傳送門:
- 《2024.5組隊學習——MetaGPT(0.8.1)智能體理論與實戰(上):MetaGPT安裝、單智能體開發》
- 《2024.5組隊學習——MetaGPT(0.8.1)智能體理論與實戰(中):訂閱智能體OSS實現》
文章目錄
- 一、 快速入門:軟件公司
- 1.1 定義動作
- 1.2 定義角色
- 1.3 定義團隊
- 二、多智能體交互機制
- 2.1 Environment
- 2.2 role
- 2.3 Team
- 三、示例
- 3.1 智能寫詩
- 3.2 軟件公司(略)
- 3.3 智能體辯論
- 3.3.1 定義動作
- 3.3.2 定義角色
- 3.3.3 創建團隊并添加角色
- 四、作業
- 4.1 基礎作業
- 4.2 進階作業:重寫babyagi
- 4.2.1 babyagi簡介
- 4.2.2 babyagi問答
- 學習資料:項目地址——hugging-multi-agent、在線閱讀、MetaGPT項目、MetaGPT中文文檔
- 優秀作業鏈接:《MetaGPT環境搭建和嘗試》、Destory的《MetaGPT教程筆記》、樂正萌的《MetaGPT教程Task3 》、 GISer Liu的《基于MetaGPT構建單智能體》、《MetaGPT課程3作業》
一、 快速入門:軟件公司
參考官方文檔《多智能體入門》、軟件公司完整代碼:build_customized_multi_agents.py
??一些復雜的任務通常需要協作和團隊合作,在MetaGPT框架下,用戶可以通過少量代碼實現多智能體交互,共同完成更復雜的任務。下面以軟件公司為示例,開發一個智能體團隊。
- 定義三個角色:一位編碼人員(寫代碼)、一名測試人員(測試代碼)和一名審閱人員(評價測試結果)。
- 基于標準作業程序(SOP)確保每個角色遵守它。通過使每個角色觀察上游的相應輸出結果,并為下游發布自己的輸出結果,可以實現這一點。
- 初始化所有角色,創建一個帶有環境的智能體團隊,并使它們之間能夠進行交互。
??在《2024.5組隊學習——MetaGPT智能體理論與實戰(上)》第三章單智能體入門中,我們實現了具有SimpleWriteCode 動作的SimpleCoder 角色,用于接收用戶的指令并編寫主要代碼。我們可以以相同的方式定義其它兩個角色SimpleTester、SimpleReviewer及其對應的動作SimpleWriteTest、SimpleWriteReview 。
1.1 定義動作
class SimpleWriteCode(Action):PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str = """Write a python function that can {instruction}.Return ```python your_code_here ```with NO other texts,your code:"""name: str = "SimpleWriteCode"async def run(self, instruction: str):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(instruction=instruction)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)code_text = parse_code(rsp)return code_text
class SimpleWriteTest(Action):PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str = """Context: {context}Write {k} unit tests using pytest for the given function, assuming you have imported it.Return ```python your_code_here ```with NO other texts,your code:"""name: str = "SimpleWriteTest"async def run(self, context: str, k: int = 3):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(context=context, k=k)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)code_text = parse_code(rsp)return code_text
class SimpleWriteReview(Action):PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str = """Context: {context}Review the test cases and provide one critical comments:"""name: str = "SimpleWriteReview"async def run(self, context: str):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(context=context)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)return rsp
1.2 定義角色
接下來,我們需要定義三個具有各自動作的Role:
SimpleCoder具有SimpleWriteCode動作,接收用戶的指令并編寫主要代碼SimpleTester具有SimpleWriteTest動作,從SimpleWriteCode的輸出中獲取主代碼并為其提供測試套件SimpleReviewer具有SimpleWriteReview動作,審查來自SimpleWriteTest輸出的測試用例,并檢查其覆蓋范圍和質量
整個軟件公司的運作機制如下:

如上圖的右側部分所示,Role的機制可以用四步來表示:
_observe:將從Environment中獲取_observeMessage。如果有一個Role_watch的特定Action引起的Message,那么這是一個有效的觀察,觸發Role的后續思考和操作。_think:Role將選擇其能力范圍內的一個Action并將其設置為要做的事情。_act:執行,即運行Action并獲取輸出,并將輸出封裝在Message中_publish:發布publish_message到Environment,由此完成了一個完整的智能體運行。
??在每個步驟中,無論是 _observe、_think 還是 _act,Role都將與其 Memory 交互,通過添加或檢索來實現。此外,MetaGPT提供了 react 過程的不同模式。這些部分的詳細內容,請參閱使用記憶 和 思考與行動,參考或者Role代碼。
??如上圖左側部分所示,每個 Role 都需要遵守SOP(觀察上游的相應輸出結果,并為下游發布自己的輸出),比如虛線框中, SimpleTester 同時 _watch SimpleWriteCode 和 SimpleWriteReview,則可以擴展 SOP。
??接下來,我們將詳細討論如何根據 SOP 來定義Role。首先對于SimpleCoder,我們需要兩件事:
self._watch([UserRequirement]): 獲取來自用戶或其他智能體的重要上游消息(這里是UserRequirement引起的Message)- 使用
set_actions為Role配備適當的Action,這與設置單智能體相同
class SimpleCoder(Role):name: str = "Alice"profile: str = "SimpleCoder"def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self._watch([UserRequirement])self.set_actions([SimpleWriteCode])
與上述相似,對于 SimpleTester,我們:
-
使用
set_actions為SimpleTester配備SimpleWriteTest動作 -
獲取來自其他智能體的重要上游消息,這里
SimpleTester將從SimpleCoder中獲取主代碼。一個擴展的問題:想一想如果我們使用
