目錄
前言
一、環境準備
1. 系統要求
2. 安裝必要依賴
二、Anaconda環境配置
1. 安裝Anaconda
2. 創建專用Python環境
3. 安裝必要的Python包
三、獲取Caffe源代碼
四、配置編譯選項
1. 修改Makefile.config
2. 修改Makefile
3. 修改CMakeLists.txt(如果使用cmake,不用可跳過)
4. 創建python3.8的鏈接庫
五、編譯Caffe
1. 使用Make編譯
① 檢查編譯環境的python版本是否符合預期
?②?檢查編譯環境的protoc版本是否符合預期
③ 編譯caffe
2. 驗證動態庫鏈接
3. 常見編譯錯誤及解決方案
① 錯誤1:fatal error: numpy/arrayobject.h: No such file or directory
② 錯誤2:undefined reference to boost::python...
③ 錯誤3:error: 'pybind11' is not a namespace-name
④ 錯誤4:error: 'class std::unordered_map' has no member named 'emplace'
⑤ 錯誤5:HDF5相關錯誤
六、安裝Python接口
1. 安裝所需的python包
2. 編譯pycaffe
七、測試Caffe
八、可能遇到的問題及解決方案
問題1:
問題2:
問題3:
問題4:
前言
網上有很多博主都寫過關于caffe編譯的教程,但是在使用教程的時候總會出現各種各樣的錯誤,但是又找不到解決方案,非常無助,博主在網上參考了不下五篇文章,終于在Linux下把cpu版本的caffe編譯成功了,因此記錄一下,以防后期更換了設備后需要重新編譯,同時也希望能幫助到有需要的小伙伴們,博主列舉了部分編譯過程中遇到的錯誤以及解決方案,同時將親測有效的Makefile.config文件也分享給大家,如果你在編譯過程中有什么疑問或者好的解決方案,歡迎評論區留言。
一、環境準備
1. 系統要求
-
Ubuntu 18.04/20.04(其他Linux發行版也可,但包管理命令可能需要調整)
-
GCC/G++ 7.5或更高版本
-
確保系統已更新:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
2. 安裝必要依賴
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y build-essential cmake git pkg-config
sudo apt-get install -y libprotobuf-dev libleveldb-dev libsnappy-dev libopencv-dev
sudo apt-get install -y libhdf5-serial-dev protobuf-compiler
sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libboost-all-dev
sudo apt-get install -y libgflags-dev libgoogle-glog-dev liblmdb-dev
sudo apt-get install -y python-dev python-numpy python-pip python-scipy二、Anaconda環境配置
1. 安裝Anaconda
從Anaconda官網下載并安裝:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2024.06-1-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Anaconda3-2024.06-1-Linux-x86_64.sh按照提示完成安裝后,激活conda環境:
source ~/.anaconda3/bin/activate2. 創建專用Python環境
conda create -n caffe python=3.8
conda activate caffe3. 安裝必要的Python包
pip install protobuf==3.20.1
pip install onnx==1.6.0
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib scikit-imageconda install -y opencv三、獲取Caffe源代碼
git clone https://github.com/BVLC/caffe.git
cd caffe
git checkout master # 或指定穩定版本,如 git checkout 1.0四、配置編譯選項
1. 修改Makefile.config
復制示例配置文件并修改:
cp Makefile.config.example Makefile.config給出修改后完整的Makefile.config
## Refer to http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/installation.html
# Contributions simplifying and improving our build system are welcome!# cuDNN acceleration switch (uncomment to build with cuDNN).
# USE_CUDNN := 1# CPU-only switch (uncomment to build without GPU support).
CPU_ONLY := 1# uncomment to disable IO dependencies and corresponding data layers
USE_OPENCV := 1
# USE_LEVELDB := 0
# USE_LMDB := 0
# This code is taken from https://github.com/sh1r0/caffe-android-lib
# USE_HDF5 := 0# uncomment to allow MDB_NOLOCK when reading LMDB files (only if necessary)
# You should not set this flag if you will be reading LMDBs with any
# possibility of simultaneous read and write
# ALLOW_LMDB_NOLOCK := 1# Uncomment if you're using OpenCV 3
OPENCV_VERSION := 4# To customize your choice of compiler, uncomment and set the following.
# N.B. the default for Linux is g++ and the default for OSX is clang++
# CUSTOM_CXX := g++# CUDA directory contains bin/ and lib/ directories that we need.
# CUDA_DIR := /usr/local/cuda
# On Ubuntu 14.04, if cuda tools are installed via
# "sudo apt-get install nvidia-cuda-toolkit" then use this instead:
# CUDA_DIR := /usr# CUDA architecture setting: going with all of them.
# For CUDA < 6.0, comment the *_50 through *_61 lines for compatibility.
# For CUDA < 8.0, comment the *_60 and *_61 lines for compatibility.
# For CUDA >= 9.0, comment the *_20 and *_21 lines for compatibility.
# CUDA_ARCH := -gencode arch=compute_20,code=sm_20 \
# -gencode arch=compute_20,code=sm_21 \
# -gencode arch=compute_30,code=sm_30 \
# -gencode arch=compute_35,code=sm_35 \
# -gencode arch=compute_50,code=sm_50 \
# -gencode arch=compute_52,code=sm_52 \
# -gencode arch=compute_60,code=sm_60 \
# -gencode arch=compute_61,code=sm_61 \
# -gencode arch=compute_61,code=compute_61# BLAS choice:
# atlas for ATLAS (default)
# mkl for MKL
# open for OpenBlas
BLAS := atlas
# Custom (MKL/ATLAS/OpenBLAS) include and lib directories.
# Leave commented to accept the defaults for your choice of BLAS
# (which should work)!
# BLAS_INCLUDE := /path/to/your/blas
# BLAS_LIB := /path/to/your/blas# Homebrew puts openblas in a directory that is not on the standard search path
# BLAS_INCLUDE := $(shell brew --prefix openblas)/include
# BLAS_LIB := $(shell brew --prefix openblas)/lib# This is required only if you will compile the matlab interface.
# MATLAB directory should contain the mex binary in /bin.
# MATLAB_DIR := /usr/local
# MATLAB_DIR := /Applications/MATLAB_R2012b.app# NOTE: this is required only if you will compile the python interface.
# We need to be able to find Python.h and numpy/arrayobject.h.
# PYTHON_INCLUDE := /usr/include/python2.7 \
# /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/numpy/core/include
# Anaconda Python distribution is quite popular. Include path:
# Verify anaconda location, sometimes it's in root.
ANACONDA_HOME := /home/anaconda3/envs/caffe/
PYTHON_INCLUDE := $(ANACONDA_HOME)/include \$(ANACONDA_HOME)/include/python3.8 \$(ANACONDA_HOME)/lib/python3.8/site-packages/numpy/core/include
PYTHON_LIB := $(ANACONDA_HOME)/lib# Uncomment to use Python 3 (default is Python 2)
PYTHON_LIBRARIES := boost_python38 python3.8
# PYTHON_INCLUDE := /usr/include/python3.5m \
# /usr/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/numpy/core/include# We need to be able to find libpythonX.X.so or .dylib.
