成策略,設置是否獲取插入后的自增長主鍵的值,默認是false,設置為true時,才會獲取自增長主鍵的值;
- (5)keyProperty:設置將獲取到的自增長主鍵值映射到實體類的哪個屬性上;
- (6)keyColumn:如果存在組合主鍵的情況,指定獲取哪個主鍵的字段名;
- 例如:
<insert id="insertEmp" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="eId" ><!--如果數據庫不支持列值自增長的話,可以使用下面的方法:selectKey:可以在增刪改操作之前或者之后執行相關屬性:order:設置執行時機(BEFORE表示之前,AFTER表示之后)keyProperty:設置將當前查詢結果放到哪個POJO的屬性上resultType:設置返回值的類型--><selectKey order="BEFORE" keyProperty="eId" resultType="int">SELECT MAX(eid)+1 FROM emp</selectKey>INSERT INTO emp (eid,e_name,e_mail,salary,did) values (#{eId},#{eName},#{eMail},#{salary},#{did})</insert>
4、基于XML的詳細使用
- POJO實體類
public class Emp{private Integer eId;private String eName;private String eMail;private Double salary;private Integer did; }public class Dept{private Integer did;private String dName; }
1、參數的獲取方式
#{}==> sql = “SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = ?”- a、會經過JDBC中的PreparedStatement對象進行預編譯處理,會根據不同的數據類型來編譯成對應數據庫所對應的數據類型;
例如:String id = “100010”,#{id} ==> sql = "SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = ‘100010’;
例如:Integer id = 100010,#{id} ==> sql = "SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = 100010; - b、能夠有效的防止SQL注入;
- a、會經過JDBC中的PreparedStatement對象進行預編譯處理,會根據不同的數據類型來編譯成對應數據庫所對應的數據類型;
${}==> sql = “SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid =” + id;- a、不會進行預編譯,會直接將獲取到的的參數直接拼接在sql中;
- b、存在SQL注入的風險;
- 特殊用法:
(1)調試時可以臨時使用,這樣可以直接將攜帶參數的完整sql語句打印在控制臺;
(2)需要動態拼接的時候,可以使用${},但是要在保證數據的安全性的前提下操作;
2、參數的傳遞方式
-
單個參數的傳遞:
-
(1)參數類型是普通數據類型時:使用
#{參數名稱}來獲取參數,即:#{id};public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpById(Integer id); }<select id="selectEmpById" resultMap="empResultSet">select * from emp where eid = #{id}</select> -
(2)參數類型是javaBean時:使用
#{屬性名}來獲取參數,emp.eId ==> #{eId}, emp.eName ==> #{eName}public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpInfo(Emp emp);}<select id="selectEmpInfo" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where eid = #{eId} and e_name = #{eName}</select> -
(3)參數類型是數組或者list集合時:mybatis會自動封裝成map
- 數組:{key:array,value:array},獲取方式:
#{arg0.下標}或者#{array.下標} - 集合:{key:list,value:list},獲取方式:
#{arg0.下標}或者#{list.下標} - 如果方法中使用了@Param()注解來指定別名,則獲取方式為:
#{別名.下標}
