目錄
- 一. 線程同步
- 1. 條件變量
- 2. 條件變量接口
- 條件變量的創建及初始化
- 條件變量的銷毀
- 條件變量等待
- 條件變量喚醒
- 3. 條件變量同步解決搶占問題
- 二. 生產者-消費者模型
- 1. 什么是生產者-消費者模型
- 2. 為什么要使用生產者-消費者模型
- 3. 生產者-消費者模型特點
- 4. 基于阻塞隊列實現生產者-消費者模型
- 單生產-單消費
- 多生產-多消費
- 4. POSIX 信號量
- 信號量的初始化及銷毀
- 信號量的申請及釋放
- 5. 基于環形隊列實現生產者-消費者模型
- 單生產-單消費
- 多生產-多消費
一. 線程同步
線程同步: 在保證數據安全的前提下, 使線程能夠按照某種特定的順序訪問臨界資源,避免饑餓問題;
例:
當去掉休眠后, 1 號線程由于先運行, 競爭鎖的能力比較強, 直接搶占了大部分的資源;
#include "Thread.hpp"pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int tickets = 50;void* func(Thread<int*>* td, int* tickets)
{while (1){//sleep(1); // 休眠, 避免一個線程直接搶完LockGuard guard(&mtx); // 申請加鎖, 離開作用域自動解鎖if (*tickets > 0)cout << "次線程: " << td->get_name() << ", " << (*tickets)-- << endl;elsebreak;}return 0;
}int main()
{int n = 10;vector<Thread<int*> > threads;for (int i=1; i<n; i++)threads.emplace_back(func, &tickets, "thread-"+to_string(i));for (int i=1; i<n; i++)threads[i-1].start();for (int i=1; i<n; i++)threads[i-1].join();cout << "---------" << endl;cout << tickets << endl;return 0;
}
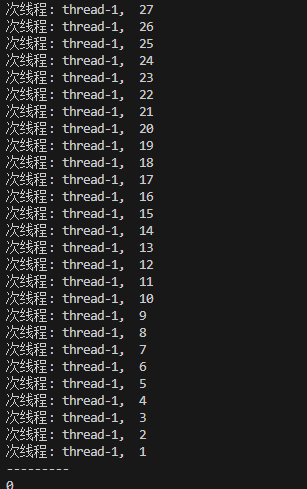
線程運行是沒有問題的, 但是不符合期望, 在原生線程庫中提供了條件變量這種方式來實現線程同步;
1. 條件變量
條件變量相當于一個隊列, 若線程不滿足運行條件, 那么推入當前條件變量的隊列當中, 等待喚醒; 當其他線程喚醒時, 從當前條件變量的隊列中推出線程; 通常條件變量和互斥鎖同時使用;
條件變量與互斥鎖不同, 互斥鎖是線程自動競爭鎖資源, 而條件變量是誘發的;
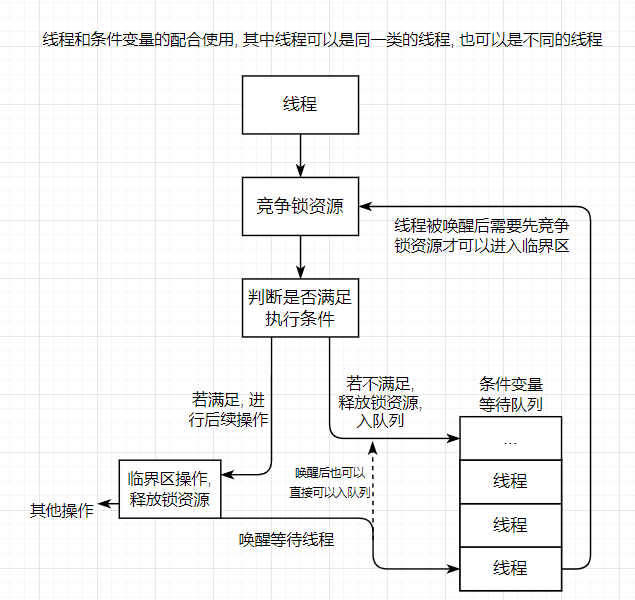
2. 條件變量接口
條件變量的創建及初始化
條件變量的類型為 pthread_cond_t, 在創建后需要進行初始化;
#include <pthread.h>// 定義條件變量
pthread_cond_t cond;// 全局/靜態的條件變量初始化
cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;// 條件變量初始化
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);
參數:
- cond: 需要條件變量的指針;
- cond_attr: 初始化時的相關屬性, 設置為 nullptr 表示使用默認屬性;
返回值:
- 若成功, 返回 0; 若失敗, 返回 error number;
全局/靜態的條件變量和互斥鎖相同, 也可以使用靜態初始化, 自動初始化, 自動銷毀;
條件變量的銷毀
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
參數:
- cond: 條件變量的地址;
返回值:
- 若成功, 返回 0; 若失敗, 返回 error number;
條件變量等待
pthread_cond_wait() 函數, 將等待當前線程, 并且釋放當前線程申請的鎖資源(避免當前鎖資源出現死鎖, 喚醒時自動競爭鎖資源);
pthread_cond_timedwait() 函數, 和 pthread_cond_wait() 函數相同, 不過會限制等待時間, 超時自動喚醒, 避免死鎖;
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const struct timespec *abstime);