# PYTHON_LIB := /usr/lib
PYTHON_LIB := $(ANACONDA_HOME)/lib# Homebrew installs numpy in a non standard path (keg only)
# PYTHON_INCLUDE += $(dir $(shell python -c 'import numpy.core; print(numpy.core.__file__)'))/include
# PYTHON_LIB += $(shell brew --prefix numpy)/lib# Uncomment to support layers written in Python (will link against Python libs)
WITH_PYTHON_LAYER := 1# Whatever else you find you need goes here.
INCLUDE_DIRS := /usr/include $(PYTHON_INCLUDE) /usr/local/include /usr/include/hdf5/serial /usr/include/opencv4
LIBRARY_DIRS := /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu $(ANACONDA_HOME)/lib $(PYTHON_LIB) /usr/local/lib /usr/lib /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/hdf5/serial# If Homebrew is installed at a non standard location (for example your home directory) and you use it for general dependencies
# INCLUDE_DIRS += $(shell brew --prefix)/include
# LIBRARY_DIRS += $(shell brew --prefix)/lib# NCCL acceleration switch (uncomment to build with NCCL)
# https://github.com/NVIDIA/nccl (last tested version: v1.2.3-1+cuda8.0)
# USE_NCCL := 1# Uncomment to use `pkg-config` to specify OpenCV library paths.
# (Usually not necessary -- OpenCV libraries are normally installed in one of the above $LIBRARY_DIRS.)
USE_PKG_CONFIG := 0# N.B. both build and distribute dirs are cleared on `make clean`
BUILD_DIR := build
DISTRIBUTE_DIR := distribute# Uncomment for debugging. Does not work on OSX due to https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/issues/171
# DEBUG := 1# The ID of the GPU that 'make runtest' will use to run unit tests.
TEST_GPUID := 0# enable pretty build (comment to see full commands)
Q ?= @# 強制使用系統版本的 Protobuf
LDFLAGS += -L/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -lprotobuf# OpenCV 庫
LIBRARIES += opencv_core opencv_highgui opencv_imgproc opencv_imgcodecs# OpenCV 4.x 版本棄用了CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR 和 CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE 宏定義
# 改用 cv::IMREAD_COLOR 和 cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE
COMMON_FLAGS += -DCV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR=cv::IMREAD_COLOR
COMMON_FLAGS += -DCV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE=cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALELDFLAGS += -L$(ANACONDA_HOME)/lib -lpython3.8LDFLAGS += -L/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -lopencv_core -lopencv_imgcodecs -lopencv_highgui# 確保使用正確的 Boost 庫
LIBRARIES += boost_filesystem boost_system由于系統中可能存在多個版本的Boost和Protobuf庫(例如anacoda虛擬環境中的庫或者自己從源碼的不同版本的庫),因此在Makefile.config中強制指定系統中的版本
2. 修改Makefile
給出修改后完整的Makefile
PROJECT := caffeCONFIG_FILE := Makefile.config
# Explicitly check for the config file, otherwise make -k will proceed anyway.
ifeq ($(wildcard $(CONFIG_FILE)),)
$(error $(CONFIG_FILE) not found. See $(CONFIG_FILE).example.)
endif
include $(CONFIG_FILE)BUILD_DIR_LINK := $(BUILD_DIR)
ifeq ($(RELEASE_BUILD_DIR),)RELEASE_BUILD_DIR := .$(BUILD_DIR)_release
endif
ifeq ($(DEBUG_BUILD_DIR),)DEBUG_BUILD_DIR := .$(BUILD_DIR)_debug
endifDEBUG ?= 0
ifeq ($(DEBUG), 1)BUILD_DIR := $(DEBUG_BUILD_DIR)OTHER_BUILD_DIR := $(RELEASE_BUILD_DIR)
elseBUILD_DIR := $(RELEASE_BUILD_DIR)OTHER_BUILD_DIR := $(DEBUG_BUILD_DIR)
endif# All of the directories containing code.
SRC_DIRS := $(shell find * -type d -exec bash -c "find {} -maxdepth 1 \\( -name '*.cpp' -o -name '*.proto' \) | grep -q ." \; -print)# The target shared library name
LIBRARY_NAME := $(PROJECT)
LIB_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/lib
STATIC_NAME := $(LIB_BUILD_DIR)/lib$(LIBRARY_NAME).a
DYNAMIC_VERSION_MAJOR := 1
DYNAMIC_VERSION_MINOR := 0
DYNAMIC_VERSION_REVISION := 0
DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT := lib$(LIBRARY_NAME).so
#DYNAMIC_SONAME_SHORT := $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_MAJOR)
DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT := $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_MAJOR).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_MINOR).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_REVISION)
DYNAMIC_NAME := $(LIB_BUILD_DIR)/$(DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT)
COMMON_FLAGS += -DCAFFE_VERSION=$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_MAJOR).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_MINOR).$(DYNAMIC_VERSION_REVISION)
# 添加系統 Protobuf 頭文件路徑(確保優先使用系統頭文件)
COMMON_FLAGS += -I/usr/include##############################
# Get all source files
##############################
# CXX_SRCS are the source files excluding the test ones.
CXX_SRCS := $(shell find src/$(PROJECT) ! -name "test_*.cpp" -name "*.cpp")
# CU_SRCS are the cuda source files
CU_SRCS := $(shell find src/$(PROJECT) ! -name "test_*.cu" -name "*.cu")
# TEST_SRCS are the test source files
TEST_MAIN_SRC := src/$(PROJECT)/test/test_caffe_main.cpp
TEST_SRCS := $(shell find src/$(PROJECT) -name "test_*.cpp")
TEST_SRCS := $(filter-out $(TEST_MAIN_SRC), $(TEST_SRCS))
TEST_CU_SRCS := $(shell find src/$(PROJECT) -name "test_*.cu")
GTEST_SRC := src/gtest/gtest-all.cpp
# TOOL_SRCS are the source files for the tool binaries
TOOL_SRCS := $(shell find tools -name "*.cpp")
# EXAMPLE_SRCS are the source files for the example binaries
EXAMPLE_SRCS := $(shell find examples -name "*.cpp")
# BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR contains any generated header files we want to include.
BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/src
# PROTO_SRCS are the protocol buffer definitions
PROTO_SRC_DIR := src/$(PROJECT)/proto
PROTO_SRCS := $(wildcard $(PROTO_SRC_DIR)/*.proto)
# PROTO_BUILD_DIR will contain the .cc and obj files generated from
# PROTO_SRCS; PROTO_BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR will contain the .h header files
PROTO_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROTO_SRC_DIR)
PROTO_BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR := $(BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR)/$(PROJECT)/proto
# NONGEN_CXX_SRCS includes all source/header files except those generated
# automatically (e.g., by proto).
NONGEN_CXX_SRCS := $(shell find \src/$(PROJECT) \include/$(PROJECT) \python/$(PROJECT) \matlab/+$(PROJECT)/private \examples \tools \-name "*.cpp" -or -name "*.hpp" -or -name "*.cu" -or -name "*.cuh")
LINT_SCRIPT := scripts/cpp_lint.py
LINT_OUTPUT_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/.lint
LINT_EXT := lint.txt
LINT_OUTPUTS := $(addsuffix .$(LINT_EXT), $(addprefix $(LINT_OUTPUT_DIR)/, $(NONGEN_CXX_SRCS)))
EMPTY_LINT_REPORT := $(BUILD_DIR)/.$(LINT_EXT)
NONEMPTY_LINT_REPORT := $(BUILD_DIR)/$(LINT_EXT)
# PY$(PROJECT)_SRC is the python wrapper for $(PROJECT)
PY$(PROJECT)_SRC := python/$(PROJECT)/_$(PROJECT).cpp
PY$(PROJECT)_SO := python/$(PROJECT)/_$(PROJECT).so
PY$(PROJECT)_HXX := include/$(PROJECT)/layers/python_layer.hpp
# MAT$(PROJECT)_SRC is the mex entrance point of matlab package for $(PROJECT)
MAT$(PROJECT)_SRC := matlab/+$(PROJECT)/private/$(PROJECT)_.cpp
ifneq ($(MATLAB_DIR),)MAT_SO_EXT := $(shell $(MATLAB_DIR)/bin/mexext)
endif
MAT$(PROJECT)_SO := matlab/+$(PROJECT)/private/$(PROJECT)_.$(MAT_SO_EXT)##############################
# Derive generated files
##############################
# The generated files for protocol buffers
PROTO_GEN_HEADER_SRCS := $(addprefix $(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/, \$(notdir ${PROTO_SRCS:.proto=.pb.h}))
PROTO_GEN_HEADER := $(addprefix $(PROTO_BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR)/, \$(notdir ${PROTO_SRCS:.proto=.pb.h}))
PROTO_GEN_CC := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${PROTO_SRCS:.proto=.pb.cc})
PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR := python/$(PROJECT)/proto
PY_PROTO_INIT := python/$(PROJECT)/proto/__init__.py
PROTO_GEN_PY := $(foreach file,${PROTO_SRCS:.proto=_pb2.py}, \$(PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/$(notdir $(file)))
# The objects corresponding to the source files
# These objects will be linked into the final shared library, so we
# exclude the tool, example, and test objects.
CXX_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${CXX_SRCS:.cpp=.o})
CU_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/, ${CU_SRCS:.cu=.o})
PROTO_OBJS := ${PROTO_GEN_CC:.cc=.o}
OBJS := $(PROTO_OBJS) $(CXX_OBJS) $(CU_OBJS)
# tool, example, and test objects
TOOL_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${TOOL_SRCS:.cpp=.o})
TOOL_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/tools
TEST_CXX_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/src/$(PROJECT)/test
TEST_CU_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/src/$(PROJECT)/test
TEST_CXX_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${TEST_SRCS:.cpp=.o})
TEST_CU_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/, ${TEST_CU_SRCS:.cu=.o})
TEST_OBJS := $(TEST_CXX_OBJS) $(TEST_CU_OBJS)
GTEST_OBJ := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${GTEST_SRC:.cpp=.o})
EXAMPLE_OBJS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${EXAMPLE_SRCS:.cpp=.o})
# Output files for automatic dependency generation
DEPS := ${CXX_OBJS:.o=.d} ${CU_OBJS:.o=.d} ${TEST_CXX_OBJS:.o=.d} \${TEST_CU_OBJS:.o=.d} $(BUILD_DIR)/${MAT$(PROJECT)_SO:.$(MAT_SO_EXT)=.d}
# tool, example, and test bins
TOOL_BINS := ${TOOL_OBJS:.o=.bin}
EXAMPLE_BINS := ${EXAMPLE_OBJS:.o=.bin}
# symlinks to tool bins without the ".bin" extension
TOOL_BIN_LINKS := ${TOOL_BINS:.bin=}
# Put the test binaries in build/test for convenience.
TEST_BIN_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/test
TEST_CU_BINS := $(addsuffix .testbin,$(addprefix $(TEST_BIN_DIR)/, \$(foreach obj,$(TEST_CU_OBJS),$(basename $(notdir $(obj))))))
TEST_CXX_BINS := $(addsuffix .testbin,$(addprefix $(TEST_BIN_DIR)/, \$(foreach obj,$(TEST_CXX_OBJS),$(basename $(notdir $(obj))))))
TEST_BINS := $(TEST_CXX_BINS) $(TEST_CU_BINS)