public interface EmpMapper {List<Emp> selectEmpByNames(List<String> names);}<select id="selectEmpByNames" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where e_name in (#{arg0.0}, #{list.1}, #{arg0.2}) </select> - 數組:{key:array,value:array},獲取方式:
- (4)參數類型是map集合時:與javaBean的參數傳遞情況一樣;
public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpByMap(Map<String,Object> paramMap); }Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap .put("id",1);paramMap .put("ename","lq");<select id="selectEmpByMap" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where eid = #{id} and e_name = #{ename}</select>
-
-
多個參數的傳遞
- mybatis會對參數按順序進行封裝,將參數封裝成map集合;
public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpByIdAndName( Integer id, String ename); }- id ==> {key : arg0,value : id的值} 或者 {key : param1,value : id的值}
- ename ==> {key : arg1,value : ename的值} 或者 {key : param2,value : ename的值}
- 可以使用
#{key}來獲取對應的值,
<select id="selectEmpByIdAndName" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where eid = #{arg0} and e_name = #{param2} </select>
- 可以給每個參數設置別名,使其具有參數意義:
- 語法:使用注解:
@Param("參數別名")
public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpByIdAndName( @Param("id")Integer id, @Param("ename")String ename); }- id ==> #{id} 或者 #{param1}
- ename ==> #{ename} 或者 #{param2}
- 可以使用
#{參數別名}來獲取對應的值
<select id="selectEmpByIdAndName" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where eid = #{id} and e_name = #{ename}</select> - 語法:使用注解:
- 如果是參數類型既有普通數據類型又有javaBean時:
public interface EmpMapper {Emp selectEmpInfoByDid(Integer did,@Param("emp") Emp emp); }- id ==> #{param1} 或者 @Param(“did”)
- emp.eName ==> #{param2.eName} 或者 emp.eName
- 注意:多個參數時,獲取JavaBean中的屬性時,使用#{參數別名.屬性名};
<select id="selectEmpInfoByDid" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where did = #{param1} and e_name = #{emp.eName}</select>
- mybatis會對參數按順序進行封裝,將參數封裝成map集合;
3、處理返回結果
- 返回類型設置:
- 如果返回單行數據,可是使用Java基礎數據類型或者POJO或者Map接收;
- 如果返回多行數據,可以使用List< POJO>或者List< Map >接收,需要在
resultType中指定List中的泛型類型;
- 當返回結果是集合的時候,返回值的類型依然寫的是集合中具體的類型
<select id="selectAllEmp" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp</select> - 在查詢時可以設置返回值的類型為map,當mybatis查詢完成之后會把列的名稱作為key,列的值作為value,轉換到map中;