參數:
- cond: 條件變量的地址;
- mutex: 互斥鎖的地址;
- abstime: 指定等待的時間(其值為系統時間 + 等待時間);
返回值:
- 若成功, 返回 0; 若失敗, 返回 error number;
條件變量喚醒
pthread_cond_signalt() 函數, 喚醒指定條件變量等待的隊頭線程;
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
參數:
- cond: 條件變量的地址;
返回值:
- 若成功, 返回 0; 若失敗, 返回 error number;
pthread_cond_broadcast() 函數, 喚醒指定條件變量等待的所有線程;
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
參數:
- cond: 條件變量的地址;
返回值:
- 若成功, 返回 0; 若失敗, 返回 error number;
3. 條件變量同步解決搶占問題
將線程推入同一條件變量隊列中, 一個一個的喚醒, 這樣就保證了資源分配均勻;
- Thread.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>using namespace std;class LockGuard
{public:LockGuard(pthread_mutex_t* mutex):_mutex(mutex){pthread_mutex_lock(_mutex);}~LockGuard(){pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);}private:pthread_mutex_t* _mutex;
};template<class T>
class Thread
{typedef function<void*(Thread<T>*, T&)> func_t;public:Thread(func_t func = nullptr, const T& args = T(), const string& name = "none"):_tid(0), _func(func), _args(args), _name(name){}static void* threadroutine(void* td){auto it = static_cast<Thread<T>*>(td);it->_func(it, it->_args);return 0;}bool start(){int flag = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, threadroutine, this);if (flag){_tid = 0;return false;}return true;}void join(){if (_tid){void* msg;int flag = pthread_join(_tid, &msg);if (flag){cerr << _name << " join fail "<< endl;exit(1);}}_tid = 0;}~Thread(){if (_tid)join();}const string& get_name(){ return _name; }private:pthread_t _tid;func_t _func;string _name;T _args;
};
- test.cpp
#include "Thread.hpp"pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int tickets = 50;void* func(Thread<int*>* td, int* tickets)
{LockGuard guard(&mtx); // 申請加鎖, 離開作用域自動解鎖while (*tickets){cout << "次線程: " << td->get_name() << ", " << (*tickets)-- << endl;pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx); // 線程等待, 自動釋放鎖資源, 下一個線程此時獲取鎖資源pthread_cond_signal(&cond); // 喚醒下一個線程}return 0;