# TEST_ALL_BIN is the test binary that links caffe dynamically.
TEST_ALL_BIN := $(TEST_BIN_DIR)/test_all.testbin##############################
# Derive compiler warning dump locations
##############################
WARNS_EXT := warnings.txt
CXX_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${CXX_SRCS:.cpp=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
CU_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/, ${CU_SRCS:.cu=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
TOOL_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${TOOL_SRCS:.cpp=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
EXAMPLE_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${EXAMPLE_SRCS:.cpp=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
TEST_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, ${TEST_SRCS:.cpp=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
TEST_CU_WARNS := $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/, ${TEST_CU_SRCS:.cu=.o.$(WARNS_EXT)})
ALL_CXX_WARNS := $(CXX_WARNS) $(TOOL_WARNS) $(EXAMPLE_WARNS) $(TEST_WARNS)
ALL_CU_WARNS := $(CU_WARNS) $(TEST_CU_WARNS)
ALL_WARNS := $(ALL_CXX_WARNS) $(ALL_CU_WARNS)EMPTY_WARN_REPORT := $(BUILD_DIR)/.$(WARNS_EXT)
NONEMPTY_WARN_REPORT := $(BUILD_DIR)/$(WARNS_EXT)##############################
# Derive include and lib directories
##############################
CUDA_INCLUDE_DIR := $(CUDA_DIR)/includeCUDA_LIB_DIR :=
# add <cuda>/lib64 only if it exists
ifneq ("$(wildcard $(CUDA_DIR)/lib64)","")CUDA_LIB_DIR += $(CUDA_DIR)/lib64
endif
CUDA_LIB_DIR += $(CUDA_DIR)/libINCLUDE_DIRS += $(BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR) ./src ./include
ifneq ($(CPU_ONLY), 1)INCLUDE_DIRS += $(CUDA_INCLUDE_DIR)LIBRARY_DIRS += $(CUDA_LIB_DIR)LIBRARIES := cudart cublas curand
endifLIBRARIES += glog gflags protobuf boost_system boost_filesystem m hdf5_serial_hl hdf5_serial# handle IO dependencies
USE_LEVELDB ?= 1
USE_LMDB ?= 1
# This code is taken from https://github.com/sh1r0/caffe-android-lib
USE_HDF5 ?= 1
USE_OPENCV ?= 1ifeq ($(USE_LEVELDB), 1)LIBRARIES += leveldb snappy
endif
ifeq ($(USE_LMDB), 1)LIBRARIES += lmdb
endif
# This code is taken from https://github.com/sh1r0/caffe-android-lib
ifeq ($(USE_HDF5), 1)LIBRARIES += hdf5_hl hdf5
endif
ifeq ($(USE_OPENCV), 1)LIBRARIES += opencv_core opencv_highgui opencv_imgprocifeq ($(OPENCV_VERSION), 3)LIBRARIES += opencv_imgcodecsendifendif
PYTHON_LIBRARIES ?= boost_python python2.7
WARNINGS := -Wall -Wno-sign-compare##############################
# Set build directories
##############################DISTRIBUTE_DIR ?= distribute
DISTRIBUTE_SUBDIRS := $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/bin $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/lib
DIST_ALIASES := dist
ifneq ($(strip $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)),distribute)DIST_ALIASES += distribute
endifALL_BUILD_DIRS := $(sort $(BUILD_DIR) $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/, $(SRC_DIRS)) \$(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/, $(SRC_DIRS)) \$(LIB_BUILD_DIR) $(TEST_BIN_DIR) $(PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR) $(LINT_OUTPUT_DIR) \$(DISTRIBUTE_SUBDIRS) $(PROTO_BUILD_INCLUDE_DIR))##############################
# Set directory for Doxygen-generated documentation
##############################
DOXYGEN_CONFIG_FILE ?= ./.Doxyfile
# should be the same as OUTPUT_DIRECTORY in the .Doxyfile
DOXYGEN_OUTPUT_DIR ?= ./doxygen
DOXYGEN_COMMAND ?= doxygen
# All the files that might have Doxygen documentation.
DOXYGEN_SOURCES := $(shell find \src/$(PROJECT) \include/$(PROJECT) \python/ \matlab/ \examples \tools \-name "*.cpp" -or -name "*.hpp" -or -name "*.cu" -or -name "*.cuh" -or \-name "*.py" -or -name "*.m")
DOXYGEN_SOURCES += $(DOXYGEN_CONFIG_FILE)##############################
# Configure build
############################### Determine platform
UNAME := $(shell uname -s)
ifeq ($(UNAME), Linux)LINUX := 1
else ifeq ($(UNAME), Darwin)OSX := 1OSX_MAJOR_VERSION := $(shell sw_vers -productVersion | cut -f 1 -d .)OSX_MINOR_VERSION := $(shell sw_vers -productVersion | cut -f 2 -d .)
endif# Linux
ifeq ($(LINUX), 1)CXX ?= /usr/bin/g++GCCVERSION := $(shell $(CXX) -dumpversion | cut -f1,2 -d.)# older versions of gcc are too dumb to build boost with -Wuninitalizedifeq ($(shell echo | awk '{exit $(GCCVERSION) < 4.6;}'), 1)WARNINGS += -Wno-uninitializedendif# boost::thread is reasonably called boost_thread (compare OS X)# We will also explicitly add stdc++ to the link target.LIBRARIES += boost_thread stdc++VERSIONFLAGS += -Wl,-soname,$(DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT) -Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../lib
endif# OS X:
# clang++ instead of g++
# libstdc++ for NVCC compatibility on OS X >= 10.9 with CUDA < 7.0
ifeq ($(OSX), 1)CXX := /usr/bin/clang++ifneq ($(CPU_ONLY), 1)CUDA_VERSION := $(shell $(CUDA_DIR)/bin/nvcc -V | grep -o 'release [0-9.]*' | tr -d '[a-z ]')ifeq ($(shell echo | awk '{exit $(CUDA_VERSION) < 7.0;}'), 1)CXXFLAGS += -stdlib=libstdc++LINKFLAGS += -stdlib=libstdc++endif# clang throws this warning for cuda headersWARNINGS += -Wno-unneeded-internal-declaration# 10.11 strips DYLD_* env vars so link CUDA (rpath is available on 10.5+)OSX_10_OR_LATER := $(shell [ $(OSX_MAJOR_VERSION) -ge 10 ] && echo true)OSX_10_5_OR_LATER := $(shell [ $(OSX_MINOR_VERSION) -ge 5 ] && echo true)ifeq ($(OSX_10_OR_LATER),true)ifeq ($(OSX_10_5_OR_LATER),true)LDFLAGS += -Wl,-rpath,$(CUDA_LIB_DIR)endifendifendif# gtest needs to use its own tuple to not conflict with clangCOMMON_FLAGS += -DGTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE=1# boost::thread is called boost_thread-mt to mark multithreading on OS XLIBRARIES += boost_thread-mt# we need to explicitly ask for the rpath to be obeyedORIGIN := @loader_pathVERSIONFLAGS += -Wl,-install_name,@rpath/$(DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT) -Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../../build/lib
elseORIGIN := \$$ORIGIN
endif# Custom compiler
ifdef CUSTOM_CXXCXX := $(CUSTOM_CXX)
endif# Static linking
ifneq (,$(findstring clang++,$(CXX)))STATIC_LINK_COMMAND := -Wl,-force_load $(STATIC_NAME)
else ifneq (,$(findstring g++,$(CXX)))STATIC_LINK_COMMAND := -Wl,--whole-archive $(STATIC_NAME) -Wl,--no-whole-archive
else# The following line must not be indented with a tab, since we are not inside a target$(error Cannot static link with the $(CXX) compiler)
endif# Debugging
ifeq ($(DEBUG), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DDEBUG -g -O0NVCCFLAGS += -G
elseCOMMON_FLAGS += -DNDEBUG -O2
endif# cuDNN acceleration configuration.
