目錄
一、紅黑樹的迭代器
1.1紅黑樹迭代器框架
1.2operator*() && operator->()
1.3operator++()
1.4operator--()
1.5operator==()? && operator!=()?
1.6begin() && end()
二、如何用紅黑樹搭配map和set(仿函數)
?三、紅黑樹封裝map和set(簡易版)
3.1紅黑樹的構造(RBTree.h)?
3.2map的模擬實現(MyMap.h)
3.3set的模擬實現(MySet.h)
3.4測試(test.cpp)
?一、紅黑樹的迭代器
前一篇章,有了紅黑樹的了解,但那只實現了紅黑樹的插入部分,那么現在要用紅黑樹封裝set、map容器,那有一個功能,就必須得實現,即迭代器,對于紅黑樹的迭代器該如何實現呢?參考前面篇章,list容器的迭代器的實現,同樣的,紅黑樹將迭代器要實現的功能封裝成了一個類,那么接下來進行一步步實現。
1.1紅黑樹迭代器框架
由于迭代器的遍歷,實際就是遍歷節點,在實現具體步驟之前,先帶上節點,再把迭代器的框架搭好。?
enum Color//對于紅黑節點,用枚舉結構來表示{RED,BLACK};template<class T>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode(const T& data, Color color = RED):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_data(data),_color(color){}RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Color _color;//默認給紅色才符合規則,若默認給黑色的話,則插入的每個節點都是黑色節點,//那么就不能保證每條路徑的黑色節點相同,違反了第4條性質。而給紅色,就可以根據規則調整。};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct RBTreeIterator{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef Node* PNode;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;PNode _node;RBTreeIterator(const PNode node):_node(node){}//.....};1.2operator*() && operator->()
T& operator*(){return _node->_data;//訪問節點數據}T* operator->(){return &(operator*());//operator*() == _node->_data}1.3operator++()
?對紅黑樹的遍歷是一個中序遍歷,遍歷完后,得到的是一個有序序列。每++一次,跳到的位置是中序序列中的下一個位置。我們知道中序的訪問順序是,左根右,那么如何在樹上進行操作而達到中序遍歷呢?
大致可以分為兩步:
1.當左子樹與根訪問完,要符合中序,得去右子樹進行訪問,同理右子樹得滿足中序遍歷,首先就得找到右子樹的最小節點,即最左節點。
抽象示意圖:
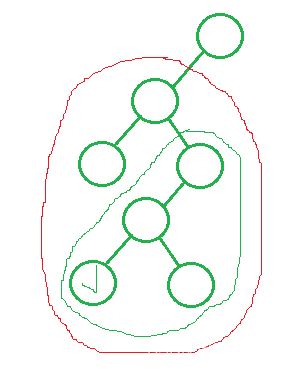
2.當左子樹未訪問完,++時,就指向父節點,
抽象示意圖:

或者當右子樹訪問完了,則說明一顆節點的整個左子樹訪問完了。那么++就是要找到這個節點
抽象示意圖:?
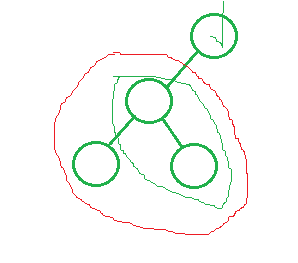
Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right)//左子樹訪問完,去訪問右子樹{_node = _node->_right;while (_node && _node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else//左子樹未訪問完,或者右子樹訪問完{PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur != parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}1.4operator--()
那么,對于--操作,它與++操作是反過來的,是從大到小的一個遍歷。
1.?當右子樹與根訪問完,要符合大到小的遍歷,得去左子樹進行訪問,同理左子樹得滿足大到小的遍歷,首先就得找到左子樹的最大節點,即最右節點。
2.當右子樹未訪問完,或者左子樹已訪問完
Self& operator--(){PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;if (_node->_left)//右子樹訪問完,去左子樹訪問{_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else//右子樹未訪問完,或者左子樹訪問完{PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;if (parent && cur != parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}
1.5operator==()? && operator!=()?