<select id="selectEmpByEmpReturnMap" resultType="map">select * from emp where empno = #{empno} </select>
4、自定義結果集
- 如果數據庫表的字段與POJO的屬性名不一致時,除了可使用
'AS'來設置別名,還可以使用resultMap來設置自定義結果集,注意:resultType與resultMap二者只能使用其一。 - 相關屬性:
id:唯一標識,需要與select標簽中的resultMap進行關聯;type:需要映射的Pojo類型;autoMapping:是否自動映射,默認為false,只要字段名與屬性名遵循映射規則就可以自動映射;extends:如果同一命名空間內,如果有多個resultMap有重復的映射,可以聲明父resultMap,將公共的映射提取出來,可以減少子resultMap的映射冗余;
<resultMap id="empResultSet" type="org.example.pojo.Emp"><!--<id>:用來指定主鍵字段的映射關系<result>:用來指定普通字段的映射關系column:需要映射的數據庫表中字段的名稱property:需要映射的POJO中的屬性名稱--><id column="eid" property="eId"/><result column="e_name" property="eName"/><result column="e_mail" property="eMail"/><result column="salary" property="salary"/><result column="did" property="did"/></resultMap><select id="selectEmp" resultMap="empResultSet">select * from emp where did = #{dept_id}</select>
5、高級結果映射
1、聯合查詢
public class EmpDeptDto extends Emp{private Dept dept;public Dept getDept() {return dept;}public void setDept(Dept dept) {this.dept = dept;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return super.toString() + "EmpDeptDto{" +"dept=" + dept +'}';}
}
1、多對一映射
- 查詢所有員工的信息以及對應的部門(多員工同屬一個部門)
<resultMap id="empAndDeptMap" extends="empResultSet" type="org.example.pojo.EmpDeptDto"><!--普通方式:對象屬性名.屬性--><!--<result property="dept.dName" column="d_name"/>--><!--<result property="dept.did" column="did"/>--><!--association方式:會強行使我們的結果映射為多對一property:指定的“一”javaType:“一“的類型(自定義映射的時候才需要指定,與resultType二者使用其一)resultMap:調用已經存在的映射關系(重用resultMap)columnPrefix: 如果出現兩張表的字段有重復時,則需要使用as來起別名,可以給字段加上前綴,在映射的時候,可以使用columnPrefix自動將前綴去掉,這樣就能映射成功--><association property="dept" columnPrefix="dept_" javaType="org.example.pojo.Dept" resultMap="org.example.mapper.DeptMapper.baseDeptMap"><!--<id property="did" column="did"/>--><!--<result property="dName" column="d_name"/>--></association></resultMap><select id="selectEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptMap">SELECTe.*,d.did AS dept_did,d.d_name AS dept_d_nameFROMemp AS eLEFT JOIN dept AS d ON e.did = d.did</select>
2、一對多映射
