
目錄
- 多線程相關
- CountDownLatch
- 賽跑的案例
- countDownLatch.await(300, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- Java其他進階
- Map的put方法
- 只放一個元素的集合
多線程相關
CountDownLatch
案例:主線程的執行需要等待子線程執行完,等各個線程執行完畢后,主線程做收尾的工作
- 初始化一個:final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
- 線程池中的子線程調用 countDown方法進行減1;
- 主線程啟動后,等待子線程不斷減1,直到為0后,主線程繼續往下執行;
package com.tianju.myTest;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class CountdownLatchTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {System. out.println("子線程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "開始執行");Thread. sleep((long) (Math. random() * 10000));System. out.println("子線程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "執行完成");latch.countDown(); // 當前線程調用此方法,則計數減一} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}};service.execute(runnable);}try {System. out.println("主線程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待子線程執行完成..." );latch.await(); // 阻塞當前線程,直到計時器的值為0System. out.println("主線程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "開始執行...");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {service.shutdown();}}
}
賽跑的案例
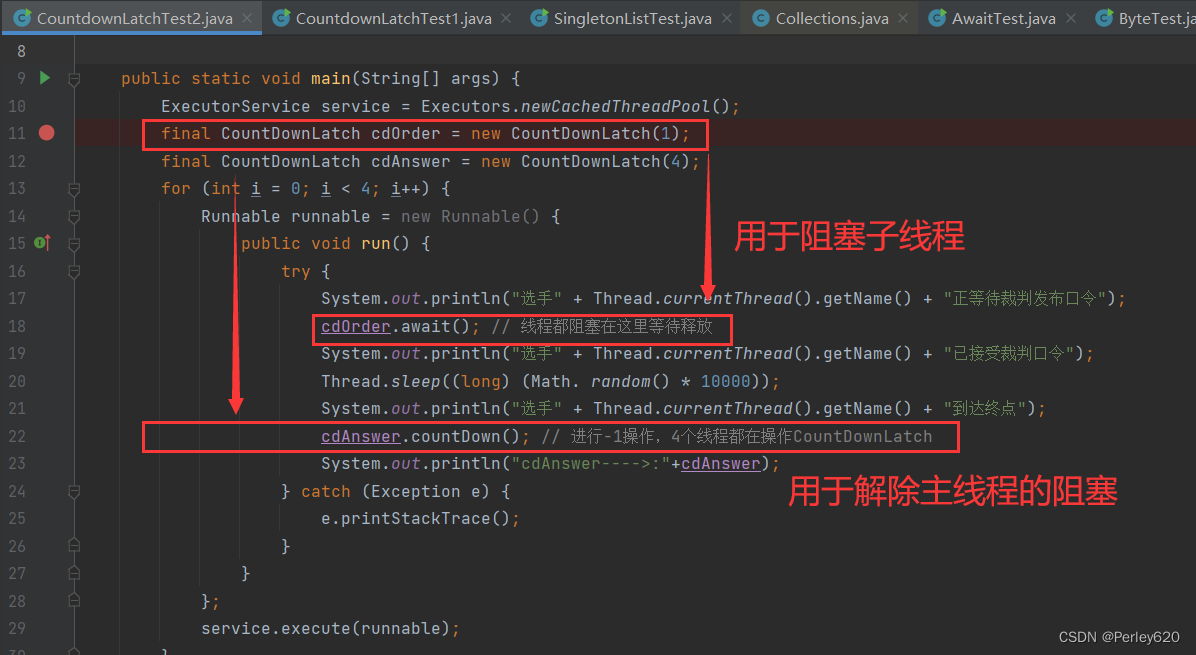
案例2:4名選手參加賽跑,選手需要等待裁判發送指令;裁判發送完指令后,需要等所有選手到達終點;所有選手到達終點后,裁判匯總成績。
- 主線程:裁判發指令,裁判等選手到達終點,到達終點后,匯總成績;
- 子線程:每個選手需要阻塞在裁判發指令之前,主線程發指令后,子線程繼續運行;此時主線程阻塞,所有子線程結束后,主線程繼續運行
實現的思路
- 定義兩個CountDownLatch,一個為1,一個為4;
- CountDownLatch(1),用來控制等待裁判指令,主線程先休眠,讓出資源,讓子線程獲得cpu資源,子線程通過await 阻塞;
- 主線程休眠結束后,對1進行-1,然后await 4 阻塞,觸發子線程,子線程繼續運行;
- 子線程在運行過程中對于4 進行-1,等到值為0時,觸發主線程的await 4 阻塞;
- 主線程繼續運行,裁判進行成績的匯總
package com.tianju.myTest;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