bool operator==(const Self& x) const{return _node == x._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}?1.6begin() && end()
搭建好了迭代器,那么如何在紅黑樹中定義begin和end(),按正常的理解, begin返回指向中序序列第一個元素的迭代器,end()返回指向中序序列最后一個元素下一個位置的迭代器。
iterator begin(){PNode cur = _Root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){ return iterator(nullptr);}begin的返回值是沒有問題,但是end就不一樣了,end指向的是nullptr,當要實行end()--操作時,迭代器就會指向最后一個元素的位置,但是end已經指向空了呀,而--的操作是通過更改指針指向,那么更改end指向,就是要對空指針進行解引用,就會報錯。
那么正確的做法就是將end()放在頭結點的位置。即構建一個頭結點用來存放begin和end,該頭結點與樹的頭結點互相指向,對于這種做法,這里并不會去實現,還是按照原來的做法進行實現。
二、如何用紅黑樹搭配map和set(仿函數)
我們可以用兩顆紅黑樹分別封裝一份map和一份set,但是這樣做的效果就帶來了代碼冗余。為了減少代碼冗余,模擬跟庫保持用一顆紅黑樹封裝map和set,但是該如何做到套用一顆樹呢,我們來進一步分析。
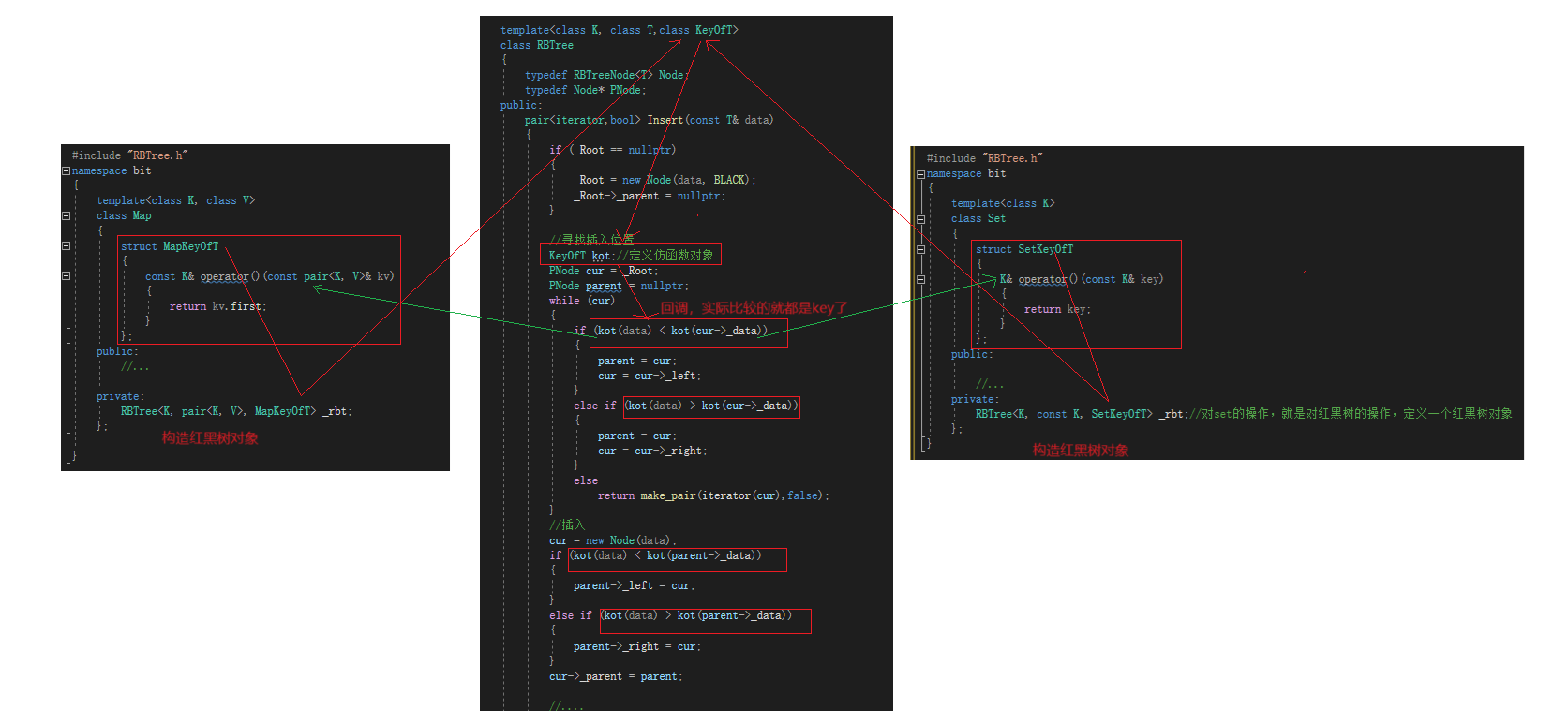
?首先對于map而言,其存放的節點值是pair,而對于set存放的是key,這對于紅黑樹節點的實現到是沒啥問題,但是對于紅黑樹內部的構造,是需要查詢插入的位置,就需要進行比較,若將比較實現成key的比較,那么對于pair類型又該如何比較,雖然知道比較的也是pair中的key,但是如何做到既滿足set中的key類型比較,又滿足pair類型中的key比較,總不能干兩份代碼吧。這個時候,我們的仿函數又派上用場了,對于set和map中都構造一個仿函數,分別表示取到set的key,和map中pair中的key,那么紅黑樹中的比較,就可以換成仿函數的比較,當往set中插入元素進行比較,調用的就是set的仿函數,當往map中插入元素進行比較,調用的就是map的仿函數從而達到回調。用一張圖來進行表示,如圖:
?三、紅黑樹封裝map和set(簡易版)
3.1紅黑樹的構造(RBTree.h)?
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;namespace bit
{enum Color//對于紅黑節點,用枚舉結構來表示{RED,BLACK};template<class T>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode(const T& data, Color color = RED):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_data(data),_color(color){}RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Color _color;//默認給紅色才符合規則,若默認給黑色的話,則插入的每個節點都是黑色節點,//那么就不能保證每條路徑的黑色節點相同,違反了第4條性質。而給紅色,就可以根據規則調整。};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct RBTreeIterator{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef Node* PNode;typedef RBTreeIterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;PNode _node;RBTreeIterator(const PNode node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*());}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right)//左子樹訪問完,去訪問右子樹{_node = _node->_right;while (_node && _node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else//左子樹未訪問完,或者右子樹訪問完{PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur != parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator--(){PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;if (_node->_left)//右子樹訪問完,去左子樹訪問{_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else//右子樹未訪問完,或者左子樹訪問完{PNode cur = _node;PNode parent = cur->_parent;if (parent && cur != parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator==(const Self& x) const{return _node == x._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}};template<class K, class T,class KeyOfT>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef Node* PNode;public:typedef RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<const T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;RBTree():_Root(nullptr){}iterator begin(){PNode cur = _Root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){ return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{PNode cur = _Root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return iterator(nullptr);}pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_Root == nullptr){_Root = new Node(data, BLACK);_Root->_parent = nullptr;return make_pair(iterator(_Root), true);}//尋找插入位置KeyOfT kot;//定義仿函數對象PNode cur = _Root;PNode parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}elsereturn make_pair(iterator(cur),false);}//插入cur = new Node(data);if (kot(data) < kot(parent->_data)){parent->_left = cur;}else if (kot(data) > kot(parent->_data)){parent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//調整while (parent && parent->_color == RED)//只要停留在情況一就繼續判斷{PNode grandparent = parent->_parent;PNode uncle = nullptr;//先定好uncle的位置,不管uncle是否存在if (parent == grandparent->_left){uncle = grandparent->_right;}else{uncle = grandparent->_left;}if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED)//p為紅、u存在且為紅{// g// p u// curparent->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandparent->_color = RED;//根節點,更新結束if (grandparent == _Root){grandparent->_color = BLACK;break;}//往上更新cur = grandparent;parent = cur->_parent;}else if (cur == parent->_left && parent == grandparent->_left )//cur為p的左孩子,p為g的左孩子,p為紅{// g// p u//curRotateR(grandparent);parent->_color = BLACK;grandparent->_color = RED;break;}else if (cur == parent->_right && parent == grandparent->_right )//cur為p的右孩子,p為g的右孩子,p為紅{// g// u p// curRotateL(grandparent);parent->_color = BLACK;grandparent->_color = RED;break;}else if (cur == parent->_right && parent == grandparent->_left )//p為g的左孩子,cur為p的右孩子,p為紅{// g//p u// curRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandparent);cur->_color = BLACK;grandparent->_color = RED;break;}else if (cur == parent->_left && parent == grandparent->_right)//p為g的右孩子,cur為p的左孩子,p為紅{// g//u p// curRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandparent);cur->_color = BLACK;grandparent->_color = RED;break;}else{assert(false);}}return make_pair(iterator(cur),true);}iterator Find(const T& data){if (_Root == nullptr)return end();PNode cur = _Root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data)){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data)){cur = cur->_left;}else return iterator(cur);}return end();}size_t _Size(PNode Root,int k){if (Root == nullptr)return 0;int leftsize = _Size(Root->_left, k);int rightsize = _Size(Root->_right, k);return leftsize + rightsize + 1;}size_t Size() {int k = 0;return _Size(_Root, k);}bool Empty(){return _Root == nullptr;}void RotateL(PNode parent){PNode subR = parent->_right;PNode subRL = subR->_left;PNode pparent = parent->_parent;if (parent == _Root)//更新根節點{_Root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{//更新parent的父節點指向if (parent == pparent->_left){pparent->_left = subR;}else{pparent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = pparent;}//parent的右指針指向subRL,subRL的父節點指向parentparent->_right = subR->_left;if (subRL)//subR的左節點可能不存在subRL->_parent = parent;//subR的左指針指向parent,parent的父節點指向subRsubR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;}//右單旋void