- 查詢部門信息以及所屬的員工信息(一個部門包含多個員工)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="org.example.mapper.DeptMapper"><resultMap id="baseDeptMap" type="org.example.pojo.Dept"><id column="did" property="did"/><result column="d_name" property="dName"/></resultMap><!--一對多映射關系property:指定的“多”ofType:“多”的類型(自定義映射的時候才需要指定,與resultType二者使用其一)resultMap:調用已經存在的映射關系(重用resultMap)無論是association還是collection,都需要查詢主鍵值--><resultMap id="deptAndEmpMap" extends="baseDeptMap" type="org.example.pojo.DeptEmpDto"><collection property="emps" ofType="org.example.pojo.Emp" resultMap="org.example.mapper.EmpMapper.empResultSet"><!--也可以自定義映射關系--><!--<id column="eid" property="eId"/>--><!--<result column="e_name" property="eName"/>--><!--<result column="e_mail" property="eMail"/>--><!--<result column="salary" property="salary"/>--><!--<result column="did" property="did"/>--></collection></resultMap><select id="getDeptAndEmp" resultMap="deptAndEmpMap">SELECTd.*,e.*FROM dept d LEFT JOIN emp eON d.did = e.did</select>
</mapper>
2、嵌套查詢
<!--嵌套查詢:分步查詢select:查詢關聯對象的sql語句column:需要傳遞的參數值的字段fetchType:懶加載(延遲查詢):嵌套查詢的對象用到的時候才回去查詢數據--><resultMap id="queryDeptAndEmpMap" type="org.example.pojo.DeptEmpDto" extends="baseDeptMap"><collection property="emps" fetchType="lazy" select="org.example.mapper.EmpMapper.selectEmp" column="did"/></resultMap><select id="queryDeptAndEmp" resultMap="queryDeptAndEmpMap">select * from dept</select>
3、延遲查詢
- 當我們在進行表關聯的時候,有可能在查詢結果的時候不需要關聯對象的屬性值,那么此時可以通過延遲加載來實現功能。在全局配置文件中添加如下屬性:
<!‐‐ 開啟延遲加載,所有分步查詢都是懶加載 (默認是立即加載)‐‐><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><!‐‐當開啟式, 使用pojo中任意屬性都會加載延遲查詢 ,默認是false<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>‐‐><!‐‐設置對象的哪些方法調用會加載延遲查詢 默認:equals,clone,hashCode,toString‐‐><setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value=""/>
- 如果設置了全局加載,但是希望在某一個sql語句查詢的時候不使用延時策略,可以添加fetchType下屬性;
<association property="dept" column="dept_id" fetchType="eager" resultMap="org.example.mapper.DeptMapper.baseDeptMap"></association>
6、動態SQL
動態 SQL 是 MyBatis 的強大特性之一。如果你使用過 JDBC 或其它類似的框架,你應該能理解根據不同條件拼接 SQL 語句有多痛苦,例如拼接時要確保不能忘記添加必要的空格,還要注意去掉列表最后一個列名的逗號。利用動態 SQL,可以徹底擺脫這種痛苦。
如果出現SQL語句中因特殊字符報錯的話,可以使用轉義字符或者<![CDATA[]]>來解決
1、動態SQL之if
- 語法:
< if test="條件表達式 可以是OGNL表達式">< /if> - 作用:完成簡單的條件判斷,加載動態條件
- 問題:如果無法確定第一個條件是否成立,導致無法確定是否拼接 and或者or 的拼接
- (1)可以設置 1=1 避免報錯
