?
lcr147.最小棧
通過兩個棧 維護實現
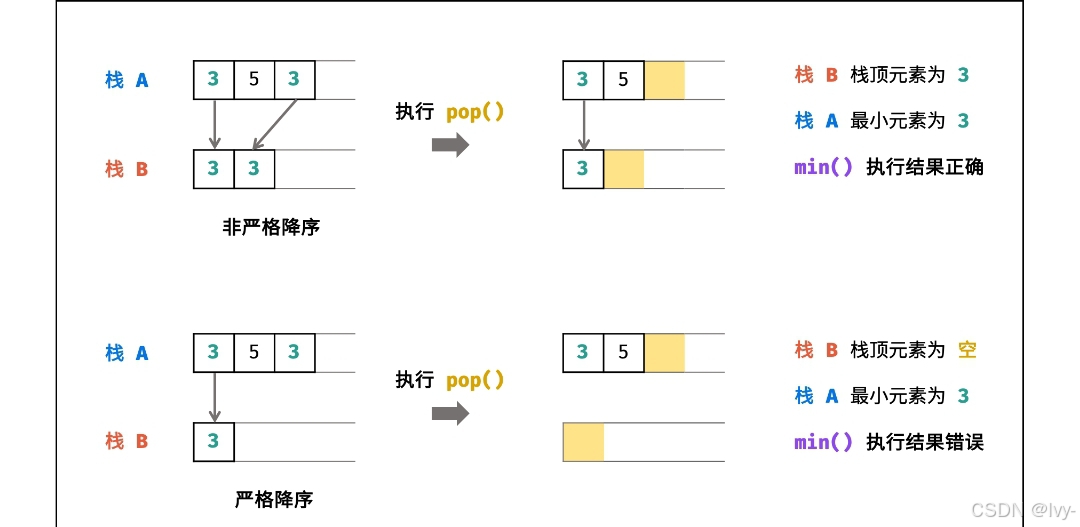
?class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> A, B;
MinStack() {}
void push(int x) {
A.push(x);
if(B.empty() || B.top() >= x)
B.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(A.top() == B.top())
B.pop();
A.pop();
}
int top() {
return A.top();
}
int getMin() {
return B.top();
}
};
?
lcr180
特判,放在循環執行的前面
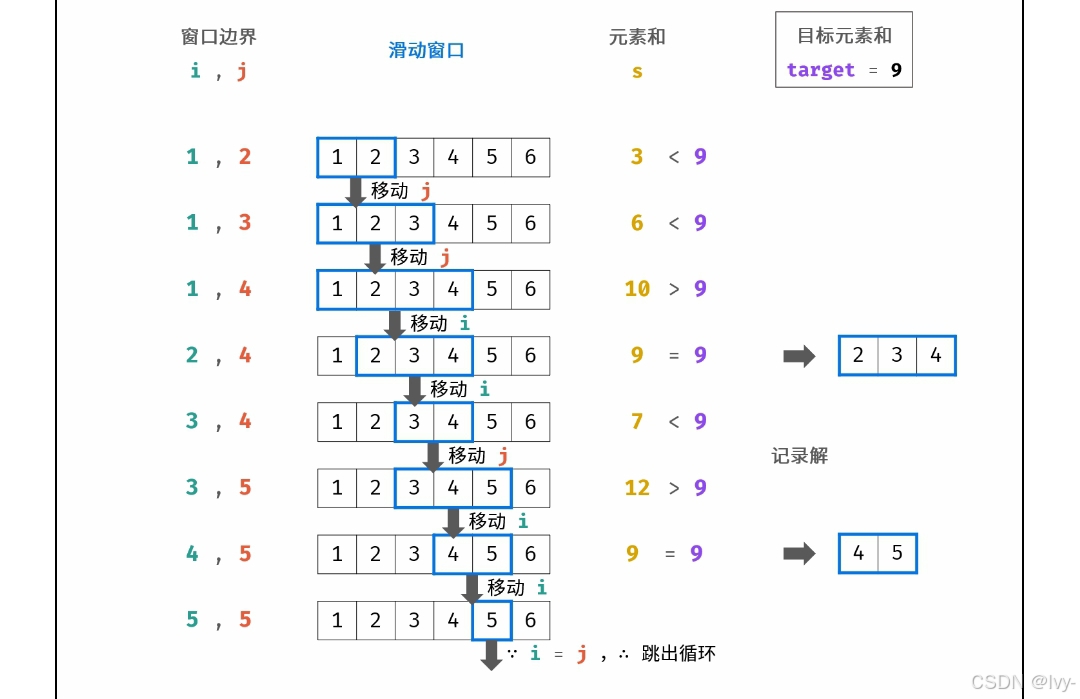
?
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fileCombination(int target) {
int i = 1, j = 2, s = 3;
vector<vector<int>> res;
while(i < j) {
if(s == target) {
vector<int> ans;
for(int k = i; k <= j; k++)
ans.push_back(k);
res.push_back(ans);
}
if(s >= target) {
s -= i;
i++;
} else {
j++;
s += j;
}
}
return res;
}
};
?
lc973
數據結構vector<pair<double,pair<int,int>>>cnt
sort后取出k個
ans.push_back(vector<int>{cnt[i].second.first, cnt[i].second.second});
class Solution {
public:
double dist(vector<int>&a){
return sqrt(a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1]);