// https://www.cnblogs.com/tstd/p/4987935.html
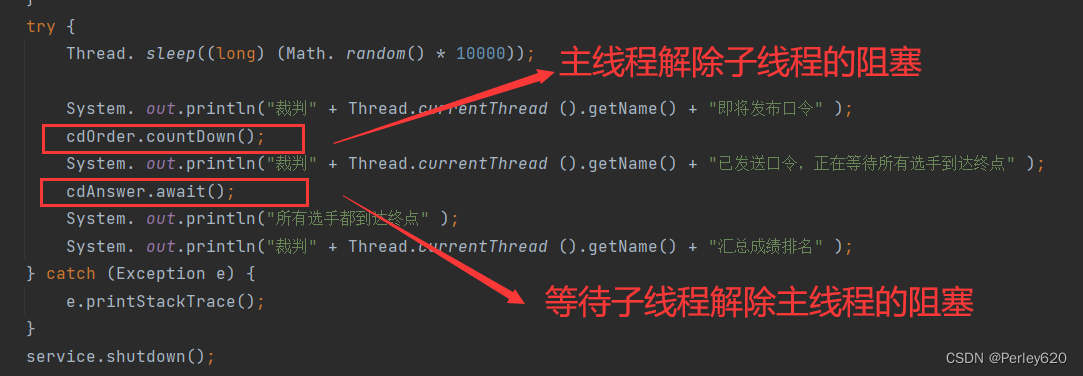
public class CountdownLatchTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();final CountDownLatch cdOrder = new CountDownLatch(1);final CountDownLatch cdAnswer = new CountDownLatch(4);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {public void run() {try {System.out.println("選手" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正等待裁判發布口令");cdOrder.await(); // 線程都阻塞在這里等待釋放System.out.println("選手" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已接受裁判口令");Thread.sleep((long) (Math. random() * 10000));System.out.println("選手" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到達終點");cdAnswer.countDown(); // 進行-1操作,4個線程都在操作CountDownLatchSystem.out.println("cdAnswer---->:"+cdAnswer);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}};service.execute(runnable);}try {Thread. sleep((long) (Math. random() * 10000));System. out.println("裁判" + Thread.currentThread ().getName() + "即將發布口令" );cdOrder.countDown();System. out.println("裁判" + Thread.currentThread ().getName() + "已發送口令,正在等待所有選手到達終點" );cdAnswer.await();System. out.println("所有選手都到達終點" );System. out.println("裁判" + Thread.currentThread ().getName() + "匯總成績排名" );} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}service.shutdown();}
}
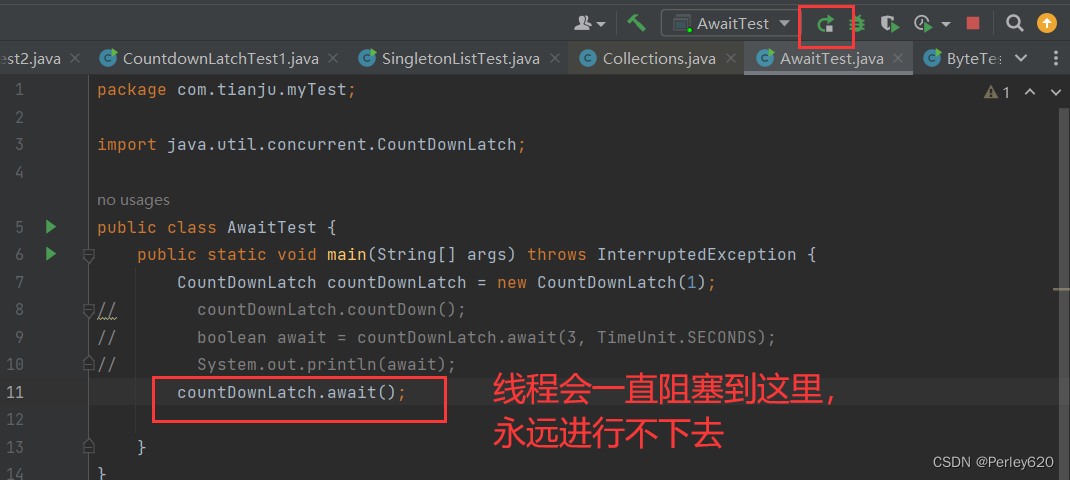
countDownLatch.await(300, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
await方法的對比
- 沒有設置時間,會一直阻塞,直到countdown為0;
- 設置了時間,在超過這個時間后,解除阻塞,返回false;
線程一直阻塞的情況
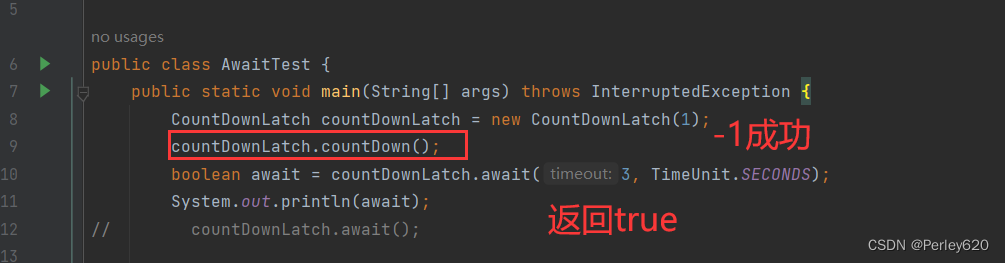
到達時間后,就解除阻塞,并返回false