- (2)可以使用< where>標簽,它會自動拼接或者刪除and或者or
- (3)可以使用< trim>標簽
<select id="queryEmps" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp where 1=1<if test="salary != null and salary != ''">AND salary <![CDATA[<=]]> #{salary}</if><if test="eName != null and salary != ''">AND e_name = #{eName}</if><if test="eId != null and salary != ''">AND eid = #{eId}</if> </select>
2、動態SQL之where
- 語法:
< where>< /where> - 作用:如果存在條件則自動拼接where關鍵字,也可以動態的刪除條件語句中的and或者or
<select id="queryEmps" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp <where><if test="salary != null and salary != ''">AND salary <![CDATA[<=]]> #{salary}</if><if test="eName != null and salary != ''">AND e_name = #{eName}</if><if test="eId != null and salary != ''">AND eid = #{eId}</if></where></select>
3、動態SQL之trim
- 語法:
< trim prefix="" prefixOverrides="" suffix="" suffixOverrides="">< /trim> - 作用:它的功能比較靈活、廣泛,可以在條件判斷完的SQL語句前后添加或者去掉指定的字符
- 相關屬性:
- prefix:前綴,需要添加的前綴
- prefixOverrides:需要去掉的前綴,例如:and|or
- suffix:后綴,需要添加的后綴
- suffixOverrides:需要去掉的后綴,例如:,
<select id="queryEmps" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or" suffix="" suffixOverrides=""><if test="salary != null and salary != ''">AND salary <![CDATA[<=]]> #{salary}</if><if test="eName != null and salary != ''">AND e_name = #{eName}</if><if test="eId != null and salary != ''">AND eid = #{eId}</if></trim></select>
4、動態SQL之choose、when、otherwise
- 作用:它有著類似于if、elseif、else的作用。
<select id="queryEmps2" resultMap="empResultSet">select * from emp<where><choose><when test="eName == 'lv'">eid = 1</when><when test="eName == 'zlq'">eid = 2</when><otherwise>eid = 3</otherwise></choose></where></select>
5、動態SQL之set
- 作用:主要用于解決修改操作中SET關鍵字以及SQL語句中可能多出的逗號問題
<update id="updateEmp">update emp<set><if test="eName != null and eName != ''">e_name = #{eName},</if><if test="eMail != null and eMail != ''">e_mail = #{eMail},</if><if test="salary != null and salary != ''">salary = #{salary},</if><if test="did != null and did != ''">did = #{did},</if></set>where eid = #{eId}</update>
6、動態SQL之foreach
- 作用:循環遍歷集合或者數組
- 相關屬性:
- collection:指定需要遍歷的集合名稱
- item:每次遍歷的集合元素
- index:遍歷時的下標
- separator:分隔符
- open:循環開始時添加的字符
- close:循環結束時添加的字符