self._watch([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleWriteReview])會意味著什么,可以嘗試這樣做 -
重寫
_act函數,就像我們在智能體入門中的單智能體設置中所做的那樣。在這里,我們希望SimpleTester將所有記憶用作編寫測試用例的上下文,并希望有5個測試用例,因此我們需要多個輸入。
class SimpleTester(Role):name: str = "Bob"profile: str = "SimpleTester"def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self.set_actions([SimpleWriteTest])self._watch([SimpleWriteCode])# self._watch([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleWriteReview]) # feel free to try this tooasync def _act(self) -> Message:logger.info(f"{self._setting}: to do {self.rc.todo}({self.rc.todo.name})")todo = self.rc.todo# context = self.get_memories(k=1)[0].content # use the most recent memory as contextcontext = self.get_memories() # use all memories as contextcode_text = await todo.run(context, k=5) # specify argumentsmsg = Message(content=code_text, role=self.profile, cause_by=type(todo))return msg
??在這里,我們調用get_memories() 函數為SimpleTester提供完整的歷史記錄。通過這種方式,如果 SimpleReviewer提供反饋,SimpleTester可以參考其先前版本修改測試用例。
??下面按照相同的過程定義 SimpleReviewer:
class SimpleReviewer(Role):name: str = "Charlie"profile: str = "SimpleReviewer"def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self.set_actions([SimpleWriteReview])self._watch([SimpleWriteTest])
1.3 定義團隊
??定義完三個 Role之后,我們需要初始化所有角色,設置一個 Team,并hire 它們。運行 Team,我們應該會看到它們之間的協作!
import asyncio
import typer
from metagpt.logs import logger
from metagpt.team import Team
app = typer.Typer()@app.command()
def main(idea: str = typer.Argument(..., help="write a function that calculates the product of a list"),investment: float = typer.Option(default=3.0, help="Dollar amount to invest in the AI company."),n_round: int = typer.Option(default=5, help="Number of rounds for the simulation."),
):logger.info(idea)team = Team()team.hire([SimpleCoder(),SimpleTester(),SimpleReviewer(),])team.invest(investment=investment)team.run_project(idea)await team.run(n_round=n_round)if __name__ == '__main__':app()
運行結果:

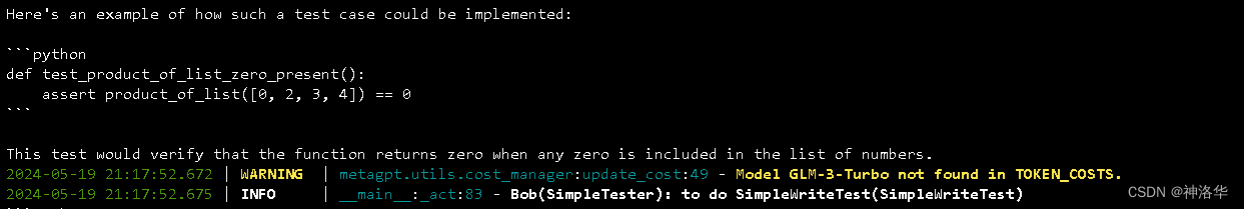
-
SimpleCoder角色(Alice)根據用戶需求編寫了一個Python函數product_of_list,該函數的作用是計算列表中所有數字的乘積。 -
SimpleTester角色(Bob)編寫了一系列測試用例,用于測試product_of_list函數的正確性。測試用例包括:- 測試空列表的情況
- 測試只有一個數字的列表
- 測試全為正數的列表
- 測試全為負數的列表
- 測試正負數混合的列表
-
SimpleReviewer角色(Charlie)審閱了測試用例,并發現測試用例缺少一種重要情況:列表中包含0。他指出乘積運算中如果有0,不論其他數字是什么,結果都應該是0。因此,他建議增加一個新的測試用例,用于測試列表包含0的情況。 -
SimpleTester(Bob)根據SimpleReviewer的反饋,補充了一個新的測試用例test_product_of_list_zero_present,用于測試列表中包含0的情況。 -
SimpleReviewer(Charlie)再次審閱測試用例,發現缺失的測試用例已經被補充
完整代碼見examples/build_customized_multi_agents.py,你也可以在直接使用以下代碼運行:
python3 examples/build_customized_multi_agents.py --idea "write a function that calculates the product of a list"
二、多智能體交互機制
源碼:Environment、Role、Team

2.1 Environment
??MetaGPT提供了一個標準的環境組件Environment,來管理agent的活動與信息交流,agents 必須按照環境中的規則進行活動。正如源碼所說,Environment承載一批角色,角色可以向環境發布消息,可以被其他角色觀察到。
class Environment(ExtEnv):"""環境,承載一批角色,角色可以向環境發布消息,可以被其他角色觀察到Environment, hosting a batch of roles, roles can publish messages to the environment, and can be observed by other roles"""model_config = ConfigDict(arbitrary_types_allowed=True)desc: str = Field(default="") # 環境描述roles: dict[str, SerializeAsAny["Role"]] = Field(default_factory=dict, validate_default=True)member_addrs: Dict["Role", Set] = Field(default_factory=dict, exclude=True)history: str = "" # For debugcontext: Context = Field(default_factory=Context, exclude=True)
desc:描述當前的環境信息role:指定當前環境中的角色member_addrs:表示當前環境中的角色以及他們對應的狀態history:用于記錄環境中發生的消息記錄
??下面是env的run方法,由此可見,當env運行時,會依次讀取環境中的role信息,默認按照聲明 role 的順序依次執行 role 的 run 方法。
async def run(self, k=1):"""Process all Role runs at once(處理一次所有信息的運行) """for _ in range(k):futures = []for role in self.roles.values():future = role.run()# 將role的運行緩存至 future list 中,在后續的 gather 方法中依次調用futures.append(future)await asyncio.gather(*futures)logger.debug(f"is idle: {self.is_idle}")
