1. 兩數之和

自己做?
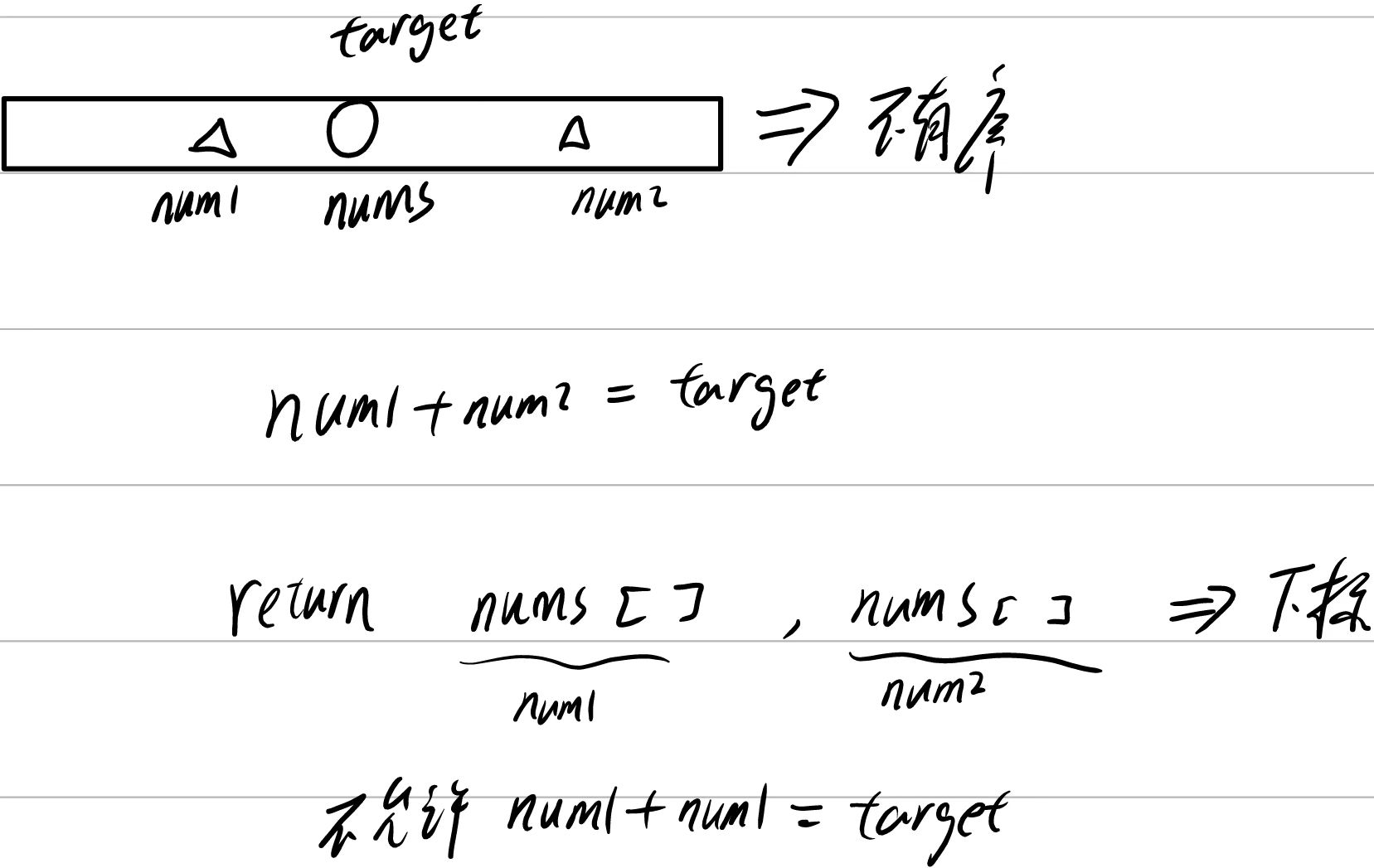
分析
解法1:暴力解
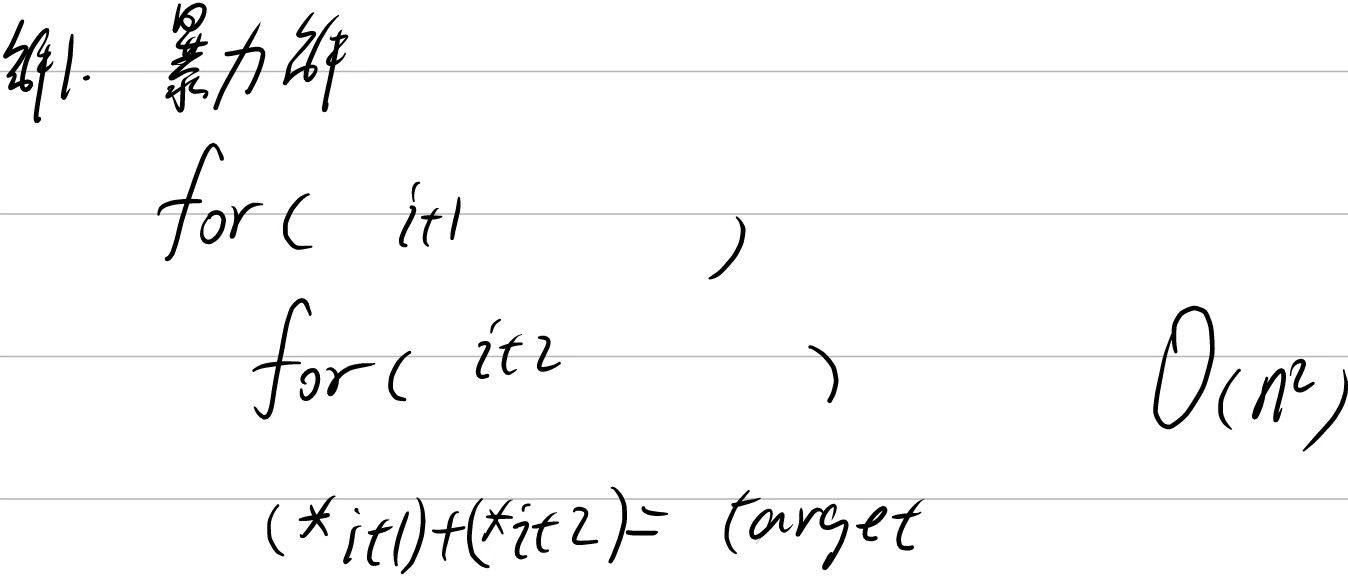
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int num1 = 0; //下標int num2 = 0;vector<int> s; //保存結果for(vector<int>::iterator it1 = nums.begin(); it1 != nums.end()-1; it1++){num2 = num1+1;for(vector<int>::iterator it2 = it1+1; it2 != nums.end(); it2++){if(*it1+*it2 == target){s.push_back(num1);s.push_back(num2);return s;}num2++;}num1++;}return {0,0}; }