<select id="queryEmpByNames" resultMap="empResultSet">select * from empwhere e_name in<foreach collection="names" item="name" index="i" separator="," open="(" close=")">#{name}</foreach></select>
7、動態SQL之sql片段
- 作用:提取重復冗余的sql語句,使其可以被共用
- 相關屬性:
- id:唯一標識,使用< include refid=“sql片段的Id” />標簽來引用
<sql id="querySQL">select * from emp</sql><select id="selectEmpByMap" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp"><include refid="querySQL"/>where eid = #{id} and e_name = #{ename}</select>
8、常用的OGNL表達式
- (1)e1 or e2:邏輯或
- (2)e1 and e2:邏輯與
- (3)e1 != e2 或者 e1 neq e2:判斷兩個對象是否不相等
- (4)e1 == e2 或者 e1 eq e2:判斷兩個對象是否相等
- (5)e1 > e2 或者 e1 gt e2:判斷e1是否大于e2
- (6)e1 >= e2 或者 e1 gte e2:判斷e1是否大于等于e2
- (7)e1 < e2 或者 e1 lt e2:判斷e1是否小于e2
- (8)e1 <= e2 或者 e1 lte e2:判斷e1是否小于等于e2
- (9)e1 instanceof e2:判斷e1是否是e2的實例
- (10)e1.method(e2):調用e1對象的method方法,并將e2作為參數傳遞給method方
- (11)e1 in e2:判斷e1是否在e2中
- (12)e1 not in e2:判斷e1是否不在e2中(13)e1 like e2:判斷e1是否和e2匹配
- (13)e1 not like e2:判斷e1是否和e2不匹配
- (14)e1 between e2 and e3:判斷e1是否在e2和e3之間
- (15)e1 not between e2 and e3:判斷e1是否不在e2和e3之間
- (16)e1 is null:判斷e1是否為null
- (17)e1 is not null:判斷e1是否不為null
- (18)!e1:邏輯非
- (19)e1+e2,e1-e2,e1*e2,e1/e2:加減乘除
7、緩存
- MyBatis 內置了一個強大的事務性查詢緩存機制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。
- 在進行配置的時候還會分為一級緩存和二級緩存:
- 一級緩存:線程級別的緩存,是本地緩存,sqlSession級別的緩存;
- 二級緩存:全局范圍的緩存,不僅局限于當前會話;
1、一級緩存
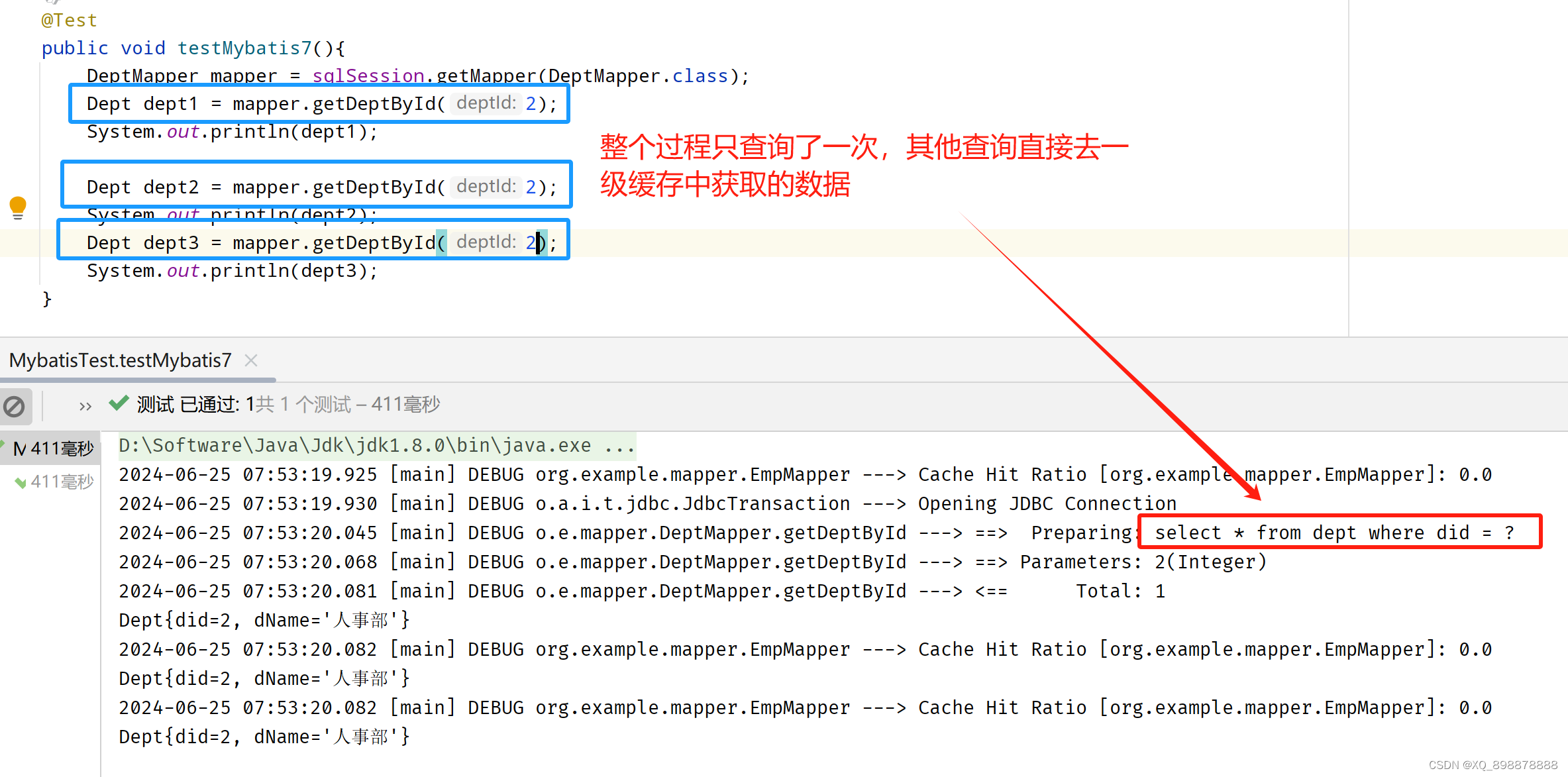
- 特性:
- 1、默認開啟,也可以關閉一級緩存,localCacheScope=STATENENT
- 2、作用域默認是基于sqlSession的,就是一次數據庫操作會話
- 3、緩存默認的實現類是:
PerpetualCache,使用map進行存儲,key ==> hashcode + sqlid + sql + hashcode + environment的id - 4、查詢完就會進行數據的緩存
- 失效情況:
- 1、不同的sqlSession會使一級緩存失效
- 2、同一個sqlSession,但是查詢語句不同,也會使一級緩存失效
- 3、同一個sqlSession,查詢語句相同,但在中間過程中執行了增刪改操作,也會使一級緩存失效
- 4、同一個sqlSession,查詢語句相同,執行手動清除緩存,會使一級緩存失效
- 例如:
2、二級緩存
- 特性:
- 1、默認開啟,但沒有實現
- 2、作用域,是全局范圍的,存儲到Java進程當中的,如果線程過多,會出現OOM
- 3、緩存默認的實現類也是
PerpetualCache,使用map進行存儲,但是,使用map存儲的是二級緩存根據不同的mapper命名空間多包了一層的map。即:key:mapper的命名空間,value:Map<k,PerpetualCache.map>; - 4、提交事務時或者sqlSession關閉的時候進行數據緩存
- 實現:
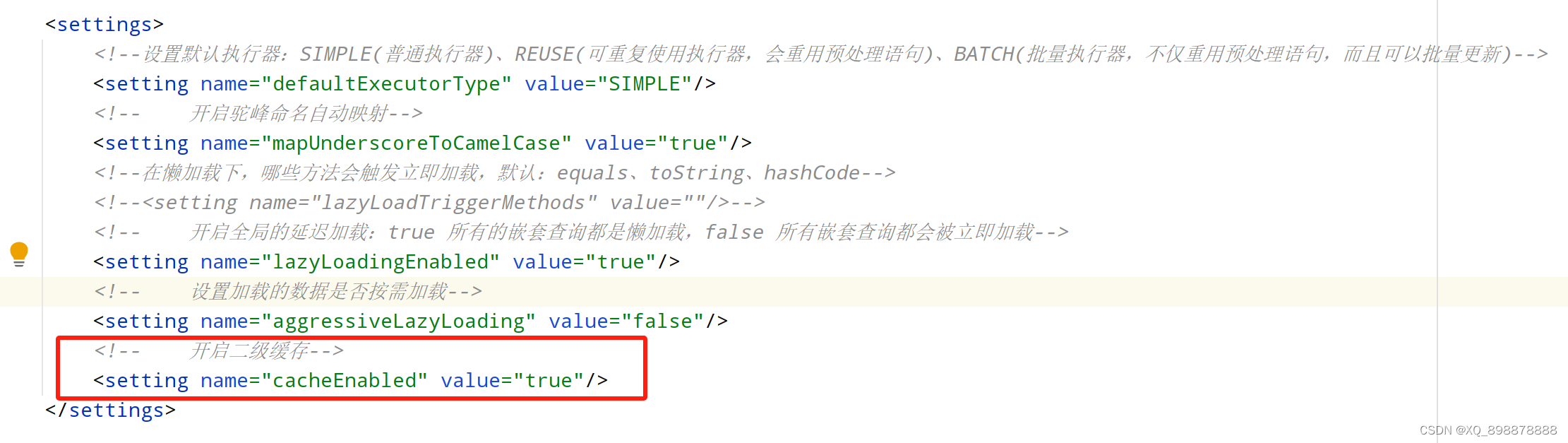
- 1、在全局配置文件中開啟二級緩存,
< setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> - 2、在需要用到二級緩存的mapper映射文件中加入,
< cache>< /cache>,它是基于Mapper映射文件來實現存儲的.