ifeq ($(USE_CUDNN), 1)LIBRARIES += cudnnCOMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_CUDNN
endif# NCCL acceleration configuration
ifeq ($(USE_NCCL), 1)LIBRARIES += ncclCOMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_NCCL
endif# configure IO libraries
ifeq ($(USE_OPENCV), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_OPENCV
endif
ifeq ($(USE_LEVELDB), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_LEVELDB
endif
ifeq ($(USE_LMDB), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_LMDB
ifeq ($(ALLOW_LMDB_NOLOCK), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DALLOW_LMDB_NOLOCK
endif
endif
# This code is taken from https://github.com/sh1r0/caffe-android-lib
ifeq ($(USE_HDF5), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_HDF5
endif# CPU-only configuration
ifeq ($(CPU_ONLY), 1)OBJS := $(PROTO_OBJS) $(CXX_OBJS)TEST_OBJS := $(TEST_CXX_OBJS)TEST_BINS := $(TEST_CXX_BINS)ALL_WARNS := $(ALL_CXX_WARNS)TEST_FILTER := --gtest_filter="-*GPU*"COMMON_FLAGS += -DCPU_ONLY
endif# Python layer support
ifeq ($(WITH_PYTHON_LAYER), 1)COMMON_FLAGS += -DWITH_PYTHON_LAYERLIBRARIES += $(PYTHON_LIBRARIES)
endif# BLAS configuration (default = ATLAS)
BLAS ?= atlas
ifeq ($(BLAS), mkl)# MKLLIBRARIES += mkl_rtCOMMON_FLAGS += -DUSE_MKLMKLROOT ?= /opt/intel/mklBLAS_INCLUDE ?= $(MKLROOT)/includeBLAS_LIB ?= $(MKLROOT)/lib $(MKLROOT)/lib/intel64
else ifeq ($(BLAS), open)# OpenBLASLIBRARIES += openblas
else# ATLASifeq ($(LINUX), 1)ifeq ($(BLAS), atlas)# Linux simply has cblas and atlasLIBRARIES += cblas atlasendifelse ifeq ($(OSX), 1)# OS X packages atlas as the vecLib frameworkLIBRARIES += cblas# 10.10 has accelerate while 10.9 has veclibXCODE_CLT_VER := $(shell pkgutil --pkg-info=com.apple.pkg.CLTools_Executables | grep 'version' | sed 's/[^0-9]*\([0-9]\).*/\1/')XCODE_CLT_GEQ_7 := $(shell [ $(XCODE_CLT_VER) -gt 6 ] && echo 1)XCODE_CLT_GEQ_6 := $(shell [ $(XCODE_CLT_VER) -gt 5 ] && echo 1)ifeq ($(XCODE_CLT_GEQ_7), 1)BLAS_INCLUDE ?= /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/$(shell ls /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/ | sort | tail -1)/System/Library/Frameworks/Accelerate.framework/Versions/A/Frameworks/vecLib.framework/Versions/A/Headerselse ifeq ($(XCODE_CLT_GEQ_6), 1)BLAS_INCLUDE ?= /System/Library/Frameworks/Accelerate.framework/Versions/Current/Frameworks/vecLib.framework/Headers/LDFLAGS += -framework AccelerateelseBLAS_INCLUDE ?= /System/Library/Frameworks/vecLib.framework/Versions/Current/Headers/LDFLAGS += -framework vecLibendifendif
endif
INCLUDE_DIRS += $(BLAS_INCLUDE)
LIBRARY_DIRS += $(BLAS_LIB)LIBRARY_DIRS += $(LIB_BUILD_DIR)# Automatic dependency generation (nvcc is handled separately)
CXXFLAGS += -MMD -MP# Complete build flags.
COMMON_FLAGS += $(foreach includedir,$(INCLUDE_DIRS),-I$(includedir))
CXXFLAGS += -pthread -fPIC $(COMMON_FLAGS) $(WARNINGS)
NVCCFLAGS += -D_FORCE_INLINES -ccbin=$(CXX) -Xcompiler -fPIC $(COMMON_FLAGS)
# mex may invoke an older gcc that is too liberal with -Wuninitalized
MATLAB_CXXFLAGS := $(CXXFLAGS) -Wno-uninitialized
LINKFLAGS += -pthread -fPIC $(COMMON_FLAGS) $(WARNINGS)USE_PKG_CONFIG ?= 0
ifeq ($(USE_PKG_CONFIG), 1)PKG_CONFIG := $(shell pkg-config opencv --libs)
elsePKG_CONFIG :=
endif
LDFLAGS += $(foreach librarydir,$(LIBRARY_DIRS),-L$(librarydir)) $(PKG_CONFIG) \$(foreach library,$(LIBRARIES),-l$(library))
PYTHON_LDFLAGS := $(LDFLAGS) $(foreach library,$(PYTHON_LIBRARIES),-l$(library))# 'superclean' target recursively* deletes all files ending with an extension
# in $(SUPERCLEAN_EXTS) below. This may be useful if you've built older
# versions of Caffe that do not place all generated files in a location known
# to the 'clean' target.
#
# 'supercleanlist' will list the files to be deleted by make superclean.
#
# * Recursive with the exception that symbolic links are never followed, per the
# default behavior of 'find'.
SUPERCLEAN_EXTS := .so .a .o .bin .testbin .pb.cc .pb.h _pb2.py .cuo# Set the sub-targets of the 'everything' target.