其它env方法:
def add_role(self, role: Role):"""增加一個在當前環境的角色Add a role in the current environment"""self.roles[role.profile] = rolerole.set_env(self)def add_roles(self, roles: Iterable[Role]):"""增加一批在當前環境的角色Add a batch of characters in the current environment"""for role in roles:self.roles[role.profile] = rolefor role in roles: # setup system message with rolesrole.set_env(self)def get_roles(self) -> dict[str, Role]:"""獲得環境內的所有角色Process all Role runs at once"""return self.rolesdef get_role(self, name: str) -> Role:"""獲得環境內的指定角色get all the environment roles"""return self.roles.get(name, None)def role_names(self) -> list[str]:return [i.name for i in self.roles.values()]
2.2 role
??在 role 的run方法中,role 首先將會根據運行時是否傳入信息(if with_message:,部分行動前可能需要前置知識消息),如果有,則將信息存入 rolecontext的 msg_buffer 中。
@role_raise_decorator
async def run(self, with_message=None) -> Message | None:"""Observe, and think and act based on the results of the observation"""if with_message:msg = Noneif isinstance(with_message, str):msg = Message(content=with_message)elif isinstance(with_message, Message):msg = with_messageelif isinstance(with_message, list):msg = Message(content="\n".join(with_message))if not msg.cause_by:msg.cause_by = UserRequirementself.put_message(msg)if not await self._observe():# If there is no new information, suspend and waitlogger.debug(f"{self._setting}: no news. waiting.")returnrsp = await self.react()# Reset the next action to be taken.self.set_todo(None)# Send the response message to the Environment object to have it relay the message to the subscribers.self.publish_message(rsp)return rsp
# rc: RoleContext = Field(default_factory=RoleContext)def put_message(self, message):"""Place the message into the Role object's private message buffer."""if not message:returnself.rc.msg_buffer.push(message)
??在多智能體環境運行中,Role的每次行動將從Environment中先_observe Message。_observe的目的是從message buffer等消息源獲取新的消息,過濾掉不相關的消息,記錄最新狀態,以供后續處理。
async def _observe(self, ignore_memory=False) -> int:"""Prepare new messages for processing from the message buffer and other sources."""# 從消息緩沖區(msg buffer)讀取未處理的消息news = []if self.recovered:news = [self.latest_observed_msg] if self.latest_observed_msg else []if not news:news = self.rc.msg_buffer.pop_all()# 在內存在存儲已讀的 messages,防止重復處理old_messages = [] if ignore_memory else self.rc.memory.get()self.rc.memory.add_batch(news)# 過濾掉不感興趣的messagesself.rc.news = [n for n in news if (n.cause_by in self.rc.watch or self.name in n.send_to) and n not in old_messages]self.latest_observed_msg = self.rc.news[-1] if self.rc.news else None # record the latest observed msg# Design Rules:# If you need to further categorize Message objects, you can do so using the Message.set_meta function.# msg_buffer is a receiving buffer, avoid adding message data and operations to msg_buffer.news_text = [f"{i.role}: {i.content[:20]}..." for i in self.rc.news]if news_text:logger.debug(f"{self._setting} observed: {news_text}")return len(self.rc.news)
- 如果是從故障恢復狀態 (
self.recovered),則從latest_observed_msg獲取上次觀測到的最新消息(沒有就是空)。 - 將新讀取到的消息添加到內存 (
self.rc.memory) 中,以防止重復處理。 - 過濾掉不感興趣的消息,即消息的
cause_by不在self.rc.watch列表中,且消息的send_to也不包含self.name。同時也過濾掉已經處理過的消息 (old_messages)。 - 記錄最新觀測到的消息
self.latest_observed_msg。 - 打印 debug 日志,顯示觀測到的新消息摘要。
- 最終返回新消息的數量
len(self.rc.news)。
該函數還強調了一些設計規則:
- 可以使用
Message.set_meta函數對消息進一步分類(如果需要的話)。 msg_buffer是接收緩沖區,應避免在其中添加或操作消息。
觀察完畢后,采取行動:
# role.pyasync def run(self, with_message=None) -> Message | None:......rsp = await self.react()# Reset the next action to be taken.self.set_todo(None)# 將消息發送到Environment對象,讓它將消息中繼給所有訂閱者self.publish_message(rsp)return rsp...