}void wait(vector<Thread<int*> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].join();
}void start(vector<Thread<int*> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].start();sleep(2);pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}void init(vector<Thread<int*> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads.emplace_back(func, &tickets, "thread-"+to_string(i+1));
}int main()
{int n = 10;vector<Thread<int*> > threads;init(threads, n);start(threads, n);wait(threads, n);cout << "---------" << endl;cout << tickets << endl;return 0;
}
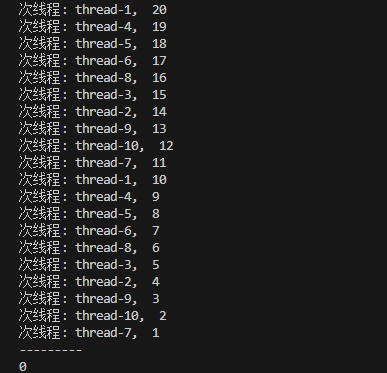
二. 生產者-消費者模型
1. 什么是生產者-消費者模型
假設有兩個線程 A, B 和一個緩沖區; A 線程向緩沖區中寫入數據, B 線程從緩沖區中讀取數據, 這就是一個簡單的生產者-消費者模型, A 為生產者, B 為消費者;
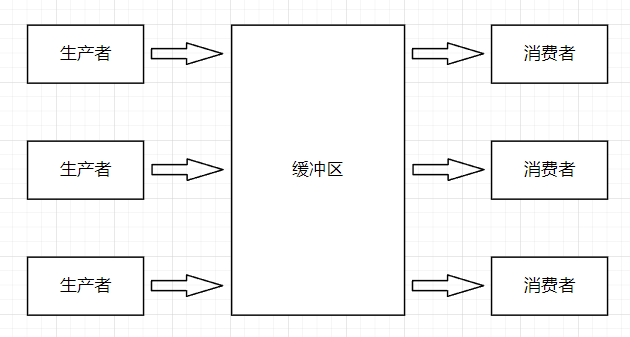
2. 為什么要使用生產者-消費者模型
-
解耦
假設生產者和消費者分別是兩個類; 若使生產者直接調用消費者的某個方法, 那么生產者對于消費者就會產生依賴(也就是耦合); 若消費者的代碼改變, 就可能會影響到生產者; 而若兩者不直接調用或通信, 兩者之間也就不會直接依賴, 耦合也就相應降低了; -
支持并發
假設生產者直接調用消費者的某個方法, 由于函數調用是同步的, 那么生產者就需要等待消費者處理方法; 而在生產者-消費者模型中, 兩者為并發的線程/進程, 只需要關心緩沖區的狀態, 在緩沖區 非空&&非滿 的情況下, 不會互相影響; -
支持忙閑不均
3. 生產者-消費者模型特點
生產者和消費者的三種關系:
-
生產者與消費者的關系:
同步: 當緩沖區滿的時候, 生產者會進入休眠狀態, 當下次消費者開始消耗緩沖區的數據時, 生產者才會被喚醒, 開始往緩沖區中添加數據; 當緩沖區空的時候, 消費者也會進入休眠狀態, 直到生產者往緩沖區中添加數據時才會被喚醒;
互斥: 同一時間, 生產者或消費者只能有一方向緩沖區添加或消耗數據; -
生產者與生產者的關系: 互斥;
-
消費者與消費者的關系: 互斥;
4. 基于阻塞隊列實現生產者-消費者模型
阻塞隊列(Blocking Queue)是一種常用于實現生產者-消費者模型的數據結構;
阻塞隊列的特定: 阻塞隊列的是有容量的;
使用阻塞隊列實現的生產者-消費者模型類似管道; 其同步和互斥特性使用條件變量和互斥鎖實現;
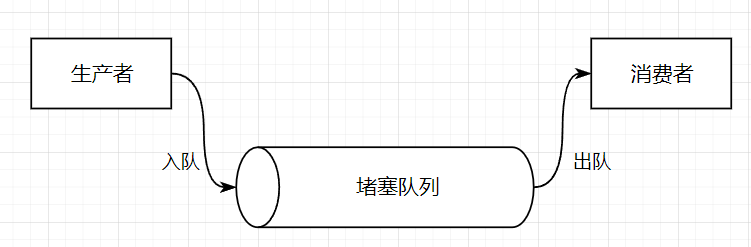
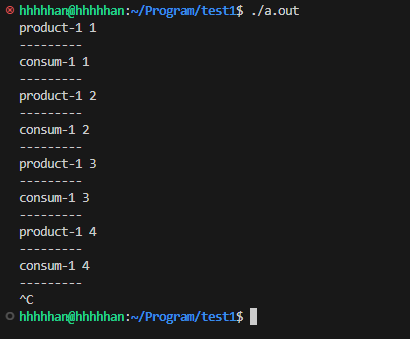
單生產-單消費
根據生產者-消費者模型特點, 搭建出所需的框架;
#include "Thread.hpp"template<class T>
class BlockingQueue
{
public:BlockingQueue(int cap = 10):_cap(cap){// 初始化鎖和條件變量pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex);pthread_cond_init(&_product_cond);pthread_cond_init(&_consum_cond);}void Push(const T& data){ }const T& Pop(){ }bool IsFull(){ return _blcok_queue.size() == _cap; }bool IsEmpty(){ return _blcok_queue.size() == 0; }~BlockingQueue(){// 銷毀鎖和條件變量pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&_product_cond);pthread_cond_destroy(&_consum_cond);}private:queue<T> _blcok_queue;int _cap;pthread_mutex_t _mutex; // 消費者之間的互斥鎖pthread_cond_t _product_cond; // 生產者的條件變量pthread_cond_t _consum_cond; // 消費者的條件變量