};?錯誤想法
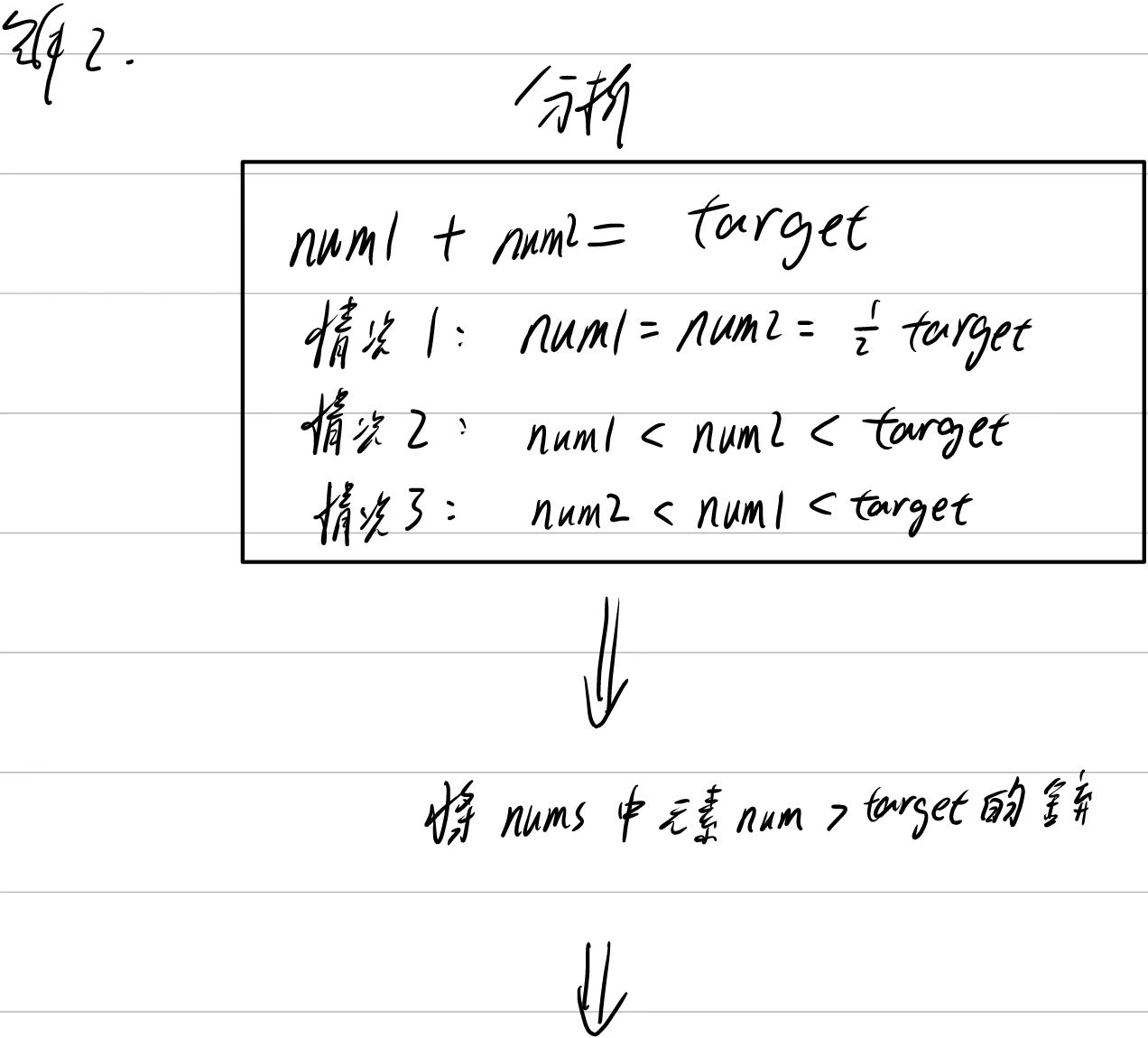
將大于target的部分舍棄縮小數組【沒有考慮到有負數的情況】
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {vector<int> new_nums = nums;for(vector<int>::iterator it = new_nums.begin(); it != new_nums.end(); ) { //刪除比target大的元素if(*it > target){it = new_nums.erase(it); //刪除,erase會返回下一個迭代器位置}elseit++;}vector<int> s1; //保存結果【兩個數】for(vector<int>::iterator it1 = new_nums.begin(); it1 != new_nums.end()-1; it1++){for(vector<int>::iterator it2 = it1+1; it2 != new_nums.end(); it2++){if(*it1+*it2 == target){s1.push_back(*it1);s1.push_back(*it2);}}}vector<int> s2; //保存結果【尋找下標】int num = 0;for(vector<int>::iterator it = nums.begin(); it != nums.end(); it++,num++){if(*it == s1[0] || *it == s1[1])s2.push_back(num);}return s2; }
};看題解【想不到】

分析
自己寫?