...
def publish_message(self, msg):"""If the role belongs to env, then the role's messages will be broadcast to env"""if not msg:returnif not self.rc.env:# 如果env不存在,就不發布messagereturnself.rc.env.publish_message(msg)
??env.publish_message方法會遍歷環境中所有角色,檢查它們是否訂閱了這條消息。如果訂閱,則調用
put_message方法將這條消息存入該角色的msg_buffer中。
2.3 Team
??Team是基于Environment之上二次封裝的結果,它提供了比Environment更多的組件。比如investment用于管理團隊成本(tokens花費),idea給出團隊目標。
class Team(BaseModel):"""Team: Possesses one or more roles (agents), SOP (Standard Operating Procedures), and a env for instant messaging,dedicated to env any multi-agent activity, such as collaboratively writing executable code."""model_config = ConfigDict(arbitrary_types_allowed=True)env: Optional[Environment] = None # 一個可選的Environment對象,用于團隊即時通訊investment: float = Field(default=10.0) # 投資金額,默認為10.0idea: str = Field(default="") # 團隊的想法或主題,默認為空字符串def __init__(self, context: Context = None, **data: Any):super(Team, self).__init__(**data)ctx = context or Context()if not self.env:self.env = Environment(context=ctx)else:self.env.context = ctx # The `env` object is allocated by deserializationif "roles" in data:self.hire(data["roles"])if "env_desc" in data:self.env.desc = data["env_desc"]
在__init__函數中:
- 調用父類BaseModel的構造函數,將傳入的數據(
**data)作為屬性初始化 - 檢查并初始化
env屬性 - 如果傳入的數據中包含
roles,它會調用hire方法添加這些角色。如果傳入的數據中包含env_desc,它會將描述設置為環境的描述。
??另外hire方法用于添加員工(roles),invest方法控制預算,_check_balance檢查是否超過預算
def hire(self, roles: list[Role]):"""Hire roles to cooperate"""self.env.add_roles(roles)def invest(self, investment: float):"""Invest company. raise NoMoneyException when exceed max_budget."""self.investment = investmentself.cost_manager.max_budget = investmentlogger.info(f"Investment: ${investment}.")
??在Team運行時,如果有idea,則先發布用戶需求,然后重復n_round輪,每輪循環調用 self.env.run() 來運行env,最后返回env中角色的歷史對話。
@serialize_decorator
async def run(self, n_round=3, idea="", send_to="", auto_archive=True):"""Run company until target round or no money"""if idea:self.run_project(idea=idea, send_to=send_to)while n_round > 0:n_round -= 1self._check_balance()await self.env.run()logger.debug(f"max {n_round=} left.")self.env.archive(auto_archive)return self.env.history
def run_project(self, idea, send_to: str = ""):"""Run a project from publishing user requirement."""self.idea = idea# Human requirement.self.env.publish_message(Message(role="Human", content=idea, cause_by=UserRequirement, send_to=send_to or MESSAGE_ROUTE_TO_ALL),peekable=False,)
_check_balance 函數用于檢查公司的預算是否足夠,超過則引發 NoMoneyException 異常。
def _check_balance(self):if self.cost_manager.total_cost >= self.cost_manager.max_budget:raise NoMoneyException(self.cost_manager.total_cost, f"Insufficient funds: {self.cost_manager.max_budget}")
另外Team還包含一些其它方法:
serialize:用于將Team對象序列化為JSON文件deserialize:用于從JSON文件中反序列化Team對象
??盡管 Team 只是在 Env上的簡單封裝,但它向我們展示了,我們該如何向多智能體系統發布啟動消息以及引入可能的人類反饋,進而開發屬于自己的智能體團隊。
三、示例
3.1 智能寫詩
??下面以智能寫詩為設定場景。我們需要一位student,根據我們要求的主題來寫詩的;還需要一位精通詩文的teacher評價詩文,給出修改意見。之后學生根據此意見修改作品,直至循環結束。
- 設定環境
import asynciofrom metagpt.actions import Action, UserRequirement
from metagpt.logs import logger
from metagpt.roles import Role
from metagpt.schema import Message
from metagpt.environment import Environmentfrom metagpt.const import MESSAGE_ROUTE_TO_ALL# 聲明一個名為classroom的Env,所有的role都在classroom里活動
classroom = Environment()
- 編寫
WritePoem和ReviewPoem
class WritePoem(Action):name: str = "WritePoem"PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str = """Here is the historical conversation record : {msg} .Write a poem about the subject provided by human, Return only the content of the generated poem with NO other texts.If the teacher provides suggestions about the poem, revise the student's poem based on the suggestions and return.your poem:"""async def run(self, msg: str):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(msg = msg)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)return rspclass ReviewPoem(Action):name: str = "ReviewPoem"PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str = """Here is the historical conversation record : {msg} .Check student-created poems about the subject provided by human and give your suggestions for revisions. You prefer poems with elegant sentences and retro style.Return only your comments with NO other texts.your comments:"""async def run(self, msg: str):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(msg = msg)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)return rsp