-1成功,返回true
Java其他進階
Map的put方法
- Map 的 put 方法其實是有返回值的

package com.tianju.myTest;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;/*** hashMap 的 put 方法其實是有返回值的*/
public class ConHashMap {public static void main(String[] args) {ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Object> concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();// 如果有了鍵為 pet,還能往里面放concurrentHashMap.put("pet", 567);Object put = concurrentHashMap.put("pet", "task");System.out.println(put);if (put!=null){System.out.println("======== current key used! ========");}System.out.println(concurrentHashMap);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put("pet", 123);Object pet = hashMap.put("pet", 561);System.out.println(pet);System.out.println(hashMap);}
}
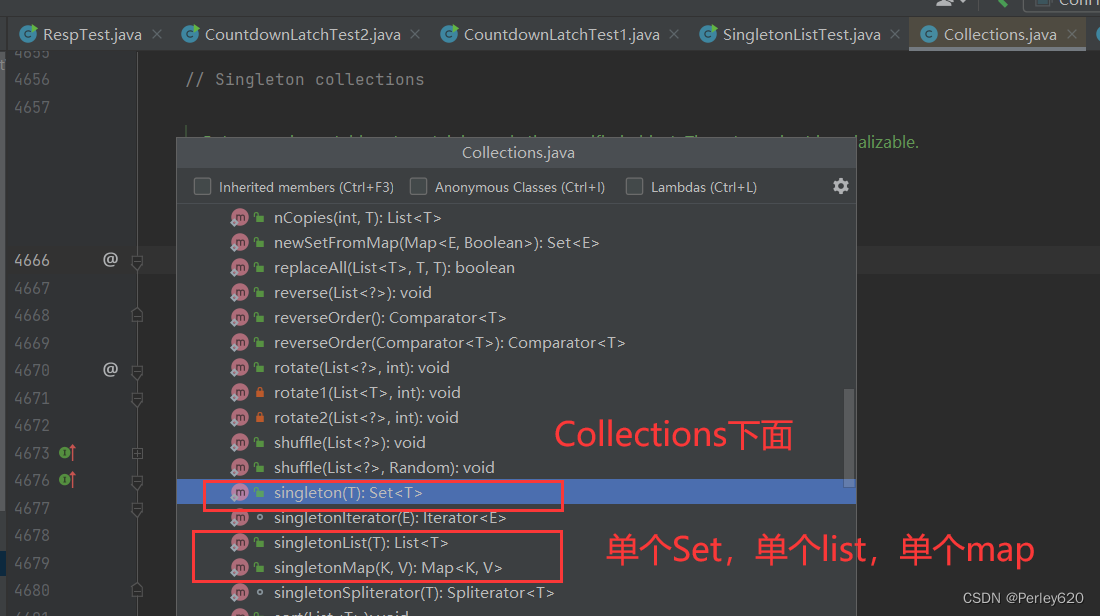
只放一個元素的集合
- 基于內存或者業務的考慮,有時候集合只放一個元素,可以用collections下面的singleton集合
package com.tianju.myTest;import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;/*** 只能存放一個元素的 List,不會造成內存空間的浪費*/
public class SingletonListTest {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello, singleton";List<String> list = Collections.singletonList(s);list.add("second element");}
}
)
: Region Of Interest(有興趣區域/找重點))









)


——獲取和為k的子數組)




】)