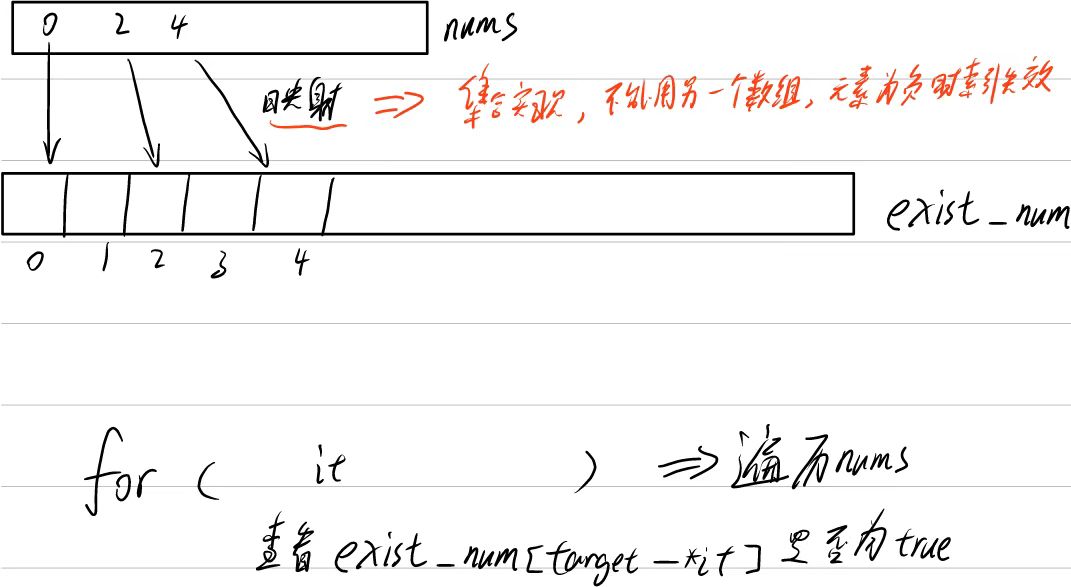
【注,最好直接用臨時變量儲存find得到的迭代器,不然反復調用find也很浪費時間】
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {map<int,int> exist_num;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ //映射到哈希表中<key,index>exist_num[nums[i]] = i;}for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ //查找target-nums[i]是否存在map<int,int>::iterator index = exist_num.find(target-nums[i]);if(index != exist_num.end() && i != index->second) //存在并且不是同一元素(下標不一致)return {index->second,i};}return {};}
};
2. 兩數相加
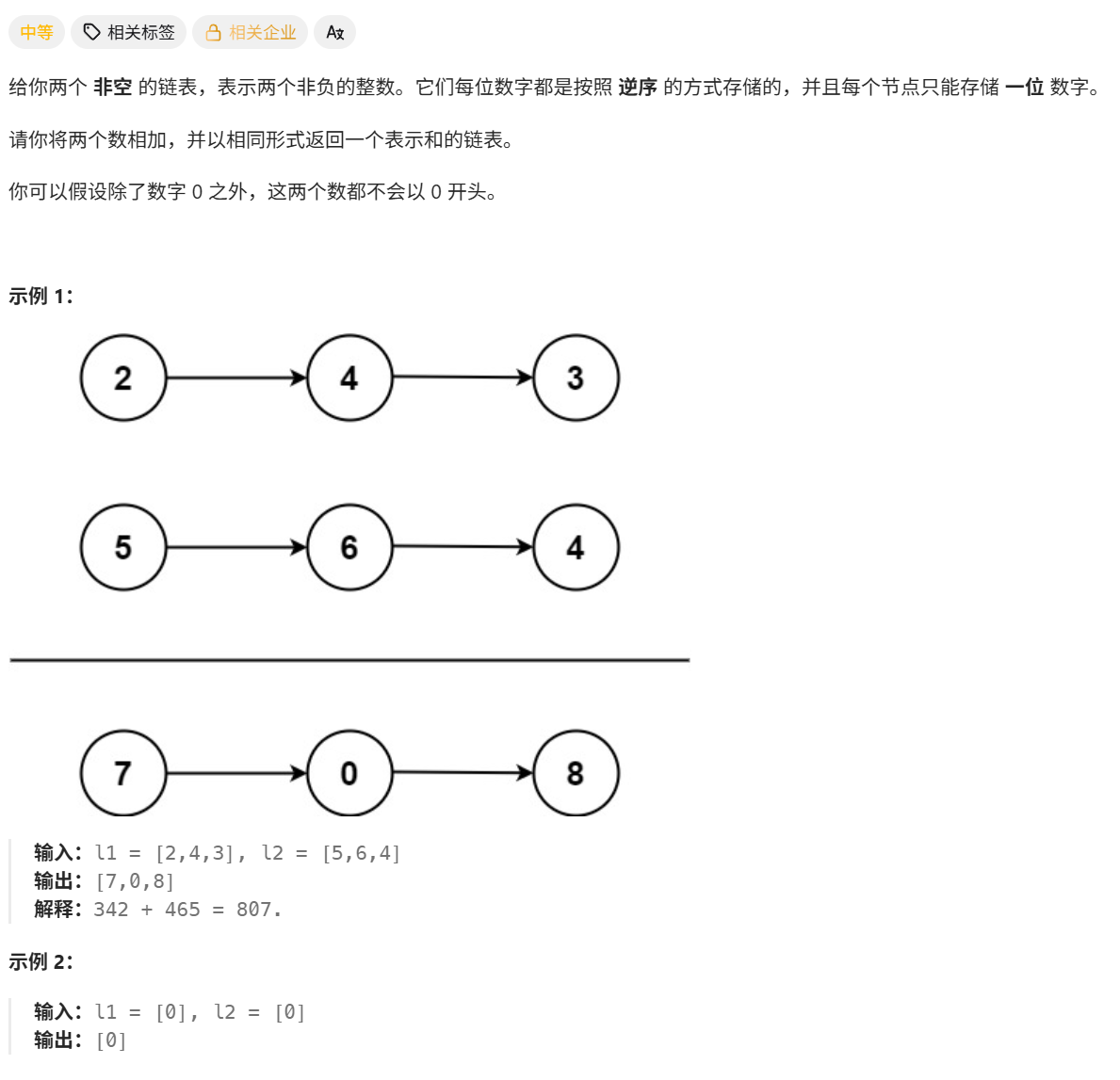
自己做
分析

解
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode *p1 = l1,*p2 = l2; //遍歷結點ListNode *p3 = new ListNode((p1->val + p2->val) % 10); //個位相加 int add =(p1->val + p2->val) / 10; //進位p1 = p1->next;p2 = p2->next;ListNode *pr = p3; //尾插用的指針while(p1 != nullptr || p2 != nullptr){ListNode *p = nullptr;if(p1 != nullptr && p2 != nullptr){ //二者都不為空的情況p = new ListNode((p1->val + p2->val + add) % 10); //創建新節點保存結果:保存余位 add = (p1->val + p2->val + add) / 10; //保存進位p1 = p1->next;p2 = p2->next;}else if(p1 != nullptr){ //p1不為空、p2為空 p = new ListNode((p1->val + add) % 10); //創建新節點保存結果:保存余位 add = (p1->val + add) / 10; //保存進位p1 = p1->next;}else if(p2 != nullptr){ //p2不為空、p1為空 p = new ListNode((p2->val + add) % 10); //創建新節點保存結果:保存余位 add = (p2->val + add) / 10; //保存進位p2 = p2->next;}pr->next = p; //尾插pr = pr->next;}if(add != 0){ //p1為空、p2為空外還有進位ListNode *p = new ListNode(add);pr->next = p; //尾插pr = pr->next;}return p3;}
};
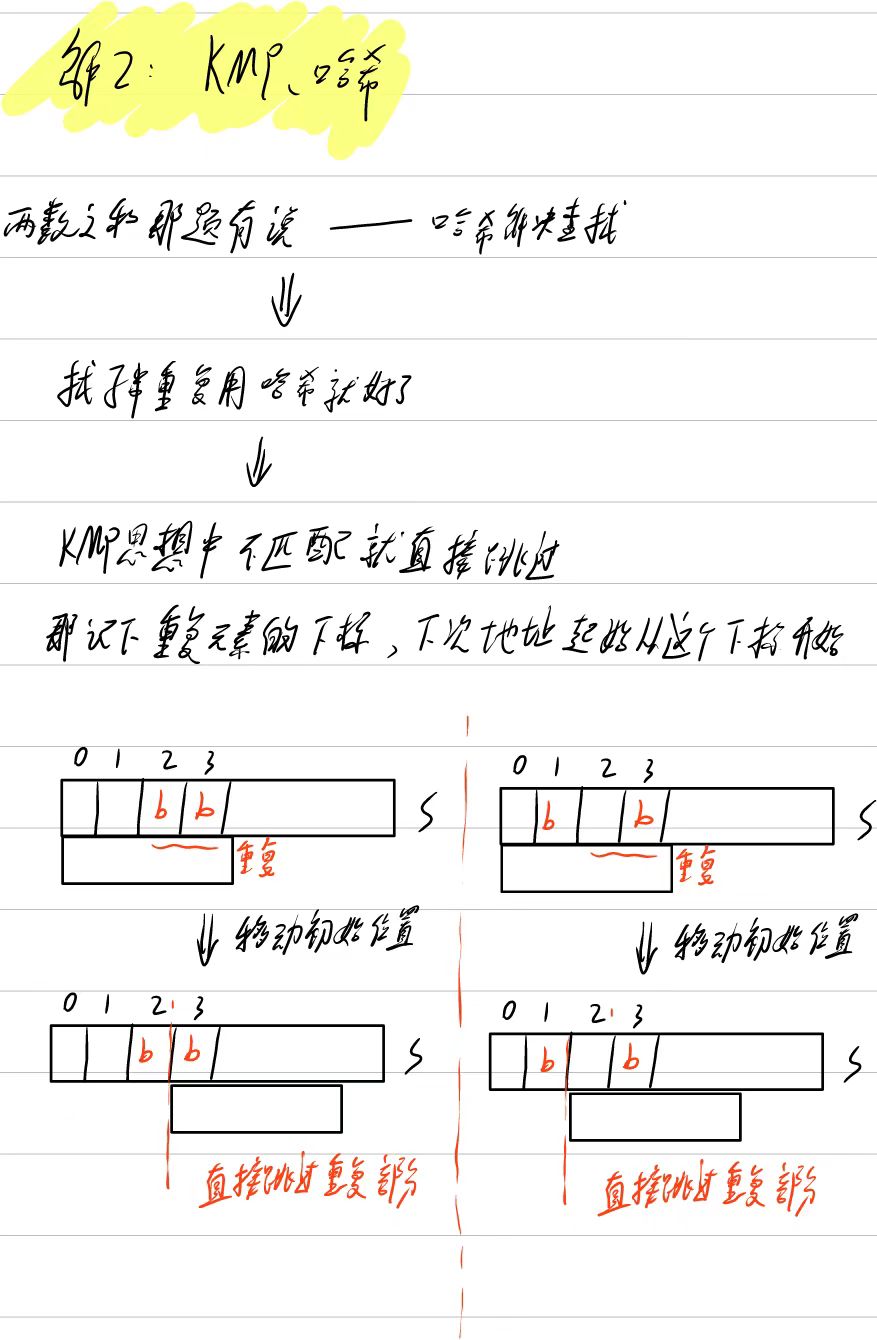
3. 無重復字符的最長子串

自己做
分析
遺漏點:string也是容器,也可以使用size、begin、end這些(之前的筆記沒補上)

解法1:暴力解
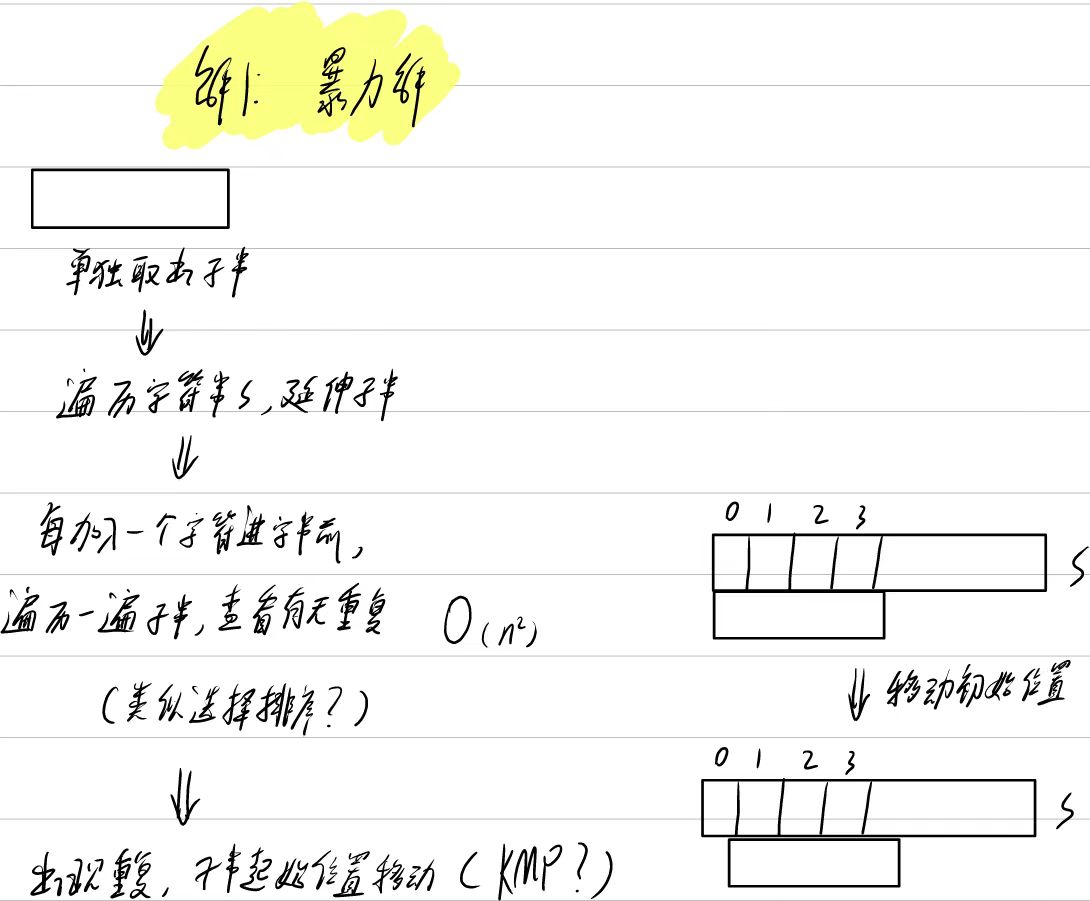