- 定義
Student和Teacher
與單智能體不同的是,定義每個角色時,需要聲明其關注的動作(self._watch),只有當關注的動作發生時,角色才開始行動。
class Student(Role):name: str = "xiaoming"profile: str = "Student"def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self._init_actions([WritePoem])self._watch([UserRequirement, ReviewPoem])async def _act(self) -> Message:logger.info(f"{self._setting}: ready to {self.rc.todo}")todo = self.rc.todomsg = self.get_memories() # 獲取所有記憶# logger.info(msg)poem_text = await WritePoem().run(msg)logger.info(f'student : {poem_text}')msg = Message(content=poem_text, role=self.profile,cause_by=type(todo))return msgclass Teacher(Role):name: str = "laowang"profile: str = "Teacher"def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self._init_actions([ReviewPoem])self._watch([WritePoem])async def _act(self) -> Message:logger.info(f"{self._setting}: ready to {self.rc.todo}")todo = self.rc.todomsg = self.get_memories() # 獲取所有記憶poem_text = await ReviewPoem().run(msg)logger.info(f'teacher : {poem_text}')msg = Message(content=poem_text, role=self.profile,cause_by=type(todo))return msg
- 定義主函數
將主題發布在classroom中并運行,env就開始工作了。你可以修改n_round數,直到達到你想要的效果。
async def main(topic: str, n_round=3):classroom.add_roles([Student(), Teacher()])classroom.publish_message(Message(role="Human", content=topic, cause_by=UserRequirement,send_to='' or MESSAGE_ROUTE_TO_ALL),peekable=False,)while n_round > 0:# self._save()n_round -= 1logger.debug(f"max {n_round=} left.")await classroom.run()return classroom.historyasyncio.run(main(topic='wirte a poem about moon'))
3.2 軟件公司(略)
3.3 智能體辯論
??下面這個場景,模擬兩位辯手互相辯論,這是一個展示如何設計多個智能體并促進它們之間的互動的理想例子。總體上,我們需要3個步驟來實現:
- 定義一個具有發言行為的辯手角色,我們建議參考智能體入門
- 處理辯手之間的通信,也就是讓雙方互聽對方的發言
- 初始化兩個辯手實例,創建一個帶有環境的團隊,并使它們能夠相互交互。
3.3.1 定義動作
class SpeakAloud(Action):"""動作:在辯論中大聲說話(爭吵)"""PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """## BACKGROUNDSuppose you are {name}, you are in a debate with {opponent_name}.## DEBATE HISTORYPrevious rounds:{context}## YOUR TURNNow it's your turn, you should closely respond to your opponent's latest argument, state your position, defend your arguments, and attack your opponent's arguments,craft a strong and emotional response in 80 words, in {name}'s rhetoric and viewpoints, your will argue:"""def __init__(self, name="SpeakAloud", context=None, llm=None):super().__init__(name, context, llm)async def run(self, context: str, name: str, opponent_name: str):prompt = self.PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(context=context, name=name, opponent_name=opponent_name)rsp = await self._aask(prompt)return rsp
3.3.2 定義角色
??我們將定義一個通用的 Role,稱為 Debator。我們設定其動作為SpeakAloud,還使用 _watch 監視了 SpeakAloud 和 UserRequirement,因為我們希望每個辯手關注來自對手的 SpeakAloud 消息,以及來自用戶的 UserRequirement(人類指令)。
class Debator(Role):def __init__(self,name: str,profile: str,opponent_name: str,**kwargs,):super().__init__(name, profile, **kwargs)self.set_actions([SpeakAloud])self._watch([UserRequirement, SpeakAloud])self.name = nameself.opponent_name = opponent_name
??接下來,我們使每個辯手聽取對手的論點,通過重寫 _observe 函數可以完成這一點。這點很重要,因為在環境中將會有來自雙方 “SpeakAloud 消息”(由 SpeakAloud 觸發的 Message)。 我們不希望一方處理自己上一輪的 “SpeakAloud 消息”,而是處理來自對方的消息。
async def _observe(self) -> int:await super()._observe()# accept messages sent (from opponent) to self, disregard own messages from the last roundself.rc.news = [msg for msg in self.rc.news if msg.send_to == self.name]return len(self.rc.news)
??最后,我們使每個辯手能夠向對手發送反駁的論點。在這里,我們從消息歷史中構建一個上下文,使 Debator 運行他擁有的 SpeakAloud 動作,并使用反駁論點內容創建一個新的 Message。請注意,我們定義每個 Debator 將把 Message 發送給他的對手。
async def _act(self) -> Message:logger.info(f"{self._setting}: ready to {self.rc.todo}")todo = self.rc.todo # 一個 SpeakAloud 的實例memories = self.get_memories()context = "\n".join(f"{msg.sent_from}: {msg.content}" for msg in memories)rsp = await todo.run(context=context, name=self.name, opponent_name=self.opponent_name)msg = Message(content=rsp,role=self.profile,cause_by=todo,sent_from=self.name,send_to=self.opponent_name,)return msg
??cause_by,sent_from,send_to分別表示產生Message的動作、角色以及要發生的角色。通過這種機制可以實現比watch更靈活的訂閱機制。
3.3.3 創建團隊并添加角色
??建立一個 Team 并hire兩個角色。在這個例子中,我們將通過將我們的指令( UserRequirement)發送給Biden,通過run_project函數的send_to參數,指定Biden先發言。
