24. 兩兩交換鏈表中的節點
這道題的關鍵在于:
1、在置換兩個節點的時候,當前節點需要在這倆節點之前一個節點。并且要提前保存cur.next以及cur.next.next。
2、每次置換完一組節點,cur = cur.next.next
3、判斷結束的標志:奇數個節點:cur.next.next != null 偶數個節點:cur.next != null 為了保證cur.next.next不會產生空指針,需要先判斷next != null
4、最終返回的是虛擬節點的下一個節點,因為最初的head節點已經不在鏈表最前面了
具體步驟如下:
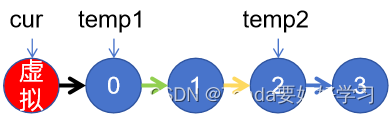
dummyNode.next = head;//對于0、1節點,需要創建一個虛擬節點.
ListNode temp1 = cur.next;
ListNode temp2 = cur.next.next.next;//并保存temp1和temp2.
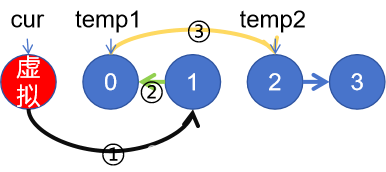
①②③步驟按序進行
①cur.next = cur.next.next;
②cur.next.next = temp1;
③ temp1.next = temp2;