EVERYTHING_TARGETS := all py$(PROJECT) test warn lint
# Only build matcaffe as part of "everything" if MATLAB_DIR is specified.
ifneq ($(MATLAB_DIR),)EVERYTHING_TARGETS += mat$(PROJECT)
endif##############################
# Define build targets
##############################
.PHONY: all lib test clean docs linecount lint lintclean tools examples $(DIST_ALIASES) \py mat py$(PROJECT) mat$(PROJECT) proto runtest \superclean supercleanlist supercleanfiles warn everythingall: lib tools exampleslib: $(STATIC_NAME) $(DYNAMIC_NAME)everything: $(EVERYTHING_TARGETS)linecount:cloc --read-lang-def=$(PROJECT).cloc \src/$(PROJECT) include/$(PROJECT) tools examples \python matlablint: $(EMPTY_LINT_REPORT)lintclean:@ $(RM) -r $(LINT_OUTPUT_DIR) $(EMPTY_LINT_REPORT) $(NONEMPTY_LINT_REPORT)docs: $(DOXYGEN_OUTPUT_DIR)@ cd ./docs ; ln -sfn ../$(DOXYGEN_OUTPUT_DIR)/html doxygen$(DOXYGEN_OUTPUT_DIR): $(DOXYGEN_CONFIG_FILE) $(DOXYGEN_SOURCES)$(DOXYGEN_COMMAND) $(DOXYGEN_CONFIG_FILE)$(EMPTY_LINT_REPORT): $(LINT_OUTPUTS) | $(BUILD_DIR)@ cat $(LINT_OUTPUTS) > $@@ if [ -s "$@" ]; then \cat $@; \mv $@ $(NONEMPTY_LINT_REPORT); \echo "Found one or more lint errors."; \exit 1; \fi; \$(RM) $(NONEMPTY_LINT_REPORT); \echo "No lint errors!";$(LINT_OUTPUTS): $(LINT_OUTPUT_DIR)/%.lint.txt : % $(LINT_SCRIPT) | $(LINT_OUTPUT_DIR)@ mkdir -p $(dir $@)@ python $(LINT_SCRIPT) $< 2>&1 \| grep -v "^Done processing " \| grep -v "^Total errors found: 0" \> $@ \|| truetest: $(TEST_ALL_BIN) $(TEST_ALL_DYNLINK_BIN) $(TEST_BINS)tools: $(TOOL_BINS) $(TOOL_BIN_LINKS)examples: $(EXAMPLE_BINS)py$(PROJECT): pypy: $(PY$(PROJECT)_SO) $(PROTO_GEN_PY)$(PY$(PROJECT)_SO): $(PY$(PROJECT)_SRC) $(PY$(PROJECT)_HXX) | $(DYNAMIC_NAME)@ echo CXX/LD -o $@ $<$(Q)$(CXX) -shared -o $@ $(PY$(PROJECT)_SRC) \-o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) $(PYTHON_LDFLAGS) \-Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../../build/libmat$(PROJECT): matmat: $(MAT$(PROJECT)_SO)$(MAT$(PROJECT)_SO): $(MAT$(PROJECT)_SRC) $(STATIC_NAME)@ if [ -z "$(MATLAB_DIR)" ]; then \echo "MATLAB_DIR must be specified in $(CONFIG_FILE)" \"to build mat$(PROJECT)."; \exit 1; \fi@ echo MEX $<$(Q)$(MATLAB_DIR)/bin/mex $(MAT$(PROJECT)_SRC) \CXX="$(CXX)" \CXXFLAGS="\$$CXXFLAGS $(MATLAB_CXXFLAGS)" \CXXLIBS="\$$CXXLIBS $(STATIC_LINK_COMMAND) $(LDFLAGS)" -output $@@ if [ -f "$(PROJECT)_.d" ]; then \mv -f $(PROJECT)_.d $(BUILD_DIR)/${MAT$(PROJECT)_SO:.$(MAT_SO_EXT)=.d}; \firuntest: $(TEST_ALL_BIN)$(TOOL_BUILD_DIR)/caffe$(TEST_ALL_BIN) $(TEST_GPUID) --gtest_shuffle $(TEST_FILTER)pytest: pycd python; python -m unittest discover -s caffe/testmattest: matcd matlab; $(MATLAB_DIR)/bin/matlab -nodisplay -r 'caffe.run_tests(), exit()'warn: $(EMPTY_WARN_REPORT)$(EMPTY_WARN_REPORT): $(ALL_WARNS) | $(BUILD_DIR)@ cat $(ALL_WARNS) > $@@ if [ -s "$@" ]; then \cat $@; \mv $@ $(NONEMPTY_WARN_REPORT); \echo "Compiler produced one or more warnings."; \exit 1; \fi; \$(RM) $(NONEMPTY_WARN_REPORT); \echo "No compiler warnings!";$(ALL_WARNS): %.o.$(WARNS_EXT) : %.o$(BUILD_DIR_LINK): $(BUILD_DIR)/.linked# Create a target ".linked" in this BUILD_DIR to tell Make that the "build" link
# is currently correct, then delete the one in the OTHER_BUILD_DIR in case it
# exists and $(DEBUG) is toggled later.
$(BUILD_DIR)/.linked:@ mkdir -p $(BUILD_DIR)@ $(RM) $(OTHER_BUILD_DIR)/.linked@ $(RM) -r $(BUILD_DIR_LINK)@ ln -s $(BUILD_DIR) $(BUILD_DIR_LINK)@ touch $@$(ALL_BUILD_DIRS): | $(BUILD_DIR_LINK)@ mkdir -p $@$(DYNAMIC_NAME): $(OBJS) | $(LIB_BUILD_DIR)@ echo LD -o $@$(Q)$(CXX) -shared -o $@ $(OBJS) $(VERSIONFLAGS) $(LINKFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) \-L/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -lprotobuf # 強制鏈接系統庫@ cd $(BUILD_DIR)/lib; rm -f $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT); ln -s $(DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT) $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT)$(STATIC_NAME): $(OBJS) | $(LIB_BUILD_DIR)@ echo AR -o $@$(Q)ar rcs $@ $(OBJS)$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o: %.cpp $(PROTO_GEN_HEADER) | $(ALL_BUILD_DIRS)@ echo CXX $<$(Q)$(CXX) $< $(CXXFLAGS) -c -o $@ 2> $@.$(WARNS_EXT) \|| (cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT); exit 1)@ cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT)$(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/%.pb.o: $(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/%.pb.cc $(PROTO_GEN_HEADER) \| $(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)@ echo CXX $<$(Q)$(CXX) $< $(CXXFLAGS) -c -o $@ 2> $@.$(WARNS_EXT) \|| (cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT); exit 1)@ cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT)$(BUILD_DIR)/cuda/%.o: %.cu | $(ALL_BUILD_DIRS)@ echo NVCC $<$(Q)$(CUDA_DIR)/bin/nvcc $(NVCCFLAGS) $(CUDA_ARCH) -M $< -o ${@:.o=.d} \-odir $(@D)$(Q)$(CUDA_DIR)/bin/nvcc $(NVCCFLAGS) $(CUDA_ARCH) -c $< -o $@ 2> $@.$(WARNS_EXT) \|| (cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT); exit 1)@ cat $@.$(WARNS_EXT)$(TEST_ALL_BIN): $(TEST_MAIN_SRC) $(TEST_OBJS) $(GTEST_OBJ) \| $(DYNAMIC_NAME) $(TEST_BIN_DIR)@ echo CXX/LD -o $@ $<$(Q)$(CXX) $(TEST_MAIN_SRC) $(TEST_OBJS) $(GTEST_OBJ) \-o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) -Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../lib$(TEST_CU_BINS): $(TEST_BIN_DIR)/%.testbin: $(TEST_CU_BUILD_DIR)/%.o \$(GTEST_OBJ) | $(DYNAMIC_NAME) $(TEST_BIN_DIR)@ echo LD $<$(Q)$(CXX) $(TEST_MAIN_SRC) $< $(GTEST_OBJ) \-o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) -Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../lib$(TEST_CXX_BINS): $(TEST_BIN_DIR)/%.testbin: $(TEST_CXX_BUILD_DIR)/%.o \$(GTEST_OBJ) | $(DYNAMIC_NAME) $(TEST_BIN_DIR)@ echo LD $<$(Q)$(CXX) $(TEST_MAIN_SRC) $< $(GTEST_OBJ) \-o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) -Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../lib# Target for extension-less symlinks to tool binaries with extension '*.bin'.