RotateR(PNode parent){PNode subL = parent->_left;PNode subLR = subL->_right;PNode pparent = parent->_parent;if (_Root == parent){_Root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{//更新parent的父節點指向if (pparent->_left == parent){pparent->_left = subL;}else{pparent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = pparent;}//parent的左指針指向subLR,subLR的父節點指向parentparent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)//subR的右節點可能不存在subLR->_parent = parent;//subL的右指針指向parent,parent的父節點指向subLsubL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;}private:PNode _Root;};}3.2map的模擬實現(MyMap.h)
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace bit
{template<class K,class V>class Map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _rbt.begin();}iterator end(){return _rbt.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _rbt.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _rbt.end();}pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv){return _rbt.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& data){pair<iterator, bool> p = _rbt.Insert(make_pair(data, V()));//插入失敗,說明data已經存在,返回指向data的迭代器return p.first->second;}iterator find(const K& data){return _rbt.Find(data);}size_t size(){return _rbt.Size();}bool empty(){return _rbt.Empty();}private:RBTree<K, pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _rbt;};}?3.3set的模擬實現(MySet.h)
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace bit
{template<class K>class Set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;//set的迭代器使用的就是紅黑樹的迭代器typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;//set的迭代器使用的就是紅黑樹的迭代器iterator begin()//獲取set的首元素位置的迭代器,即獲取紅黑樹的最小元素的迭代器{return _rbt.begin();}iterator end(){return _rbt.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _rbt.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _rbt.end();}pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)//插入元素實際就是插入到紅黑樹節點中去{return _rbt.Insert(key);}iterator find(const K& data){return _rbt.Find(data);}size_t size(){return _rbt.Size();}bool empty(){return _rbt.Empty();}private:RBTree<K,const K,SetKeyOfT> _rbt;//對set的操作,就是對紅黑樹的操作,定義一個紅黑樹對象};
}3.4測試(test.cpp)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma warning(disable:6031)#include "MyMap.h"
#include "MySet.h"void TestMapRBTree()
{int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };bit::Map<int, int> t;for (auto e : a){t.insert(make_pair(e, e));}bit::Map<int, int>::iterator it = t.begin();while (it != t.end()){cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;
}void TestSetRBTree()
{//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };bit::Set<int> t;for (auto e : a){t.insert(e);}bit::Set<int>::iterator it = t.begin();while (it != t.end()){cout << *it << endl;++it;}cout << t.size() << endl;cout << boolalpha << t.empty() << endl;
}int main()
{TestMapRBTree();TestSetRBTree();return 0;
}輸出結果:

以上實現的是一個紅黑樹簡易版,雖然功能并不齊全,但目標是為了進一步學習對紅黑樹、map和set的掌握理解。end~
)












)