};
當生產者生產數據時, 也就是插入數據時, 條件為是否存在空間, 若沒有, 就需要阻塞等待; 若有空間, 那么直接插入數據, 并且需要通知消費者插入了數據;
void Push(const T &in)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex); // 申請加鎖if (IsFull()) // 插入判滿pthread_cond_wait(&_product_cond, &_mutex);_blcok_queue.push(in); // 插入數據pthread_cond_signal(&_consum_cond); // 喚醒消費者pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex); // 解鎖
}
消費者同理
void Pop(T &out)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);if (IsEmpty()) // 刪除判空pthread_cond_wait(&_consum_cond, &_mutex);out = _blcok_queue.front();_blcok_queue.pop(); // 插入數據pthread_cond_signal(&_product_cond); // 喚醒生產者pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);}
創建測試, 生產者先運行 2 秒, 然后消費者開始消費;
#include "BlockingQueue.hpp"template<class T>
void* Product(Thread<T>* self, T& args)
{BlockingQueue<int>* blcok_queue = (BlockingQueue<int>*)args;int n = 1;while (1){cout << self->get_name() << " " << n << endl;cout << "---------" << endl;blcok_queue->Push(n++);sleep(1);}return 0;
}template<class T>
void* Consum(Thread<T>* self, T& args)
{int n;BlockingQueue<int>* blcok_queue = (BlockingQueue<int>*)args;while (1){blcok_queue->Pop(n);cout << self->get_name() << " " << n << endl;cout << "---------" << endl;sleep(1);}return 0;
}template<class T>
void Wait(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].join();
}template<class T>
void Start(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].start();//sleep(2);
}template<class T>
void Init(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n, T func(Thread<T>*,T&), void* data = nullptr, const char* name = "thread-")
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads.emplace_back(func, data, name+to_string(i+1));
}int main()