}
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k)
{
vector<pair<double, pair<int,int>>>cnt;
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++){
double d = dist(points[i]);
cnt.push_back({d, {points[i][0], points[i][1]}});
}
//按照坐標點進行升序排序
sort(cnt.begin(), cnt.end(), [](pair<double,pair<int,int>>&a,pair<double,pair<int,int>>&b)
? ? ? {
return a.first < b.first;
});
//記錄答案
vector<vector<int>>ans;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
? ? ? {
ans.push_back(vector<int>{cnt[i].second.first, cnt[i].second.second});
}
return ans;
}
};
?
?
?
換根dp?
最開始想到的是bfs的暴力遍歷,也能歸納出數學關系優化
題解是由 父子關系-> 加減關系-dp tree
正解
詳見oi-wiki dp tree
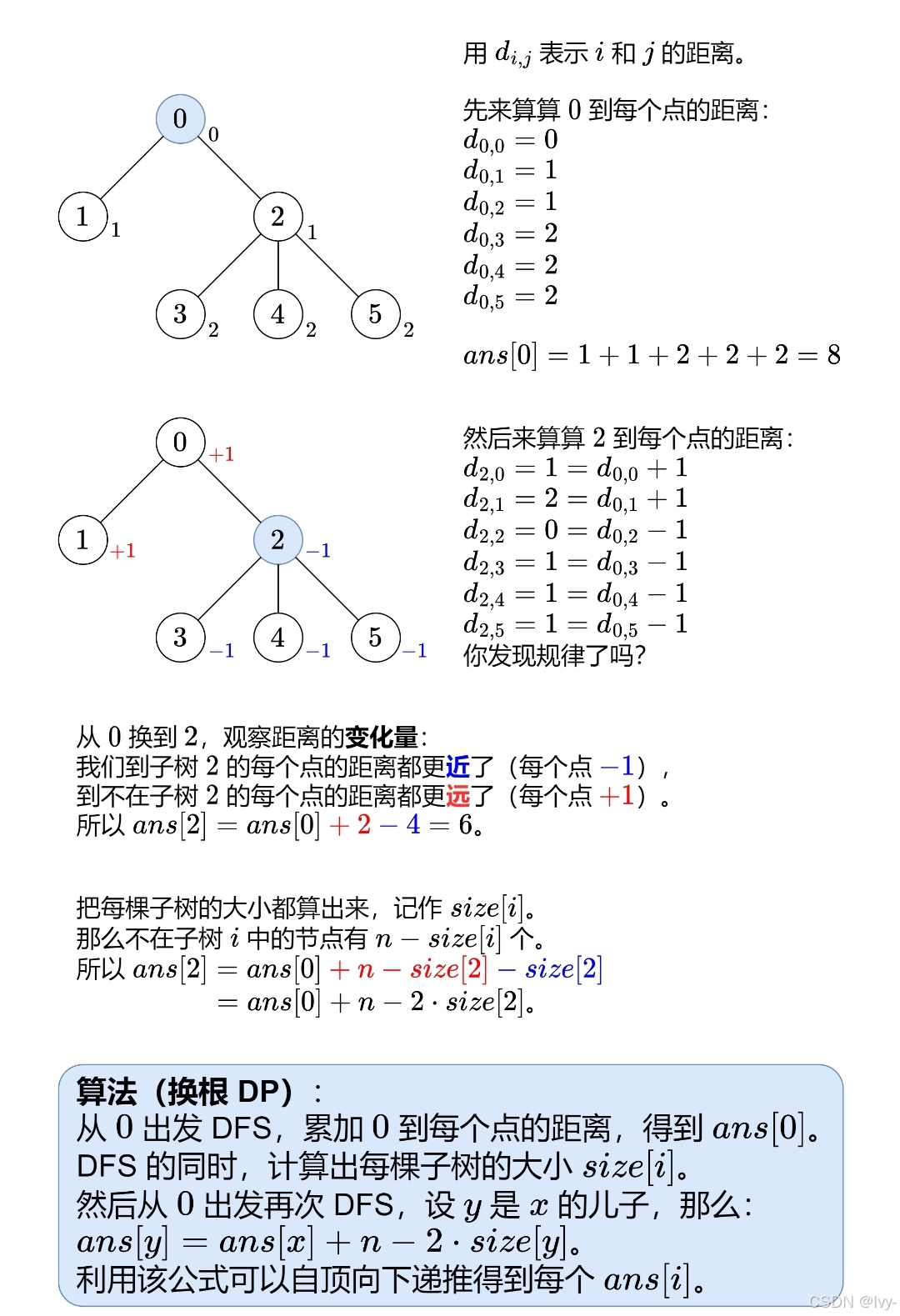
?
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n); // g[x] 表示 x 的所有鄰居
for (auto& e: edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x);
}
? ? ? ? vector<int> ans(n);
vector<int> size(n, 1); // 注意這里初始化成 1 了,下面只需要累加兒子的子樹大小
auto dfs = [&](auto&& dfs, int x, int fa, int depth) -> void {