- 1、在全局配置文件中開啟二級緩存,
- 查詢順序:
- 先從二級緩存中獲取,再從一級緩存中獲取,如果都沒有,則查詢數據庫
- 失效情況:
- 1、同一個命名空間下進行增刪改操作,會使二級緩存失效
- 2、如果不想增刪改操作后緩存被清空,則可以給對應的增刪改sql設置
flushCache="false",但是設置要慎重,因為會造成數據臟讀問題。 - 3、讓查詢到的數據不緩存到二級緩存中:設置useCache=“false” 即:
<select id="getDeptById" useCache="false"> - 4、如果希望其他mapper映射文件的命名空間執行了增刪改也清空另外的命名空間的緩存,可以在某個命名空間下使用:
< cache-ref namespace=""/>
- 例如


8、分頁插件
- Mybatis通過提供插件機制,讓我們可以根據自己的需要去增強Mybatis的功能。Mybatis的插件可以在不修改原來代碼的情況下,通過攔截的方式,改變四大核心對象的行為,例如:處理參數、處理SQL、處理結果等等;
- Mybatis的分頁默認是基于內存分頁的(查出所有,再截取),在數據量大的情況下效率較低,不過使用mybatis插件可以改變該行為,只需要攔截StatementHandler類的prepare方法,改變要執行的SQL語句為分頁語句即可;
1、應用過程
1、添加依賴
<!--mybatis分頁插件依賴--><dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId><version>5.1.11</version></dependency>
2、插件注冊
- 在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中進行注冊:
<plugins><!--注冊分頁插件--><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"><!--設置當前數據庫的方言(默認會自動檢查當前數據庫環境實用的數據庫)--><property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/><!--自動合理化設置分頁參數--><property name="reasonable" value="true"/><!--支持通過Mapper接口的參數來傳遞分頁參數,默認值為false,分頁參數名稱為:pageNum、pageSize--><property name="supportMethodsArguments" value="true"/></plugin></plugins>
3、調用