{int n = 1;int m = 1;// vector<Thread<void*> > threads;BlockingQueue<int> blcok_queue;vector<Thread<void*> > product;vector<Thread<void*> > consum;Init(product, n, Product, &blcok_queue, "product-");Init(consum, m, Consum, &blcok_queue, "consum-");Start(product, n);Start(consum, m);Wait(product, n);Wait(consum, m);cout << "---------" << endl;return 0;
}
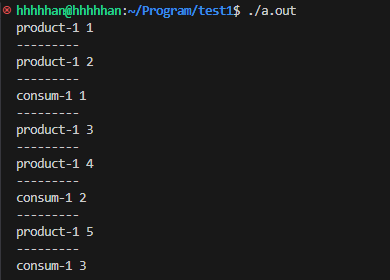
多生產-多消費
在單生產-單消費模型中, 插入和刪除數據的條件判斷使用的 if 判斷, 那么當 pthread_cond_wait() 函數被喚醒時, 就會直接向下執行; 這種判斷在實際上是有誤的, 因為 pthread_cond_wait() 函數可能存在調用失敗(誤喚醒, 偽喚醒)的情況;
而在 多生產-多消費 模型中, pthread_cond_wait() 函數調用失敗 或 調用pthread_cond_broadcast() 函數導致非法喚醒的情況更多, 所以需要將條件判斷的 if 改為 while, 持續進行條件判斷, 不合法的喚醒需要重新堵塞等待;
void Push(const T &in)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex); // 申請加鎖while (IsFull()) // 插入判滿pthread_cond_wait(&_product_cond, &_mutex);_blcok_queue.push(in); // 插入數據pthread_cond_signal(&_consum_cond); // 喚醒消費者pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex); // 解鎖
}void Pop(T &out)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);while (IsEmpty()) // 刪除判空pthread_cond_wait(&_consum_cond, &_mutex);out = _blcok_queue.front();_blcok_queue.pop(); // 插入數據pthread_cond_signal(&_product_cond); // 喚醒生產者pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
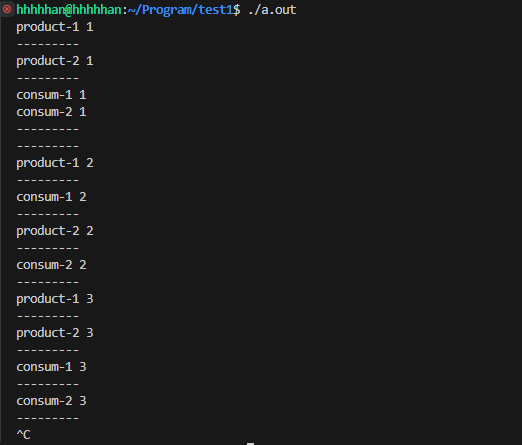
4. POSIX 信號量
信號量的本質就是一個計數器; 信號量的 PV 操作是原子的, 可以使用信號量實現l臨界資源的互斥和同步;
信號量主要作用是描述臨界資源中的資源數目;
- 若申請信號量成功, 計數器 - - (P 操作)
- 若釋放信號量成功, 計數器 ++ (V 操作)
若將臨界資源看作一個整體, 這種信號量就是二元信號量, 類似互斥鎖, 信號量只有兩種狀態: 0, 1;
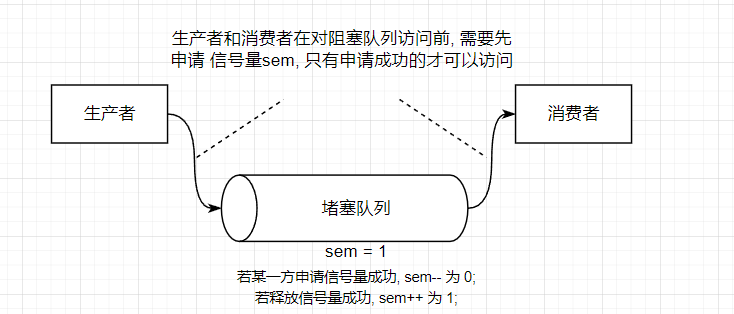
若將臨界資源中的資源數目劃分為多份, 這種信號量就是多元信號量, 類似條件變量, 只有申請資源成功的, 才可以進行臨界區操作;
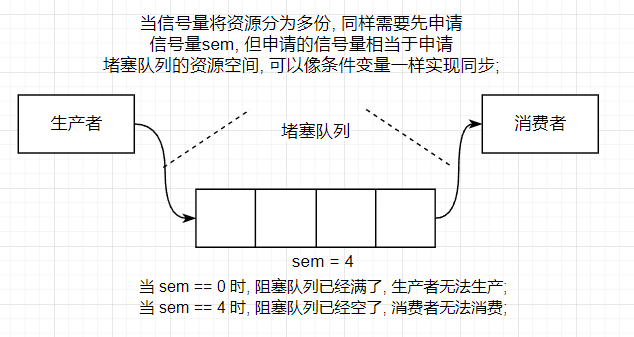
信號量的初始化及銷毀
#include <semaphore.h>// 創建信號量
sem_t sem; // 初始化信號量
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);// 銷毀信號量
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
參數:
- sem: 指定的信號量;
- pshared: 當前信號量的共享狀態. 傳遞 0 表示線程間共享, 傳遞 非0 表示進程間共享;
- value: 信號量的初始值, 相當于資源的數目;
返回值: 若成功返回 0; 若失敗返回 -1, 并設置錯誤碼;
信號量的申請及釋放
#include <semaphore.h>// 申請信號量
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); // 堵塞等待直至申請成功
int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem); // 只會申請一次