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {int max = 0; //記錄最大值string c; //子串for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {c = s[i]; //子串起始位置從i開始bool exist_double = false; //判斷是否重復 for (int j = i + 1; j < s.size() && exist_double == false; j++) { //子串擴展for (int z = 0; z < c.size(); z++) {if (s[i + c.size()] == c[z]) //子串的下一個字符s[i+c.size()]與子串存在重復exist_double = true; //存在重復,調整起始位置}//不存在重復if (!exist_double)c += (s[i + c.size()]); //拼接子串}//判斷該輪取得的子串大小if (c.size() > max)max = c.size();}return max; //返回子串大小}
};解法2:滑動窗口
這里我自己寫的還不如暴力解
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {int max = 0; //記錄最大值string c; //子串map<char, int> m; //哈希記錄子串<word,index>,其中index為字符串s的下標int index = 0; //子串c的起始下標while (index + c.size() < s.size()) {c = s[index]; //子串起始位置從index開始 m[s[index]]=index; //插入哈希表for (int j = index + 1; j < s.size(); j++) { //子串擴展map<char, int>::iterator it = m.find(s[j]); //哈希查找if (it != m.end()) { //子串的下一個字符s[i+c.size()]與子串存在重復【在哈希表中找到元素】index = it->second+1; //更改索引,跳出重復值m.clear(); //清空哈希表break; //本次查找失敗,直接進入下一輪【跳出for循環】}else { //不存在重復c += s[j]; //拼接子串m[s[j]] = index; //插入哈希表}}//判斷該輪取得的子串大小if (c.size() > max)max = c.size();}return max; //返回子串大小}
};效率低原因:
嵌套循環結構和頻繁的哈希表清空操作
看題解【敲不出】

知識點unordered_set:
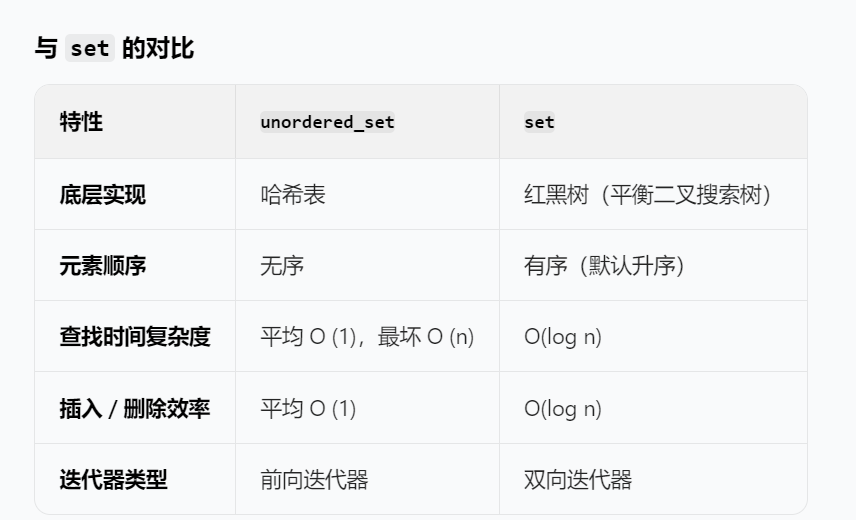
仿寫官方思路?
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {unordered_set<char> c;int rear = -1;int max = 0;for(int front = 0; front < s.size(); front++){if(front != 0){ //左指針移動c.erase(s[front - 1]); //刪除移出哈希表的數據}while(rear + 1 < s.size() && !c.count(s[rear+1])){//右指針移動c.insert(s[rear+1]); //插入哈希表rear++;}if(rear - front + 1 > max)max = rear - front + 1;}return max;}
};
優化自己的實現