$(TOOL_BUILD_DIR)/%: $(TOOL_BUILD_DIR)/%.bin | $(TOOL_BUILD_DIR)@ $(RM) $@@ ln -s $(notdir $<) $@$(TOOL_BINS): %.bin : %.o | $(DYNAMIC_NAME)@ echo CXX/LD -o $@$(Q)$(CXX) $< -o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) $(LDFLAGS) \-Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../lib$(EXAMPLE_BINS): %.bin : %.o | $(DYNAMIC_NAME)@ echo CXX/LD -o $@$(Q)$(CXX) $< -o $@ $(LINKFLAGS) -l$(LIBRARY_NAME) $(LDFLAGS) \-Wl,-rpath,$(ORIGIN)/../../libproto: $(PROTO_GEN_CC) $(PROTO_GEN_HEADER)$(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/%.pb.cc $(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/%.pb.h : \$(PROTO_SRC_DIR)/%.proto | $(PROTO_BUILD_DIR)@ echo PROTOC $<$(Q)protoc --proto_path=$(PROTO_SRC_DIR) --cpp_out=$(PROTO_BUILD_DIR) $<$(PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR)/%_pb2.py : $(PROTO_SRC_DIR)/%.proto \$(PY_PROTO_INIT) | $(PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR)@ echo PROTOC \(python\) $<$(Q)protoc --proto_path=src --python_out=python $<$(PY_PROTO_INIT): | $(PY_PROTO_BUILD_DIR)touch $(PY_PROTO_INIT)clean:@- $(RM) -rf $(ALL_BUILD_DIRS)@- $(RM) -rf $(OTHER_BUILD_DIR)@- $(RM) -rf $(BUILD_DIR_LINK)@- $(RM) -rf $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)@- $(RM) $(PY$(PROJECT)_SO)@- $(RM) $(MAT$(PROJECT)_SO)supercleanfiles:$(eval SUPERCLEAN_FILES := $(strip \$(foreach ext,$(SUPERCLEAN_EXTS), $(shell find . -name '*$(ext)' \-not -path './data/*'))))supercleanlist: supercleanfiles@ \if [ -z "$(SUPERCLEAN_FILES)" ]; then \echo "No generated files found."; \else \echo $(SUPERCLEAN_FILES) | tr ' ' '\n'; \fisuperclean: clean supercleanfiles@ \if [ -z "$(SUPERCLEAN_FILES)" ]; then \echo "No generated files found."; \else \echo "Deleting the following generated files:"; \echo $(SUPERCLEAN_FILES) | tr ' ' '\n'; \$(RM) $(SUPERCLEAN_FILES); \fi$(DIST_ALIASES): $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)$(DISTRIBUTE_DIR): all py | $(DISTRIBUTE_SUBDIRS)# add protocp -r src/caffe/proto $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/# add includecp -r include $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/mkdir -p $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/include/caffe/protocp $(PROTO_GEN_HEADER_SRCS) $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/include/caffe/proto# add tool and example binariescp $(TOOL_BINS) $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/bincp $(EXAMPLE_BINS) $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/bin# add librariescp $(STATIC_NAME) $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/libinstall -m 644 $(DYNAMIC_NAME) $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/libcd $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/lib; rm -f $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT); ln -s $(DYNAMIC_VERSIONED_NAME_SHORT) $(DYNAMIC_NAME_SHORT)# add python - it's not the standard way, indeed...cp -r python $(DISTRIBUTE_DIR)/-include $(DEPS)
3. 修改CMakeLists.txt(如果使用cmake,不用可跳過)
如果需要使用cmake而不是make:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCPU_ONLY=ON -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$(which python) ..4. 創建python3.8的鏈接庫
配置文件中是默認調用py2.7的boost,我們需要創建python3.8的鏈接庫
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libboost_python38.so.1.71.0 /usr/local/lib/libboost_python3.so五、編譯Caffe
1. 使用Make編譯
① 檢查編譯環境的python版本是否符合預期
# 檢查 Python 路徑
which python
# 應輸出:/home/anaconda3/envs/caffe/bin/python# 檢查版本
python --version
# 應輸出:Python 3.8.20
如果 Python 路徑輸出為:/usr/bin/python,版本輸出為: Python 2.7.18?,那說明當前環境中用的是系統自帶的python而不是anacoda虛擬環境中的python,需要修改一下系統路徑,使其強制使用anacoda虛擬環境中的python
# 臨時修復(僅在當前終端生效)
export PATH="/home/anaconda3/envs/caffe/bin:$PATH"# 永久修復(添加到 ~/.bashrc)
echo 'export PATH="/home/anaconda3/envs/caffe/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc?②?檢查編譯環境的protoc版本是否符合預期
# 檢查protoc路徑
which protoc
# 應該輸出 /usr/bin/protoc# 檢查protoc版本
protoc --version
# 應該輸出系統版本(如 3.6.1)如果 protoc 輸出路徑為:/home/protobuf-3.11.2/build/bin/protoc ,版本輸出為 protoc?3.11.2,說明當前環境中使用的是從源碼編譯的其他版本的protoc,需要修改環境變量使其強制使用系統版本的protoc
# 臨時生效(僅當前終端窗口)
export PATH=/usr/bin:$PATH# 永久生效(添加到 ~/.bashrc)