<select id="queryEmpList" resultType="org.example.pojo.Emp">select * from emp</select>
@Testpublic void testMybatis9(){EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);PageHelper.startPage(1,2);List<Emp> emps = mapper.queryEmpList();System.out.println(emps);//PageInfo對象中包含了很多分頁相關的屬性,例如,當前頁,總頁數,總記錄數,是否有上/下一頁等等PageInfo<Emp> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(emps);pageInfo.getList().forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println(pageInfo.getTotal());System.out.println(Arrays.toString(pageInfo.getNavigatepageNums()));}
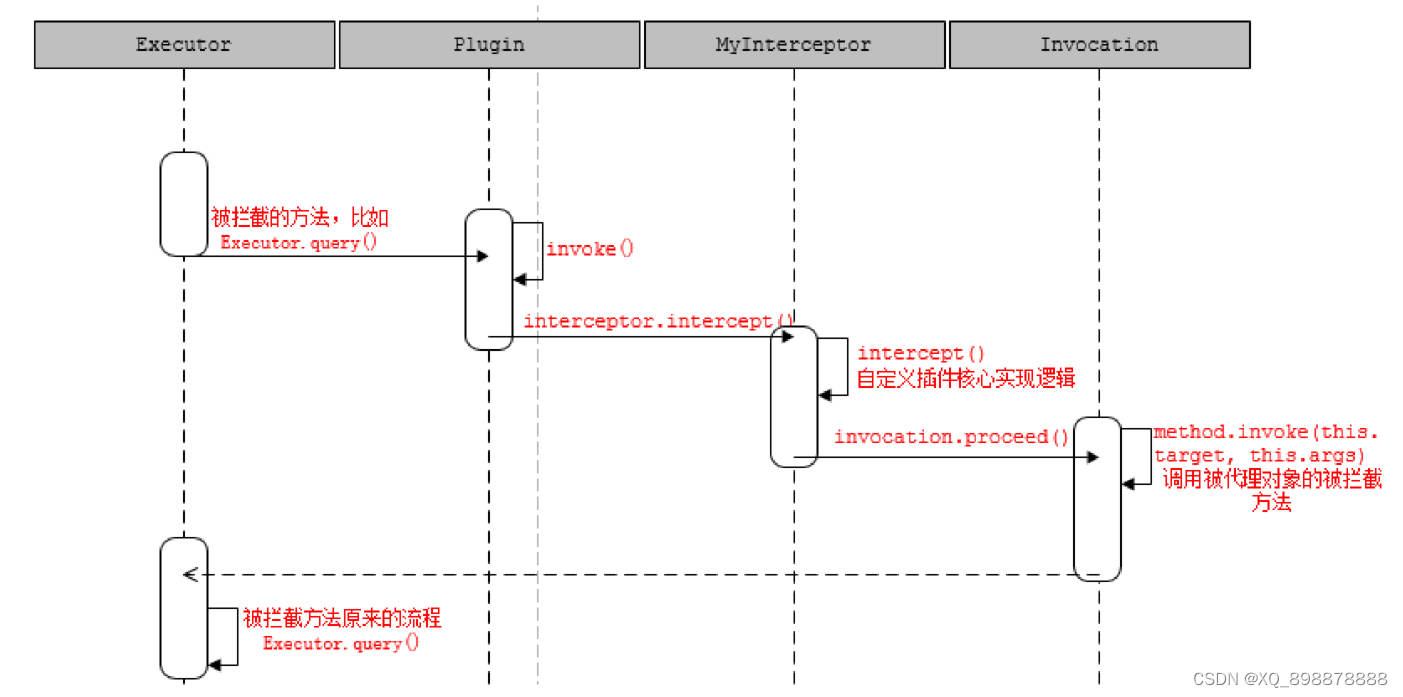
2、代理和攔截的實現
- 四大對象什么時候被代理
- Executor 是openSession()的時候創建的;
- StatementHandler 是SimpleExecutor.doQuery()創建的,里面包含了處理參數的ParameterHandler 和 處理結果集的ResultSetHandler 的創建,創建之后即調用InterceptorChain.pluginAll(),返回層層代理后的對象。
- 代理是由Plugin 類創建。在我們重寫的plugin() 方法里面可以直接調用returnPlugin.wrap(target, this)?返回代理對象。
- 因為代理類是Plugin,所以最后調用的是Plugin 的invoke()方法。它先調用了定義的攔截器的intercept()方法。可以通過invocation.proceed()調用到被代理對象被攔截的方法。

- 調用流程時序圖
)







![[分布式網絡通訊框架]----MprpcController以及Logger類](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[分布式網絡通訊框架]----MprpcController以及Logger類)

--直流電機驅動)
方法——判斷字符串是否只包含十進制字符)
(2))