async def debate(idea: str, investment: float = 3.0, n_round: int = 5):"""運行拜登-特朗普辯論,觀看他們之間的友好對話 :) """Biden = Debator(name="Biden", profile="Democrat", opponent_name="Trump")Trump = Debator(name="Trump", profile="Republican", opponent_name="Biden")team = Team()team.hire([Biden, Trump])team.invest(investment)team.run_project(idea, send_to="Biden") # 將辯論主題發送給拜登,讓他先說話await team.run(n_round=n_round)import asyncio
import platform
import typer
from metagpt.team import Team
app = typer.Typer()@app.command()
def main(idea: str = typer.Argument(..., help="Economic Policy: Discuss strategies and plans related to taxation, employment, fiscal budgeting, and economic growth."),investment: float = typer.Option(default=3.0, help="Dollar amount to invest in the AI company."),n_round: int = typer.Option(default=5, help="Number of rounds for the simulation."),
):""":param idea: Debate topic, such as "Topic: The U.S. should commit more in climate change fighting"or "Trump: Climate change is a hoax":param investment: contribute a certain dollar amount to watch the debate:param n_round: maximum rounds of the debate:return:"""if platform.system() == "Windows":asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(asyncio.WindowsSelectorEventLoopPolicy())asyncio.run(debate(idea, investment, n_round))if __name__ == '__main__':app()
以上完整代碼見debate.py,也可運行以下命令:
python3 examples/debate.py --idea "Talk about how the U.S. should respond to climate change"
運行結果如下:

四、作業
4.1 基礎作業
??基于 env 或 team 設計一個你的多智能體團隊,嘗試讓他們完成 你畫我猜文字版 。你需要要定義兩個agent,一個負責接收來自用戶提供的物體描述,并轉告另一個agent;另一個agent將猜測用戶給出的物體名稱,兩個agent將不斷交互直到另一個給出正確的答案,只要完成基礎作業就視為學習完成。
你也可以在系統之上繼續擴展,比如引入一個agent來生成詞語,而人類參與你畫我猜的過程中
4.2 進階作業:重寫babyagi
4.2.1 babyagi簡介
??衡量Agent的學習效果,關鍵在于能否將傳統人工處理的問題SOP轉換為Metaget框架下的Role和Action,并通過多智能體協作完成。如果能夠做到這一點,則說明學習目標已經實現。BabyAGI的重寫是一個合適的任務,因為它涉及到將人類決策過程和知識編碼進智能體中,這是我們想要掌握的關鍵技能。
??babyagi是其作者yoheinakajima日常任務規劃任務優先級的一套SOP,以下是babyagi的實現流程及代碼,任務為三個agent進行協同組織。

- 執行第一個任務并返回結果。
- 從存儲庫中檢索上下文并將其存儲在向量數據庫中。
- 創建新的任務并將它們添加到待辦事項列表中。
- 對任務進行重新排序并優先級調整。
import openai
import pinecone
import time
from collections import deque
from typing import Dict, List# 設置API密鑰和環境變量
OPENAI_API_KEY = ""
PINECONE_API_KEY = ""
PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT = "us-east1-gcp" #Pinecone Environment (eg. "us-east1-gcp")# 定義變量
YOUR_TABLE_NAME = "test-table"
OBJECTIVE = "Solve world hunger." # 解決世界饑餓問題
YOUR_FIRST_TASK = "Develop a task list." # 制定任務清單# 打印目標
print("\033[96m\033[1m"+"\n*****OBJECTIVE*****\n"+"\033[0m\033[0m")
print(OBJECTIVE)# 配置OpenAI和Pinecone
openai.api_key = OPENAI_API_KEY
pinecone.init(api_key=PINECONE_API_KEY, environment=PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT)# 創建Pinecone索引
table_name = YOUR_TABLE_NAME
dimension = 1536
metric = "cosine"
pod_type = "p1"# 檢查在Pinecone中是否已經存在指定的索引(表名為table_name)
if table_name not in pinecone.list_indexes():pinecone.create_index(table_name, dimension=dimension, metric=metric, pod_type=pod_type)# 連接到索引
index = pinecone.Index(table_name)# 初始化任務列表:
task_list = deque([])# 添加任務
def add_task(task: Dict):task_list.append(task)# 獲取文本嵌入
def get_ada_embedding(text):text = text.replace("\n", " ")return openai.Embedding.create(input=[text], model="text-embedding-ada-002")["data"][0]["embedding"]
pinecone.list_indexes():返回當前在Pinecone中存在的所有索引的列表。pinecone.create_index(...):創建一個新的索引,名稱為table_name,索引的維度為dimension(每個向量的長度),比較向量相似度的度量方法為“cosine”(余弦相似度),指定Pinecone的計算資源類型為“p1”。
def task_creation_agent(objective: str, result: Dict, task_description: str, task_list: List[str]):prompt = f"You are an task creation AI that uses the result of an execution agent to create new tasks with the following objective: {objective}, The last completed task has the result: {result}. This result was based on this task description: {task_description}. These are incomplete tasks: {', '.join(task_list)}. Based on the result, create new tasks to be completed by the AI system that do not overlap with incomplete tasks. Return the tasks as an array."response = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003",prompt=prompt,temperature=0.5,max_tokens=100,top_p=1,frequency_penalty=0,presence_penalty=0)new_tasks = response.choices[0].text.strip().split('\n')return [{"task_name": task_name} for task_name in new_tasks]def prioritization_agent(this_task_id:int):global task_list# 從全局任務列表task_list中提取所有任務的名稱,生成一個任務名稱列表。