int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout); // 若失敗, 等待 abs_timeout 后再次申請;// 釋放信號量
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
參數:
- sem: 指定的信號量;
- abs_timeout: 休眠時間, 若申請失敗, 會在 abs_timeout 后再次申請;
返回值: 若成功返回 0; 若失敗返回 -1, 并設置錯誤碼;
5. 基于環形隊列實現生產者-消費者模型
生產者-消費者模型的緩沖區也可以使用環形隊列進行實現;
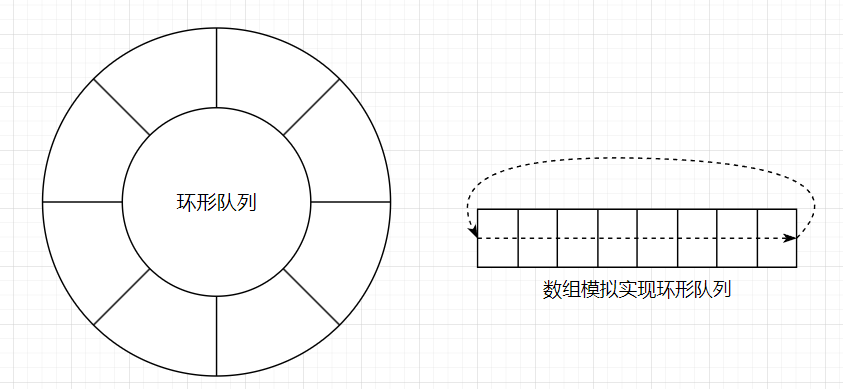
在環形隊列中, 生產者只關心是否有空間放數據, 消費者只關心是否能從空間中取到數據, 只要申請資源成功, 生產者可以和消費者并發訪問環形隊列;
那么可以分別記錄兩者的下標, 若下標位置不同, 那么雙方一定是有資源的;
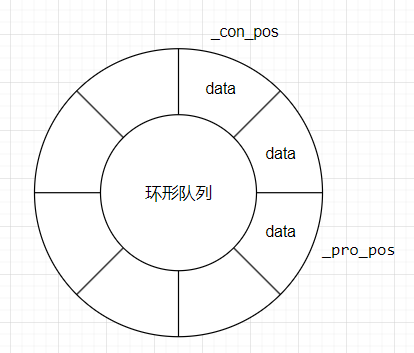
若下標位置相同, 那么只可能為一方空, 一方滿;
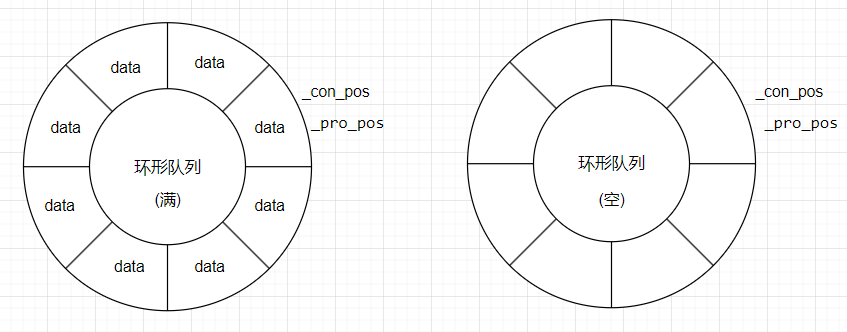
單生產-單消費
單生產-單消費模型中, 當兩者信號量都不為 0 時, 兩者可以并發執行;
當生產者信號量為 0 時, 生產者阻塞等待, 等待消費者消費; 當消費者信號量為 0 時, 消費者會阻塞等待, 等待生產者生產; 當對方生產/消費后, 自己就會喚醒, 保證了同步和互斥;
#include "Thread.hpp"template <class T>
class RingQueue
{private:void P(sem_t& sem){sem_wait(&sem);}void V(sem_t& sem){sem_post(&sem);}public:RingQueue(int cap = 10): _cap(cap), _pro_pos(0), _con_pos(0){_queue.resize(cap);// 初始化信號量sem_init(&_pro_sem, 0, cap);sem_init(&_con_sem, 0, 0);}void Push(const T &in){P(_pro_sem); // 申請信號量// 至當前位置, 一定申請成功, 就一定會有資源_queue[_pro_pos++] = in; // 插入數據_pro_pos %= _cap;V(_con_sem); // 釋放信號量, 但釋放的是消費者的信號量, 增加消費者可用資源數目}void Pop(T &out){P(_con_sem); // 申請信號量// 至當前位置, 一定申請成功, 就一定會有資源out = _queue[_con_pos++]; // 刪除數據_con_pos %= _cap;V(_pro_sem); // 釋放信號量, 但釋放的是生產者的信號量, 增加生產者可用資源數目}~RingQueue(){// 銷毀信號量sem_destroy(&_pro_sem);sem_destroy(&_con_sem);}private:vector<T> _queue;int _cap;size_t _pro_pos; // 生產者下標size_t _con_pos; // 消費者下標sem_t _pro_sem; // 生產者的信號量sem_t _con_sem; // 消費者的信號量
};
#include "BlockingQueue.hpp"
#include "RingQueue.hpp"LockGuard guard;template<class T>
void* Product(Thread<T>* self, T& args)
{RingQueue<int>* _queue = (RingQueue<int>*)args;int n = 1;while (1){cout << self->get_name() << " " << n << endl;cout << "---------" << endl;_queue->Push(n++);sleep(1);}return 0;
}template<class T>
void* Consum(Thread<T>* self, T& args)
{int n;RingQueue<int>* _queue = (RingQueue<int>*)args;while (1){_queue->Pop(n);cout << self->get_name() << " " << n << endl;cout << "---------" << endl;sleep(1);}return 0;