echo 'export PATH=/usr/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc③ 編譯caffe
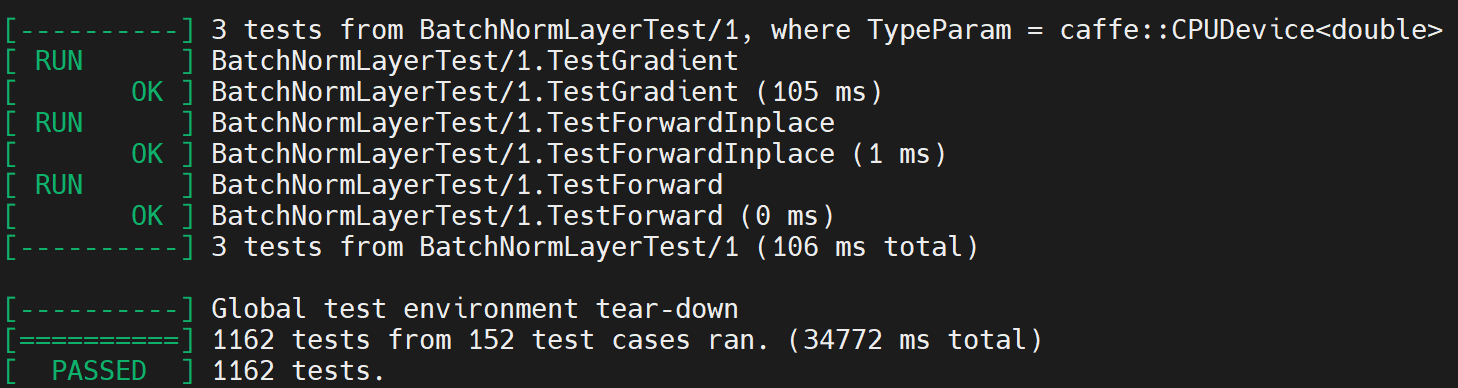
# 在caffe的主目錄下,依次執行:sudo make all -j$(nproc)sudo make test -j$(nproc)sudo make runtest -j$(nproc)最后假如得到是passed的話,那就代表你編譯成功了
2. 驗證動態庫鏈接
# 檢查 _caffe.so 鏈接的 Python 版本
ldd python/caffe/_caffe.so | grep python# 輸出如下,說明成功鏈接了python3.8
libpython3.8.so.1.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpython3.8.so.1.0 (0x00007fe800ec8000)
libboost_python38.so.1.71.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libboost_python38.so.1.71.0 (0x00007fe800c70000)
3. 常見編譯錯誤及解決方案
① 錯誤1:fatal error: numpy/arrayobject.h: No such file or directory
解決方案:
確保numpy已安裝且路徑正確。可以嘗試:
sudo apt install python3-numpy
# 或
pip install numpy --upgrade然后在Makefile.config中檢查numpy路徑是否正確。
② 錯誤2:undefined reference to boost::python...
解決方案:
確保boost-python版本匹配:
sudo apt install libboost-python-dev
# 或指定版本
sudo apt install libboost-python1.65-dev在Makefile.config中檢查PYTHON_LIBRARIES是否設置為boost_python38 python3.8。
③ 錯誤3:error: 'pybind11' is not a namespace-name
解決方案:
安裝pybind11:
pip install pybind11
conda install pybind11④ 錯誤4:error: 'class std::unordered_map' has no member named 'emplace'
解決方案:
需要更新GCC版本:
sudo apt install gcc-7 g++-7
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-7 100
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-7 100⑤ 錯誤5:HDF5相關錯誤
解決方案:
安裝hdf5開發包并設置正確路徑:
sudo apt install libhdf5-serial-dev libhdf5-dev在Makefile.config中取消注釋并修改:
INCLUDE_DIRS := $(PYTHON_INCLUDE) /usr/local/include /usr/include/hdf5/serial
LIBRARY_DIRS := $(PYTHON_LIB) /usr/local/lib /usr/lib /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/hdf5/serial六、安裝Python接口
1. 安裝所需的python包
在caffe的主目錄下,進入python文件夾。安裝requirements.txt所需的包
cd /home/caffe/python
pip install -r requirements.txt另外,需要升級里面的matplotlib
pip?install --upgrade matplotlib2. 編譯pycaffe
為caffe/python添加環境變量
export PYTHONPATH=/home/caffe/python:$PYTHONPATH
# 或永久添加到.bashrc
echo 'export PYTHONPATH=/home/caffe/python:$PYTHONPATH' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc進入caffe的主目錄,開始編譯
cd ..
sudo make pycaffe -j$(nproc)假如沒有報錯的話,那基本就成功了。
驗證安裝:
#依次輸入
python
import caffe
print(caffe.__version__)如果輸入結果如下圖就說明成功了,恭喜你,到這里就編譯完成了!?

七、測試Caffe
運行MNIST示例:
./data/mnist/get_mnist.sh
./examples/mnist/create_mnist.sh
./examples/mnist/train_lenet.sh八、可能遇到的問題及解決方案
問題1:caffe導入相關
ImportError: No module named caffe解決方案:
-
確保
PYTHONPATH包含caffe/python目錄 -
確保已運行
make pycaffe -
檢查Python環境是否正確(使用
which python確認)
問題2:Protobuf 相關
.build_release/src/caffe/proto/caffe.pb.h:10:10: fatal error: google/protobuf/port_def.inc: No such file or directory10 | #include <google/protobuf/port_def.inc>| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.解決方案:
遇到?Protobuf 相關的問題,說明系統中Protobuf 的版本不唯一,檢查當前編譯環境中的Protobuf 版本是否是自己想要的版本,如果不是那么修改環境變量指定版本
問題3:Opencv相關
src/caffe/layers/window_data_layer.cpp: In member function ‘virtual void caffe::WindowDataLayer<Dtype>::load_batch(caffe::Batch<Dtype>*)’:
src/caffe/layers/window_data_layer.cpp:293:42: error: ‘CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR’ was not declared in this scope293 | cv_img = cv::imread(image.first, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
make: *** [Makefile:595: .build_release/src/caffe/layers/window_data_layer.o] Error 1解決方案:
caffe源碼中和opencv相關的部分是按照3.x版本寫的,在4.x版本中有一些改動,OpenCV 4.x 版本棄用了CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR 和 CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE 宏定義,因此需要在Makefile.config中增加如下兩條
COMMON_FLAGS += -DCV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR=cv::IMREAD_COLOR
COMMON_FLAGS += -DCV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE=cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE問題4:caffe運行相關
ImportError: dynamic module does not define init function (init_caffe)解決方案:
Caffe報這個錯誤有兩種原因:
第一,有可能是python的版本不對。比如在python2.7下面編譯的caffe但是在python3下面運行了import caffe命令;或者相反。
第二,檢查自己是否運行了make pycaffe命令。


—— 政安晨:將小智AI代碼中的display與ota部分移除)



)


![[學習] 多項濾波器在信號插值和抽取中的應用:原理、實現與仿真(完整仿真代碼)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[學習] 多項濾波器在信號插值和抽取中的應用:原理、實現與仿真(完整仿真代碼))