ans[0] += depth; // depth 為 0 到 x 的距離
for (int y: g[x]) { // 遍歷 x 的鄰居 y
if (y != fa) { // 避免訪問父節點
dfs(dfs, y, x, depth + 1); // x 是 y 的父節點
size[x] += size[y]; // 累加 x 的兒子 y 的子樹大小
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 0, -1, 0); // 0 沒有父節點
? ? ? ? auto reroot = [&](auto&& reroot, int x, int fa) -> void {
for (int y: g[x]) { // 遍歷 x 的鄰居 y
if (y != fa) { // 避免訪問父節點
ans[y] = ans[x] + n - 2 * size[y];
reroot(reroot, y, x); // x 是 y 的父節點
}
}
};
reroot(reroot, 0, -1); // 0 沒有父節點
return ans;
}
};
?
?
數學歸納法
?
 ?
?
?
lc2944.選不選
遍歷i,
for j? 處理其影響范圍,每步取最小的cache
o n^2,但是可以正向遍歷,挺好想的

?class Solution {
public:
int minimumCoins(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<int> dp(n + 1, 0x3f3f3f3f);?
dp[0] = 0; ?
? ? ? ? for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)?
{?
int end = min(2 * i, n);?
//處理其影響范圍,每步取最小的cache
for (int j = i; j <= end; ++j)
{?
dp[j] = min(dp[j],dp[i - 1] + prices[i - 1]);?
}
}
? ? ? ? return dp[n];
}
};
?
?

與共識客戶端(CL))

處理鳶尾花(iris)數據集)


)



)





)
)