}template<class T>
void Wait(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].join();
}template<class T>
void Start(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n)
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads[i].start();//sleep(2);
}template<class T>
void Init(vector<Thread<T> >& threads, int n, T func(Thread<T>*,T&), void* data = nullptr, const char* name = "thread-")
{for (int i=0; i<n; i++)threads.emplace_back(func, data, name+to_string(i+1));
}int main()
{int n = 1;int m = 1;// vector<Thread<void*> > threads;//BlockingQueue<int> blcok_queue;RingQueue<int> _queue;vector<Thread<void*> > product;vector<Thread<void*> > consum;Init(product, n, Product, &_queue, "product-");Init(consum, m, Consum, &_queue, "consum-");Start(product, n);Start(consum, m);Wait(product, n);Wait(consum, m);cout << "---------" << endl;return 0;
}
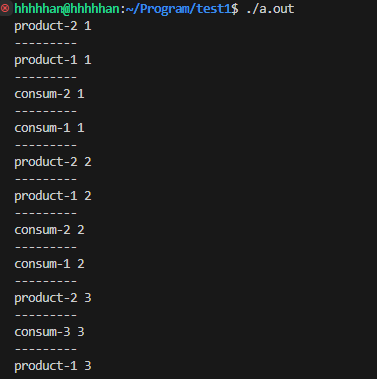
多生產-多消費
但在多生產-多消費中需要注意, 由于生產者和生產者, 消費者和消費者之間存在互斥關系, 所以需要增加兩把鎖;
#include "Thread.hpp"template <class T>
class RingQueue
{private:void P(sem_t &sem){sem_wait(&sem);}void V(sem_t &sem){sem_post(&sem);}public:RingQueue(int cap = 10): _cap(cap), _pro_pos(0), _con_pos(0){_queue.resize(cap);// 初始化信號量sem_init(&_pro_sem, 0, cap);sem_init(&_con_sem, 0, 0);}void Push(const T &in){P(_pro_sem); // 申請信號量_pro_mutex.Lock(); // 申請加鎖// 至當前位置, 一定申請成功_queue[_pro_pos++] = in; // 插入數據_pro_pos %= _cap;_pro_mutex.Unlock(); // 申請解鎖V(_con_sem); // 釋放信號量, 但釋放的是消費者的信號量, 增加消費者可用資源數目}void Pop(T &out){P(_con_sem); // 申請信號量_con_mutex.Lock(); // 申請加鎖// 至當前位置, 一定申請成功out = _queue[_con_pos++]; // 刪除數據_con_pos %= _cap;_con_mutex.Unlock(); // 申請解鎖V(_pro_sem); // 釋放信號量, 但釋放的是生產者的信號量, 增加生產者可用資源數目}~RingQueue(){// 銷毀信號量sem_destroy(&_pro_sem);sem_destroy(&_con_sem);}private:vector<T> _queue;int _cap;size_t _pro_pos; // 生產者下標size_t _con_pos; // 消費者下標sem_t _pro_sem; // 生產者的信號量sem_t _con_sem; // 消費者的信號量LockGuard _pro_mutex; // 生產者的信號量LockGuard _con_mutex; // 消費者的信號量
};

)






)



)



~致敬鳥山明簡略版)
)