task_names = [t["task_name"] for t in task_list]next_task_id = int(this_task_id)+1 # 計算下一個任務的ID"""prompt用于指導OpenAI的語言模型進行任務的格式化和重新排序,提示包括:1. 當前任務列表(task_names)。2. 團隊的最終目標(OBJECTIVE)。要求最終返回一個編號列表,從next_task_id開始。"""prompt = f"""You are an task prioritization AI tasked with cleaning the formatting of and reprioritizing the following tasks: {task_names}. Consider the ultimate objective of your team:{OBJECTIVE}. Do not remove any tasks. Return the result as a numbered list, like:#. First task#. Second taskStart the task list with number {next_task_id}."""response = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003",prompt=prompt,temperature=0.5,max_tokens=1000,top_p=1,frequency_penalty=0,presence_penalty=0)# 將生成的任務列表按行分割成單獨的任務new_tasks = response.choices[0].text.strip().split('\n')task_list = deque() # 初始化一個新的任務隊列task_listfor task_string in new_tasks: # 遍歷生成的任務列表,將每個任務拆分為任務ID和任務名稱,并重新添加到任務隊列中task_parts = task_string.strip().split(".", 1)if len(task_parts) == 2:task_id = task_parts[0].strip()task_name = task_parts[1].strip()task_list.append({"task_id": task_id, "task_name": task_name})
task_creation_agent:根據執行結果生成新任務prioritization_agent:對任務列表進行格式化和重新排序,然后更新全局任務隊列。
def execution_agent(objective:str,task: str) -> str:#context = context_agent(index="quickstart", query="my_search_query", n=5)context=context_agent(index=YOUR_TABLE_NAME, query=objective, n=5)#print("\n*******RELEVANT CONTEXT******\n")#print(context)response = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003",prompt=f"You are an AI who performs one task based on the following objective: {objective}. Your task: {task}\nResponse:",temperature=0.7,max_tokens=2000,top_p=1,frequency_penalty=0,presence_penalty=0)# 提取生成的文本結果,并去除前后的空白字符return response.choices[0].text.strip()def context_agent(query: str, index: str, n: int):query_embedding = get_ada_embedding(query)index = pinecone.Index(index_name=index)results = index.query(query_embedding, top_k=n,include_metadata=True)#print("***** RESULTS *****")#print(results)sorted_results = sorted(results.matches, key=lambda x: x.score, reverse=True) return [(str(item.metadata['task'])) for item in sorted_results]
context_agent:從Pinecone索引中檢索與給定查詢最相關的上下文信息。get_ada_embedding:將查詢文本轉換為嵌入向量pinecone.Index:連接到指定的Pinecone索引index.query:在Pinecone索引中進行相似性搜索,返回與query_embedding最相關的前n個結果,include_metadata=True表示在結果中包含元數據return語句:從排序后的結果中提取每個匹配項的元數據中的任務信息,最后返回一個包含任務信息的列表。
execution_agent:根據給定的目標和任務執行具體的操作,并生成任務的結果。它首先檢索與目標相關的上下文信息,然后生成執行任務的響應。context_agent...:從指定的Pinecone索引中檢索與目標(objective)相關的前5個上下文信息。prompt包含執行任務的總體目標objective和任務描述task。
# 添加第一個任務
first_task = {"task_id": 1,"task_name": YOUR_FIRST_TASK
}add_task(first_task)
# 主循環
task_id_counter = 1
while True:if task_list:# Print the task listprint("\033[95m\033[1m"+"\n*****TASK LIST*****\n"+"\033[0m\033[0m")for t in task_list:print(str(t['task_id'])+": "+t['task_name'])# Step 1: 拉取第一個任務task = task_list.popleft()print("\033[92m\033[1m"+"\n*****NEXT TASK*****\n"+"\033[0m\033[0m")print(str(task['task_id'])+": "+task['task_name'])# 根據目標(OBJECTIVE)和任務名稱執行任務,獲取當前任務的task_id并打印結果。result = execution_agent(OBJECTIVE,task["task_name"])this_task_id = int(task["task_id"])print("\033[93m\033[1m"+"\n*****TASK RESULT*****\n"+"\033[0m\033[0m")print(result)# Step 2: 豐富結果并存儲到Pineconeenriched_result = {'data': result} result_id = f"result_{task['task_id']}"vector = enriched_result['data'] # extract the actual result from the dictionaryindex.upsert([(result_id, get_ada_embedding(vector),{"task":task['task_name'],"result":result})])# Step 3: 創建新任務并重新調整任務列表優先級new_tasks = task_creation_agent(OBJECTIVE,enriched_result, task["task_name"], [t["task_name"] for t in task_list])for new_task in new_tasks:task_id_counter += 1new_task.update({"task_id": task_id_counter})add_task(new_task)prioritization_agent(this_task_id)time.sleep(1) # Sleep before checking the task list again
-
Step 1:拉取并執行第一個任務 -
Step 2- 將任務執行的結果封裝在一個字典中(如有必要,可以在這里對結果進行豐富處理)
- 生成
result_id,并獲取結果的嵌入向量vector - 將結果及其元數據(任務名稱和結果)存儲到Pinecone索引中。
-
Step 3- 調用
task_creation_agent函數,根據目標、任務結果和當前任務名稱創建新任務。 - 為每個新任務分配一個新的任務ID,并將其添加到任務列表中。
- 調用
prioritization_agent函數,對任務列表進行重新排序。
- 調用
??babyagi的效果演示見babyagi-ui,可以先體驗一下了解一下babyagi的輸入輸出工作流,然后結合上圖,用MetaGPT進行重寫(MG已經抽象好了許多上層類,以及react的規劃模式和actions列表)。你不一定要完全依據源碼的邏輯進行重寫,嘗試找到更優秀的SOP.