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {int max = 0;unordered_map<char, int> m;int front = 0, rear = 0; //首位指針cout << s.size() << endl;//往哈希表中設置第一個元素if (s.size() != 0) { //預防空字符串m[s[rear]] = rear;max++; //已經添加一個字符進去了,即最大值最小也是1while (rear < s.size() - 1) {unordered_map<char, int>::iterator it = m.find(s[rear + 1]); //查看下一個元素是否已經在哈希表中if (it != m.end()) { //在哈希表中找到元素【有重復】int old = front; //記錄舊位置front = it->second + 1; //偏移起始位置//移除窗口以外的值【front偏移了,前面的值都要刪除】for (int i = old; i < front; i++) {m.erase(s[i]);}}//無重復,或重復問題被front偏移解決m[s[rear + 1]] = rear + 1; //修改哈希表【重新修改值】rear++;if (rear - front + 1 > max)max = rear - front + 1;}}return max;}
};
【注:這過程中發現了之前都沒有注意到的——size()返回的是無符號整數,而int是有符合整數,所以當我設置while循環的時候,往往出現size()返回的是0,結果設置的size()-1就變的極大,同理,設置rear從-1開始,結果rear轉為無符號整數后就廢了】
今天結束總結
之前做的博客筆記幫大忙了,剛學完的很多都有些忘了,還好之前做好了筆記可以來回翻
第十四章 STL(string容器、vector容器、deque容器)-CSDN博客
第十五章 STL(stack、queue、list、set、map容器使用)-CSDN博客









)



)