cur = cur.next.next;
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();dummyNode.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyNode;while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){ListNode temp1 = cur.next;ListNode temp2 = cur.next.next.next;cur.next = cur.next.next;cur.next.next = temp1;temp1.next = temp2;cur = cur.next.next;}return dummyNode.next;}
}
19.刪除鏈表的倒數第N個節點
法一:遍歷鏈表得出鏈表長度length,用length - n定位要刪除的節點,缺點是需要第二次遍歷鏈表
代碼:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {int length = 0;ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();dummyNode.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyNode;while(cur.next != null){length++;cur = cur.next;}ListNode cur2 = dummyNode;for(int i = 0;i < length - n;i++){cur2 = cur2.next;}cur2.next = cur2.next.next;return dummyNode.next;}
}
法二:讓快指針先走n步,然后快慢指針同時走。
這個思想很巧妙也很好理解,關鍵是臨界值的設定很容易出錯,可以用只有一個節點的鏈表刪除倒數第一個節點的特殊情況去寫臨界值。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();dummyNode.next = head;ListNode fast = dummyNode;ListNode slow = dummyNode;for(int i = 0;i < n-1;i++){fast = fast.next;}//假設只有一個節點的鏈表要刪除倒數第一個節點,n=1,此時快慢節點不需要中間有差值,slow和fast都指向dummyNodewhile(fast.next.next != null){fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}//因為fast.next.next == null,fast和slow都不需要往下移動slow.next = slow.next.next;//刪除第一個節點return dummyNode.next;}
}
或者這樣也可以:
這倆區別在于如果在
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}中i移動的條件為這個,fast為向下移動一位。那么響應的下面
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}中while的判定條件由fast.next.next!= null變為fast.next != null
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode();dummyNode.next = head;ListNode fast = dummyNode;ListNode slow = dummyNode;for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){fast = fast.next;}while(fast.next != null){fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}slow.next = slow.next.next;return dummyNode.next;}
}
142.環形鏈表II
這道題老是犯一個錯誤,就是控制fast和slow相遇的循環條件寫成fast != slow,slow和fast就移動,但是要注意一點,slow和fast在初始的時候就應該分別向下移動一位和兩位,以防止while進入死循環。
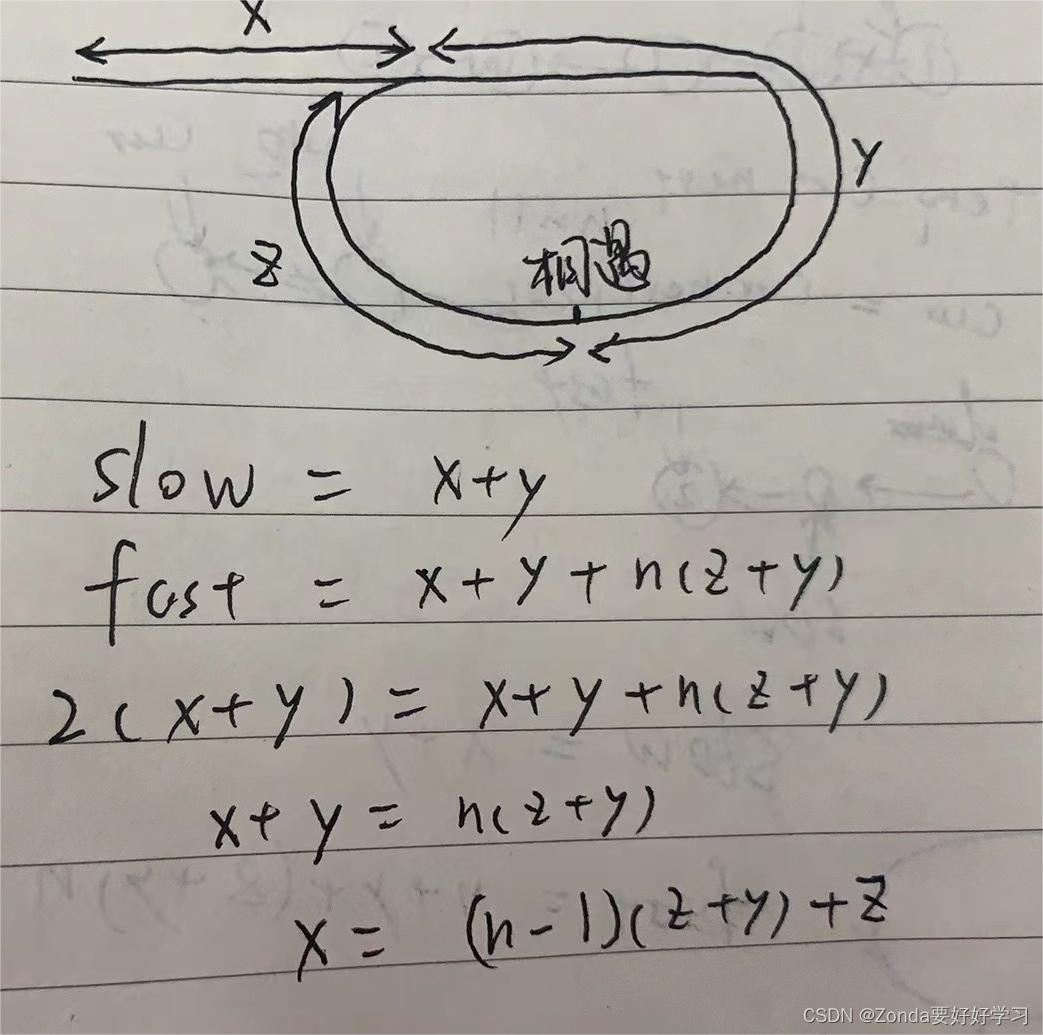
定義slow和fast兩個快慢指針,slow每次移動一位,fast每次移動兩位,直到相遇。slow和fast走過的路程分別為
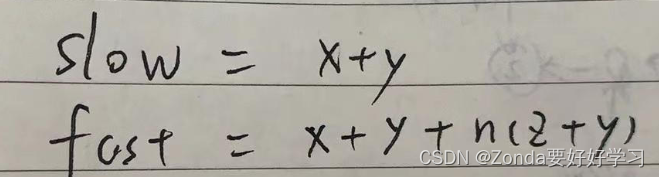
fast是slow的兩倍,可以得到等式,最終得到x和z、y的關系式
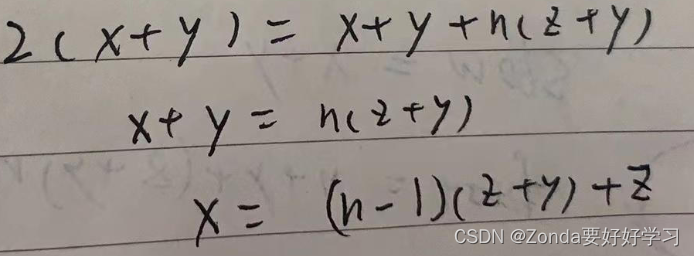
這個時候slow和fast在同一位置,再定義一個res節點指針指向head,res和slow指針同時一位一位向下移動,當兩個指針相遇的時候,這個節點就是環形的入口。
代碼如下:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null) return null;if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) return null;ListNode fast = head.next.next;ListNode slow = head.next;while(fast != slow){if(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){fast = fast.next.next;}else{return null;}slow = slow.next;}ListNode res = head;while(slow != res){slow = slow.next;res = res.next;}return res;}
}
這里尋找fast和slow相遇節點的while循環可以優化一下:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null) return null;if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) return null;ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(true){if(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) fast = fast.next.next;else return null;slow = slow.next;if(slow == fast) break;}ListNode res = head;while(slow != res){slow = slow.next;res = res.next;}return res;}
}
面試題 02.07. 鏈表相交
思路:
先計算出兩條鏈表的長度,再將短的那一條鏈表的指針先移動鏈表長度差值個,然后再一起向下遍歷直到相遇,如果沒有相遇,最終都會到達null,返回停下之后的那個節點即可。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode curA = headA;ListNode curB = headB;int lengthA = 0;int lengthB = 0;while(curA != null){curA = curA.next;lengthA++;}while(curB != null){curB = curB.next;lengthB++;}if(lengthA > lengthB){for(int i = 0;i < lengthA-lengthB;i++){headA = headA.next;} }else{for(int i = 0;i < lengthB-lengthA;i++){headB = headB.next;} }while(headA != null && headA != headB){headA = headA.next;headB = headB.next;}return headA;}
}







![P3128 [USACO15DEC] Max Flow P題解(樹上差分,最近公共祖先,圖論)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/P3128 [USACO15DEC] Max Flow P題解(樹上差分,最近公共祖先,圖論))



)
)
)

)
)

)