4.2.2 babyagi問答
- 什么是
enrich?
??在代碼和任務管理系統中,“enrich”通常指的是對數據或結果進行補充和改進,以增加其價值和有用性。在本示例中,enrich義可以總結為:
- 提取和整理結果
將執行代理生成的結果封裝在一個字典enriched_result中,方便后續處理和存儲 - 準備和處理數據
準備好需要存儲的結果數據,如果需要,可以對結果進行進一步處理或補充,以提高數據的完整性和質量。 - 存儲到數據庫
生成結果的嵌入表示并將其與任務信息一起存儲到Pinecone索引中,以便后續檢索和使用
- 何時應該creat new task,何時應該排序任務優先級?
??每當一個任務執行完畢并獲得結果后(即在調用execution_agent函數并處理結果之后),就會調用task_creation_agent函數,根據當前任務的結果生成新任務。
??任務優先級的排序發生在創建新任務之后(prioritization_agent(this_task_id)),對任務列表進行重新排序,以確保任務按照優先級順序執行。
- 新的new task應該觀察什么作為創建的依據(當前任務列表/目標/已完成的任務結果)
在創建新的任務時,系統需要觀察和考慮以下幾個關鍵因素(在prompt中體現):
Objective:任務的總體目標。新任務應該始終與總體目標(在本例中是“解決世界饑餓”)保持一致Result:當前任務的結果。新任務的創建應基于當前任務的結果,當前任務的結果可以揭示接下來的步驟需要做什么,以及下一步的具體內容Incomplete Tasks:未完成的任務列表。創建新任務時,必須避免與當前未完成的任務重復Task Description:任務描述。當前任務的具體描述有助于決定新任務的內容和方向
- 人類是否可以介入這個流程,比如新任務的合入審核,任務執行時的拆解.
人類可以在這個SOP流程中介入,以下是一些可能的介入點:
-
新任務合入審核
在task_creation_agent函數中生成新任務列表后,可以引入人工審核環節,人工審核新生成的任務是否合理、是否重復、是否需要調整等。審核通過后再將新任務加入task_list。 -
任務執行前的拆解
在執行代理execution_agent執行任務前,可以讓人工介入,對當前待執行的任務進行審核和拆解。如果任務過于復雜,可以由人工將其拆解為多個子任務,再將這些子任務加入task_list中。 -
任務執行結果審核
在execution_agent完成任務后,可以讓人工審核執行結果的合理性和質量,并決定是否需要重新執行該任務或調整后續生成的新任務。 -
優先級調整
在prioritization_agent重新確定任務優先級后,可以讓人工介入審核和調整新的優先級排序。 -
知識庫維護
定期由人工審核和更新Pinecone索引index中存儲的知識庫數據,確保其準確性和時效性。
??要實現人工介入,可以在相應的函數中添加人工審核和調整的接口,例如在Web UI上提供審核入口等。根據具體需求,可以對流程進行定制化調整,以最大程度發揮人機協作的效能。
??以下是一個示例,review_task_result函數,它會創建一個GUI窗口,顯示任務描述和執行結果。用戶可以選擇"通過"或"拒絕"來審核結果。如果結果被拒絕,可以在reject_result函數中添加重新執行任務的邏輯(以下代碼是claude AI生成,未審核)。
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import scrolledtext# 任務執行結果審核函數
def review_task_result(result, task):# 創建審核窗口review_window = tk.Toplevel()review_window.title(f"審核任務 {task['task_id']}: {task['task_name']}")# 顯示任務描述task_label = tk.Label(review_window, text=f"任務: {task['task_name']}", font=('Arial', 12, 'bold'))task_label.pack(pady=10)# 顯示執行結果result_label = tk.Label(review_window, text="執行結果:", font=('Arial', 12, 'bold'))result_label.pack(pady=5)result_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(review_window, width=60, height=10)result_text.insert('end', result)result_text.configure(state='disabled')result_text.pack()# 審核選項def approve_result():review_window.destroy()print(f"任務 {task['task_id']} 執行結果已審核通過")def reject_result():review_window.destroy()print(f"任務 {task['task_id']} 執行結果已拒絕,需重新執行")# 在這里可以添加重新執行任務的邏輯approve_button = tk.Button(review_window, text="通過", command=approve_result)reject_button = tk.Button(review_window, text="拒絕", command=reject_result)approve_button.pack(side='left', padx=10, pady=10)reject_button.pack(side='left', padx=10, pady=10)# 在執行代理中調用審核函數
def execution_agent(objective: str, task: str) -> str:# ... (執行任務的代碼)result = "這是任務的執行結果"# 調用審核函數review_task_result(result, task)return result# 啟動GUI
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw() # 隱藏主窗口








)
)

)





)

